Why Java opens 3 ports when JMX is configured?
Categories:
Understanding Java JMX Port Allocation: Why Three Ports?
Explore the intricate process of Java Management Extensions (JMX) port allocation, demystifying why a single JMX configuration often results in three open ports and how to manage them effectively.
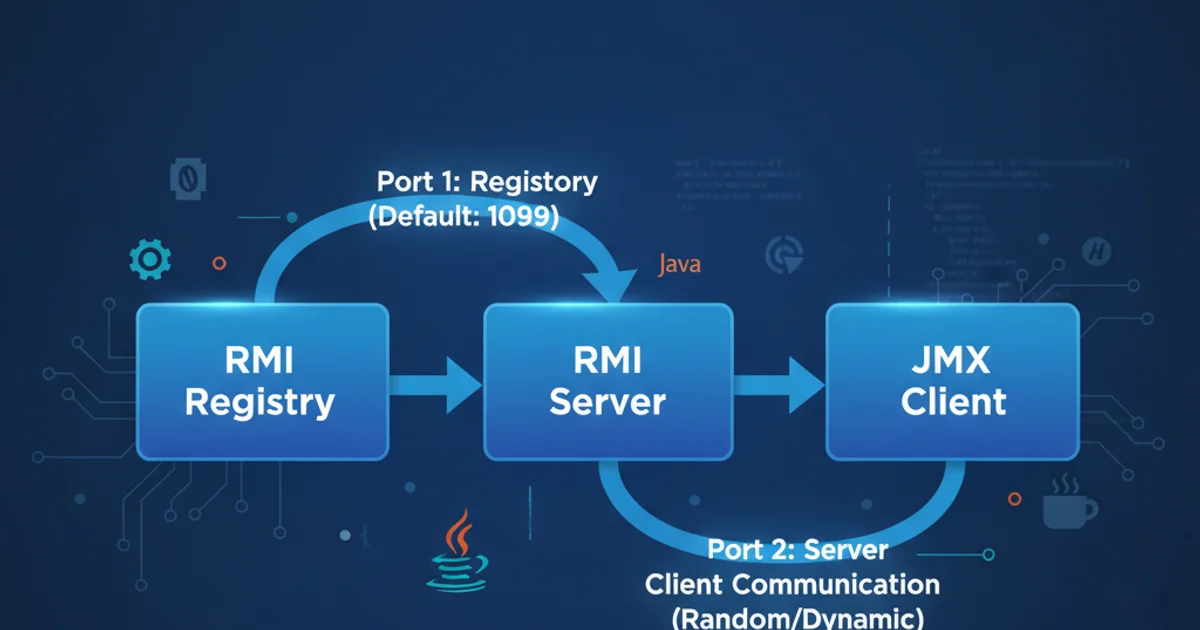
When configuring Java Management Extensions (JMX) for monitoring or management, it's common to observe that your Java application opens not one, but typically three network ports. This behavior can be confusing, especially when dealing with firewall rules or network security policies. This article will break down the reasons behind this multi-port allocation, focusing on the underlying Remote Method Invocation (RMI) technology that JMX leverages, and provide guidance on how to understand and manage these ports.
The Role of RMI in JMX
JMX relies heavily on Remote Method Invocation (RMI) for remote communication. RMI is a Java API that allows an object running in one Java Virtual Machine (JVM) to invoke methods on an object running in another JVM, potentially on a different host. This distributed nature is what enables remote monitoring and management capabilities for JMX. When you enable JMX remote access, you're essentially setting up an RMI server within your application.
flowchart TD
A[JMX Client] --> B["RMI Registry (Port 1)"]
B --> C["JMX RMI Server (Port 2)"]
C --> D["JMX MBean Server (Internal)"]
D --> E["Application MBeans"]
A --> C
subgraph JVM
B
C
D
E
endSimplified JMX-RMI communication flow
The Three Ports Explained
The three ports typically observed when JMX is configured are for distinct purposes related to RMI communication:
RMI Registry Port: This is the well-known port you explicitly configure (e.g.,
1099). The RMI Registry acts as a naming service, allowing clients to look up remote objects by name. When a JMX client wants to connect, it first contacts the RMI Registry to find the JMX RMI server object.JMX RMI Server Port: This port is opened by the JMX RMI server itself. When the JMX RMI server object is exported to the RMI Registry, it binds to an available ephemeral port (a randomly assigned port from a dynamic range). This is the port that the JMX client will directly connect to after looking up the server in the RMI Registry. This port is often the second one you'll see.
