Difference between xs and xsd in XML schema file?
Categories:
Understanding XML Schema: The Difference Between 'xs' and 'xsd' Prefixes
Explore the fundamental distinction between the 'xs' and 'xsd' prefixes in XML Schema Definition (XSD) files, clarifying their usage and importance in defining XML document structures.
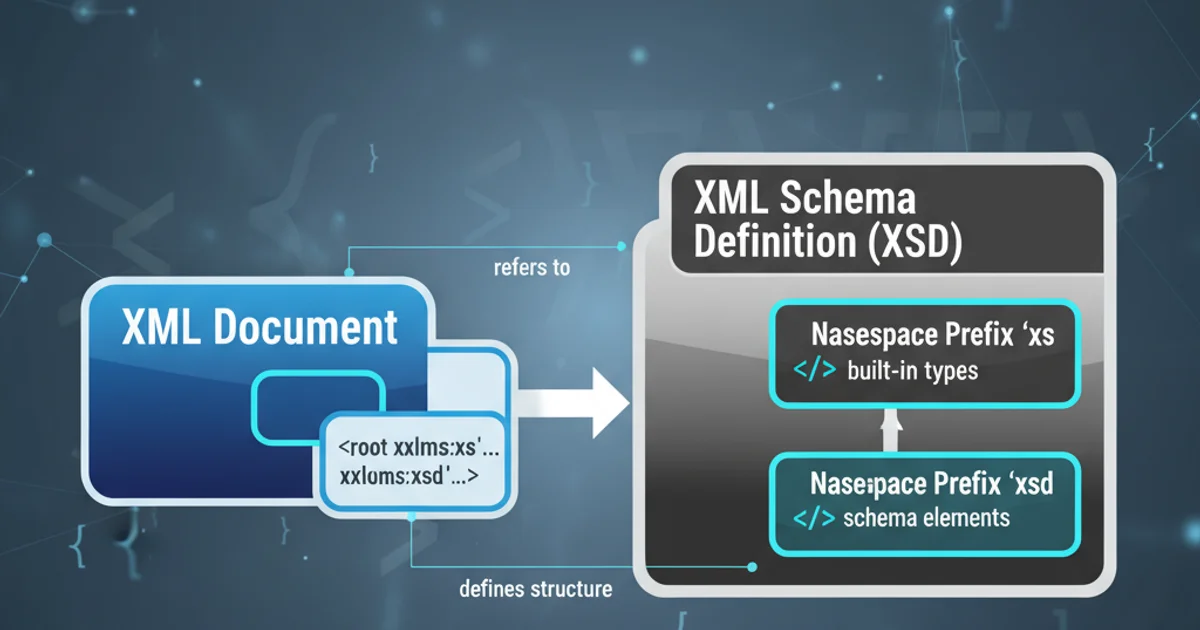
When working with XML Schema Definition (XSD) files, you'll frequently encounter prefixes like xs and xsd. While they often appear interchangeably, understanding their precise roles is crucial for correctly defining and validating XML documents. This article will demystify these prefixes, explain their origins, and demonstrate their proper application in your schema files.
The Role of Namespaces in XML Schema
Before diving into xs and xsd, it's essential to grasp the concept of XML namespaces. Namespaces provide a method for qualifying element and attribute names used in XML documents by associating them with URIs. This prevents name collisions when combining XML documents from different applications. In the context of XSD, a specific namespace is reserved for the schema definition language itself.
flowchart TD
A[XML Document] --> B{Uses Namespaces?}
B -->|Yes| C[Avoids Name Collisions]
B -->|No| D[Potential Name Collisions]
C --> E[References XSD Namespace]
E --> F["Defines Elements/Attributes (e.g., xs:element)"]How Namespaces Prevent Collisions and Reference XSD
Understanding 'xs' and 'xsd'
Both xs and xsd are common namespace prefixes used to refer to the XML Schema namespace. The official URI for this namespace is http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema. The choice between xs and xsd is purely conventional and does not affect the schema's functionality or validity. The W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) specifications often use xs in their examples, making it a widely adopted convention. However, xsd is also very common, especially in older documentation or tools.
xs and xsd are valid, consistency is key. Choose one prefix for the XML Schema namespace within your project or organization and stick to it to improve readability and maintainability.Practical Application in XSD Files
In an XSD file, you declare the XML Schema namespace using an xmlns attribute on the root <schema> element. This declaration associates a chosen prefix (e.g., xs or xsd) with the official schema URI. Once declared, you use this prefix to qualify all elements and attributes that are part of the XML Schema language itself, such as <xs:element>, <xs:complexType>, <xs:attribute>, and built-in data types like xs:string or xs:integer.
<!-- Using 'xs' prefix -->
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<xs:element name="person">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="firstName" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="lastName" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>
Example XSD using the 'xs' prefix
<!-- Using 'xsd' prefix -->
<xsd:schema xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<xsd:element name="product">
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="name" type="xsd:string"/>
<xsd:element name="price" type="xsd:decimal"/>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
</xsd:schema>
Example XSD using the 'xsd' prefix
http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema is what truly identifies the XML Schema language. The prefix (xs or xsd) is merely a local alias for that URI within the document.