Google OAuth 2 authorization - Error: redirect_uri_mismatch
Categories:
Resolving Google OAuth 2 'redirect_uri_mismatch' Errors
Understand and fix the common 'redirect_uri_mismatch' error when integrating Google OAuth 2.0 into your applications, ensuring a smooth authentication flow.
The redirect_uri_mismatch error is one of the most frequent hurdles developers encounter when implementing Google OAuth 2.0. This error indicates that the redirect_uri parameter sent in your authorization request does not exactly match one of the authorized redirect URIs configured in your Google Cloud Project. This article will guide you through understanding the root causes of this error and provide practical solutions to resolve it, ensuring your Google authentication flow works seamlessly.
Understanding the 'redirect_uri_mismatch' Error
Google OAuth 2.0 uses redirect_uri to securely return an authorization code or access token to your application after a user grants permission. For security reasons, Google strictly enforces that the redirect_uri provided in the authorization request must precisely match one of the URIs you have registered in your Google Cloud Console for that specific OAuth 2.0 Client ID. Any discrepancy, no matter how small, will result in the redirect_uri_mismatch error.
sequenceDiagram
participant User
participant ClientApp as "Your Application"
participant GoogleAuth as "Google Authorization Server"
User->>ClientApp: Clicks "Sign in with Google"
ClientApp->>GoogleAuth: 1. Authorization Request (includes redirect_uri)
GoogleAuth-->>GoogleAuth: 2. Validate redirect_uri
alt Mismatch Found
GoogleAuth-->>ClientApp: 3. Error: redirect_uri_mismatch
ClientApp->>User: Display Error
else Match Found
GoogleAuth->>User: 3. User Consent Screen
User->>GoogleAuth: 4. Grants/Denies Access
GoogleAuth->>ClientApp: 5. Redirect with Authorization Code (to redirect_uri)
ClientApp->>GoogleAuth: 6. Token Exchange Request
GoogleAuth->>ClientApp: 7. Access Token
ClientApp->>User: Logged In
endGoogle OAuth 2.0 Flow with redirect_uri Validation
Common Causes and Solutions
The redirect_uri_mismatch error typically stems from a few common issues. Identifying which one applies to your situation is the first step to a fix.
redirect_uri in both your application code and the Google Cloud Console. Even a trailing slash or a difference in HTTP vs. HTTPS can cause a mismatch.1. 1. Verify Authorized Redirect URIs in Google Cloud Console
Navigate to the Google Cloud Console, select your project, then go to 'APIs & Services' > 'Credentials'. Edit your OAuth 2.0 Client ID. Under 'Authorized redirect URIs', ensure that the exact URI your application is sending is listed. Add any missing URIs. Remember to save your changes.
2. 2. Check for Trailing Slashes
A common mistake is a mismatch in trailing slashes. If your application sends https://example.com/auth/google/callback but your console lists https://example.com/auth/google/callback/, or vice-versa, it will cause an error. Ensure consistency.
3. 3. HTTP vs. HTTPS Discrepancy
If your application is running on HTTPS, but your registered URI is HTTP (or vice-versa), this will cause a mismatch. Always use HTTPS for production applications and ensure your registered URIs reflect this.
4. 4. Port Number Mismatches (Local Development)
During local development, you might be using a specific port (e.g., http://localhost:3000/callback). Ensure this exact URI, including the port, is registered in the Google Cloud Console. For development, you might need to add multiple localhost URIs for different ports or environments.
5. 5. Subdomain or Domain Mismatches
Ensure the domain or subdomain used in your redirect_uri exactly matches the one registered. For example, https://www.example.com is different from https://example.com.
6. 6. URL Encoding Issues
While less common, ensure your redirect_uri is correctly URL-encoded if it contains special characters. Most OAuth libraries handle this automatically, but it's worth checking if other issues are ruled out.