RMI Server Stub Port (Optional/Ephemeral): In some RMI configurations, especially older ones or specific scenarios, the RMI server might open an additional ephemeral port for the RMI server stub. This port is used for the actual data transfer and method invocation between the client and the remote object. While often consolidated with the JMX RMI Server Port in modern JVMs, it can sometimes appear as a separate, third port, particularly if the RMI server needs to export additional remote objects or if there are specific network configurations. This port is also dynamically assigned.
Configuring JMX Ports for Predictability
While the RMI Registry port is explicitly set, the JMX RMI server port is often ephemeral by default. This can be problematic for firewall configurations. Fortunately, you can configure the JMX RMI server to use a fixed port as well. This ensures that only two predictable ports are opened (RMI Registry and JMX RMI Server), simplifying network management.
import java.lang.management.ManagementFactory;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import javax.management.remote.JMXConnectorServer;
import javax.management.remote.JMXConnectorServerFactory;
import javax.management.remote.JMXServiceURL;
import javax.management.MBeanServer;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class FixedPortJMX {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Define the JMX RMI Registry port
int rmiRegistryPort = 1099;
// Define the JMX RMI Server port
int rmiServerPort = 1100;
// Create an RMI Registry on the specified port
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(rmiRegistryPort);
// Get the MBeanServer
MBeanServer mbs = ManagementFactory.getPlatformMBeanServer();
// Create JMXServiceURL with fixed RMI server port
// The 'server' parameter specifies the port for the RMI server object
JMXServiceURL url = new JMXServiceURL(
"service:jmx:rmi://localhost:" + rmiServerPort + "/jndi/rmi://localhost:" + rmiRegistryPort + "/jmxrmi"
);
// Set RMI server host to avoid issues with multiple network interfaces
System.setProperty("java.rmi.server.hostname", "localhost");
// Create JMXConnectorServer
JMXConnectorServer cs = JMXConnectorServerFactory.newJMXConnectorServer(url, null, mbs);
// Start the JMX connector server
cs.start();
System.out.println("JMX Agent started on RMI Registry port " + rmiRegistryPort + " and RMI Server port " + rmiServerPort);
System.out.println("Press Enter to stop...");
System.in.read();
cs.stop();
System.out.println("JMX Agent stopped.");
}
}
Java code to configure JMX with fixed RMI Registry and RMI Server ports.
java.rmi.server.hostname, ensure it's accessible by your JMX clients. Using localhost is fine for local testing, but for remote access, use the actual IP address or hostname of the server.JVM Arguments for JMX Configuration
For most applications, JMX is enabled and configured using JVM arguments. Here's how you can specify the RMI Registry port and, crucially, the RMI server port to ensure predictability.
java \
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote \
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=1099 \
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.rmi.port=1100 \
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false \
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false \
-Djava.rmi.server.hostname=your_server_ip_or_hostname \
-jar YourApplication.jar
JVM arguments to enable JMX with fixed RMI Registry (1099) and RMI Server (1100) ports.
In this configuration:
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=1099sets the RMI Registry port.-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.rmi.port=1100explicitly sets the JMX RMI server port, preventing it from binding to an ephemeral port.-Djava.rmi.server.hostname=your_server_ip_or_hostnameis critical for remote access, ensuring the RMI server advertises the correct IP address to clients.
com.sun.management.jmxremote.rmi.port, you typically reduce the number of dynamically allocated ports to just the two fixed ones, simplifying firewall management significantly.