How to execute a Windows command on a remote PC?
Categories:
Executing Commands on Remote Windows PCs

Learn how to securely and efficiently execute commands on remote Windows machines using built-in tools like PsExec and PowerShell Remoting.
Executing commands on a remote Windows PC is a fundamental task for system administrators and developers. Whether you need to deploy software, retrieve logs, or troubleshoot issues, understanding the available tools and their proper usage is crucial. This article will guide you through the most common and effective methods, focusing on security and best practices.
Method 1: Using PsExec for Basic Remote Execution
PsExec is a lightweight telnet-replacement that lets you execute processes on other systems, complete with full interactivity for console applications, without having to manually install client software. It's part of the Sysinternals Suite from Microsoft and is widely used for its simplicity and effectiveness in many scenarios. PsExec works by copying a small service executable to the remote machine, starting it, and then removing it after the command completes.
sequenceDiagram
participant LocalPC as Local PC
participant RemotePC as Remote PC
LocalPC->>RemotePC: PsExec connects (SMB/RPC)
LocalPC->>RemotePC: Copies PsExecSvc.exe
RemotePC->>RemotePC: Starts PsExecSvc.exe
LocalPC->>RemotePC: Sends command to PsExecSvc
RemotePC->>RemotePC: Executes command
RemotePC-->>LocalPC: Returns output
RemotePC->>RemotePC: Stops PsExecSvc.exe
LocalPC->>RemotePC: Deletes PsExecSvc.exePsExec Remote Command Execution Flow
psexec \\RemotePCNameOrIP -u Domain\Username -p Password cmd.exe /c "ipconfig /all > C:\temp\ipconfig.txt"
Method 2: PowerShell Remoting (WinRM)
PowerShell Remoting, built on Windows Remote Management (WinRM), offers a more secure and robust way to execute commands and scripts remotely. It uses encrypted communication (HTTPS by default if configured) and allows for persistent sessions, making it ideal for complex automation tasks. WinRM must be enabled on the target machine for PowerShell Remoting to work.
1. Enable WinRM on the Remote PC
On the remote machine, open an elevated PowerShell prompt and run Enable-PSRemoting -Force. This configures the necessary firewall rules and starts the WinRM service.
2. Establish a Remote Session (Optional but Recommended)
You can create a persistent session to the remote computer, which is efficient for running multiple commands. Use New-PSSession to create the session and Enter-PSSession to interactively connect.
3. Execute Commands
Use Invoke-Command to run scripts or commands on the remote machine. You can pass script blocks, arguments, and even execute local scripts remotely.
# Enable WinRM on the remote machine (run on remote PC)
# Enable-PSRemoting -Force
# Example 1: Execute a single command
Invoke-Command -ComputerName RemotePCNameOrIP -ScriptBlock { Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.Status -eq 'Running'} }
# Example 2: Execute a local script remotely
# Assume you have a script named 'MyScript.ps1' locally
# Invoke-Command -ComputerName RemotePCNameOrIP -FilePath C:\Scripts\MyScript.ps1
# Example 3: Using a persistent session
$session = New-PSSession -ComputerName RemotePCNameOrIP -Credential (Get-Credential)
Invoke-Command -Session $session -ScriptBlock { Get-Process | Select-Object -First 5 }
Remove-PSSession -Session $session
Choosing the Right Tool
The choice between PsExec and PowerShell Remoting depends on your specific needs and security requirements. PsExec is quick and easy for ad-hoc tasks, especially in environments where WinRM might not be configured. PowerShell Remoting, however, is the preferred method for robust, secure, and scriptable remote administration, offering more features and better integration with the Windows ecosystem.
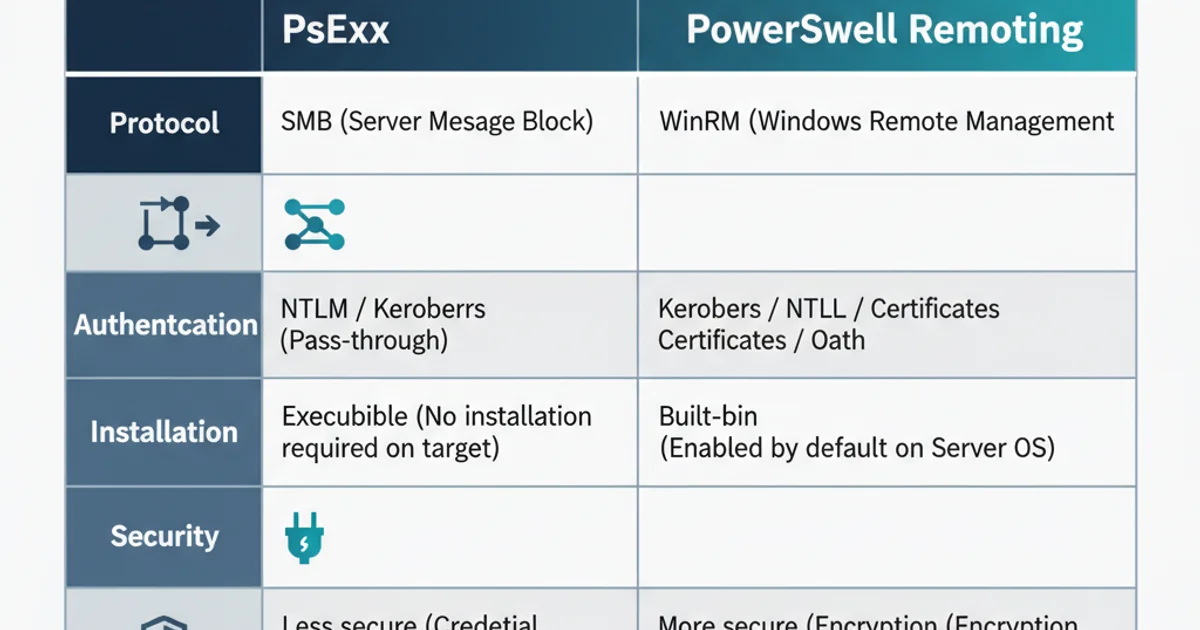
Feature Comparison: PsExec vs. PowerShell Remoting