What is the difference between "bundle update" and "gem update"?
Categories:
Understanding 'bundle update' vs. 'gem update' in Ruby Projects

Explore the critical differences between bundle update and gem update, and learn when to use each command to manage your Ruby and Rails project dependencies effectively.
In the Ruby ecosystem, managing dependencies is a fundamental task. Two commands often cause confusion for newcomers and even seasoned developers: bundle update and gem update. While both interact with RubyGems, their scope, purpose, and impact on your project's dependencies are distinctly different. Understanding these differences is crucial for maintaining stable, reproducible, and up-to-date Ruby applications, especially in a Ruby on Rails context.
The Role of RubyGems and gem update
RubyGems is Ruby's standard package manager, providing a format for distributing Ruby programs and libraries (gems) and a tool to manage their installation. When you run gem update, you are interacting directly with the RubyGems system. This command checks for and installs the latest available versions of all gems installed on your system, or specific gems if you provide their names. It operates globally or per Ruby version (if using RVM/rbenv), without considering project-specific dependency constraints.
# Update all installed gems to their latest versions
gem update
# Update a specific gem (e.g., 'rails') to its latest version
gem update rails
Examples of using the gem update command.
gem update without specifying a gem can lead to unexpected behavior in your projects. It updates gems globally, potentially breaking applications that rely on older, specific gem versions.The Role of Bundler and bundle update
Bundler is a dependency manager for Ruby projects. Unlike RubyGems, Bundler focuses on ensuring that your application runs with the exact gems and versions it needs. It reads your project's Gemfile to determine dependencies and their version constraints, then records the precise versions it resolves in the Gemfile.lock file. This Gemfile.lock is critical for reproducibility, guaranteeing that everyone working on the project (and the production server) uses the same gem versions.
# Update all gems in the Gemfile to the latest versions allowed by Gemfile constraints
bundle update
# Update a specific gem (e.g., 'rails') and its dependencies
bundle update rails
# Install gems based on Gemfile.lock (or resolve if Gemfile.lock is missing)
bundle install
Examples of using bundle update and bundle install commands.
flowchart TD
A[Start]
A --> B{`gem update` or `bundle update`?}
B -->|`gem update`| C[Updates ALL installed gems globally]
C --> D[Potentially breaks other projects]
B -->|`bundle update`| E[Updates project's `Gemfile.lock`]
E --> F[Respects `Gemfile` constraints]
F --> G[Ensures project reproducibility]
D --> H[End]
G --> H[End]Decision flow for choosing between gem update and bundle update.
Key Differences and When to Use Each
The fundamental distinction lies in their scope and purpose. gem update is a system-wide operation, while bundle update is project-specific and constraint-aware. Here's a breakdown:
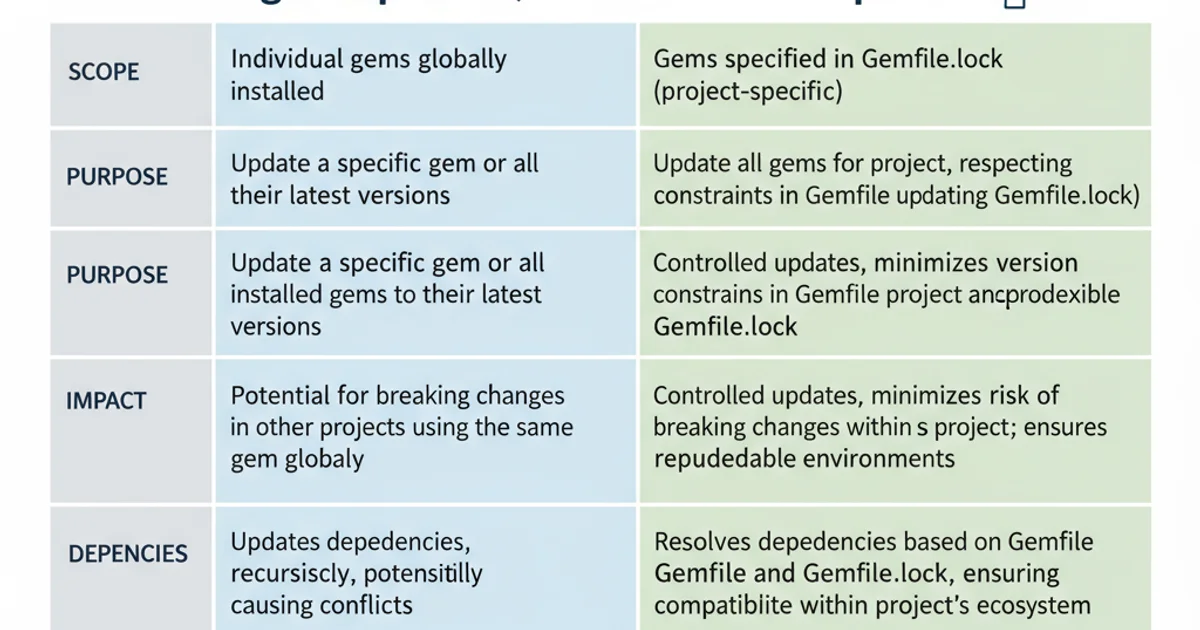
Comparison of gem update and bundle update.
bundle install (to install dependencies as specified in Gemfile.lock) and bundle update (to intentionally upgrade dependencies within Gemfile constraints). Avoid gem update in the context of a Bundler-managed project.Practical Scenarios
Let's consider common scenarios to illustrate when to use each command:
1. Starting a new project or cloning an existing one
Use bundle install. This command reads your Gemfile.lock (if present) and installs the exact gem versions. If Gemfile.lock is missing, it resolves dependencies based on Gemfile and creates the lock file.
2. Adding a new gem to your project
Add the gem to your Gemfile, then run bundle install. Bundler will install the new gem and update Gemfile.lock accordingly, without updating existing gems unless necessary for the new gem's dependencies.
3. Intentionally upgrading a specific gem
If you want to upgrade a gem (e.g., rails) to its latest compatible version as per your Gemfile constraints, use bundle update rails. This will update rails and any of its dependencies that also need updating, then modify Gemfile.lock.
4. Upgrading all project gems (with caution)
To update all gems in your Gemfile to their latest compatible versions, use bundle update. This can be a significant change and should be done with thorough testing, as it modifies Gemfile.lock for all dependencies.
5. Updating your system's RubyGems itself
If you need to update the RubyGems system software (the gem command itself), you would use gem update --system. This is distinct from updating individual gems.