Overwrite or override
Categories:
Overwrite vs. Override: Understanding Key Terminology in Programming
Explore the distinct meanings of 'overwrite' and 'override' in software development, clarifying their usage and impact on code behavior.
In the world of programming, precise terminology is crucial for clear communication and effective development. Two terms that often cause confusion, especially for newcomers, are 'overwrite' and 'override'. While they might sound similar, they describe fundamentally different actions with distinct implications for your code. Understanding this difference is key to writing robust, maintainable, and predictable software.
What Does 'Overwrite' Mean?
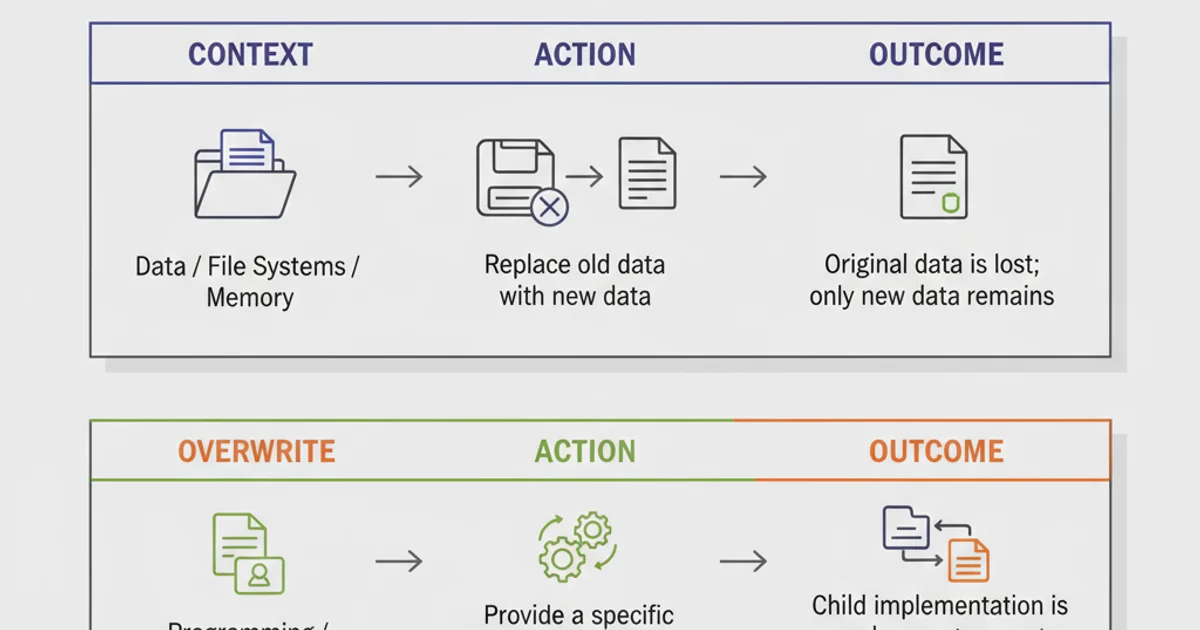
'Overwrite' generally refers to the act of replacing existing data or code entirely with new data or code. When something is overwritten, the original content is usually lost and cannot be recovered (unless a version control system or backup is in place). This concept applies broadly across various contexts, from file systems to memory management and even variable assignments.
flowchart TD
A[Original Data/Code] --> B{New Data/Code Arrives}
B --> C[Original Content is Replaced]
C --> D[New Content is Now Present]
D --> E(Original Content is Lost)The process of overwriting data or code.
Consider a simple example: saving a file. If you open an existing document, make changes, and then save it with the same filename, you are overwriting the original file. The previous version is gone. In programming, assigning a new value to an existing variable also constitutes overwriting its previous value.
my_variable = 10 # Initial assignment
print(f"Initial value: {my_variable}")
my_variable = 20 # Overwriting the previous value
print(f"Overwritten value: {my_variable}")
# Overwriting a file (conceptual)
# with open('my_file.txt', 'w') as f:
# f.write('This is new content.') # This would overwrite existing content
Examples of overwriting a variable's value in Python.
What Does 'Override' Mean?
'Override' is a concept primarily associated with object-oriented programming (OOP) and inheritance. It refers to the ability of a subclass (child class) to provide a specific implementation for a method that is already defined in its superclass (parent class). When a method is overridden, the subclass's version of the method is executed instead of the superclass's version when called on an object of the subclass type.
classDiagram
class Animal {
+makeSound()
}
class Dog {
+makeSound()
}
class Cat {
+makeSound()
}
Animal <|-- Dog
Animal <|-- Cat
Dog : makeSound() overrides Animal.makeSound()
Cat : makeSound() overrides Animal.makeSound()Class diagram illustrating method overriding in OOP.
The key distinction here is that the original method in the superclass still exists; it's just that the subclass provides its own specialized behavior. This is a fundamental principle of polymorphism, allowing different objects to respond to the same method call in their own unique ways. Overriding is often used to extend or modify the behavior of inherited methods without altering the base class.
class Animal {
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Animal makes a sound");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Dog barks");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Cat meows");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal myAnimal = new Animal();
Animal myDog = new Dog(); // Polymorphism
Animal myCat = new Cat(); // Polymorphism
myAnimal.makeSound(); // Output: Animal makes a sound
myDog.makeSound(); // Output: Dog barks
myCat.makeSound(); // Output: Cat meows
}
}
Java example demonstrating method overriding.
@Override annotation (in Java) or similar mechanisms in other languages. This helps the compiler catch errors if you accidentally misspell the method name or change its signature, ensuring you are indeed overriding and not just creating a new method.Key Differences Summarized
To solidify your understanding, here's a quick comparison of the two terms:
Comparison of Overwrite vs. Override
In essence, 'overwrite' is about replacement and loss of original content, while 'override' is about specialization and providing an alternative implementation within an inheritance hierarchy, with the original definition still existing in the parent class.