Example Code Snippets and Configuration
Here are examples of how redirect_uri is typically configured in both your application and the Google Cloud Console.
const express = require('express');
const passport = require('passport');
const GoogleStrategy = require('passport-google-oauth20').Strategy;
const app = express();
passport.use(new GoogleStrategy({
clientID: process.env.GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID,
clientSecret: process.env.GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET,
callbackURL: '/auth/google/callback' // This is the redirect_uri relative path
},
function(accessToken, refreshToken, profile, cb) {
// User authentication logic
return cb(null, profile);
}
));
app.get('/auth/google', passport.authenticate('google', { scope: ['profile', 'email'] }));
app.get('/auth/google/callback',
passport.authenticate('google', { failureRedirect: '/login' }),
function(req, res) {
// Successful authentication, redirect home.
res.redirect('/');
});
// For this example, if your app is at https://myapp.com,
// the full redirect_uri sent to Google would be:
// https://myapp.com/auth/google/callback
Example redirect_uri in a Node.js (Express/Passport) application
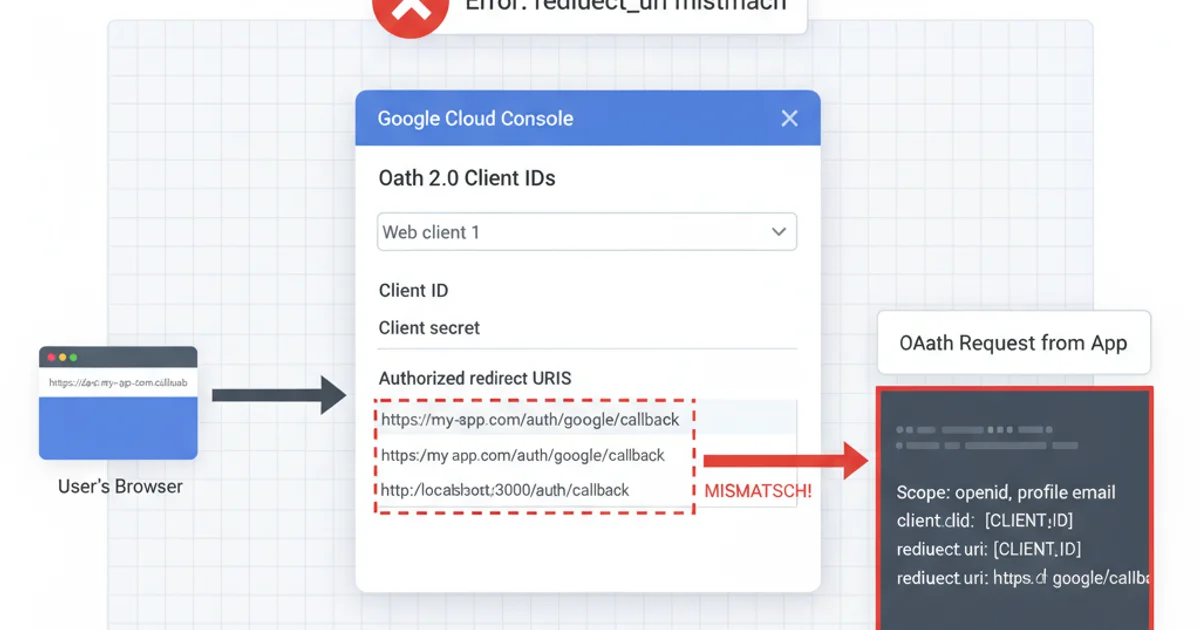
Configuring 'Authorized redirect URIs' in Google Cloud Console
In the Google Cloud Console, under your OAuth 2.0 Client ID, you would add the full URI, for example: https://myapp.com/auth/google/callback or http://localhost:3000/auth/google/callback for local development.
http://localhost or http://127.0.0.1 for production applications. Always use HTTPS and a fully qualified domain name for security best practices.Troubleshooting Tips
If you're still facing issues, consider these additional troubleshooting steps:
1. 1. Inspect the Authorization Request URL
Use your browser's developer tools (Network tab) to inspect the actual authorization request URL sent to Google. Look for the redirect_uri parameter and compare it character-by-character with what's configured in your Google Cloud Console.
2. 2. Clear Browser Cache and Cookies
Sometimes, old session data or cached redirects can interfere. Clearing your browser's cache and cookies can help ensure a fresh authentication flow.
3. 3. Check for Multiple Client IDs
Ensure you are using the correct Client ID and Client Secret for the OAuth 2.0 Client ID where you configured your redirect URIs. It's easy to mix them up if you have multiple projects or client IDs.
4. 4. Consult Google's Documentation
Refer to the official Google OAuth 2.0 documentation for the most up-to-date information and specific guidelines for your chosen platform or language.
By systematically checking these potential issues, you should be able to pinpoint and resolve the redirect_uri_mismatch error, allowing your users to authenticate with Google seamlessly.