what's the main difference between B-Rep and Parametric representation
Categories:
B-Rep vs. Parametric Modeling: Understanding the Core Differences

Explore the fundamental distinctions between Boundary Representation (B-Rep) and Parametric modeling in CAD, their strengths, weaknesses, and typical applications.
In the world of Computer-Aided Design (CAD), the way a 3D model is represented internally significantly impacts its flexibility, editability, and the types of operations that can be performed on it. Two primary methods dominate the landscape: Boundary Representation (B-Rep) and Parametric modeling. While both are used to create and manipulate 3D geometry, they approach the problem from fundamentally different perspectives. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone working with CAD software, from mechanical engineers to product designers.
Boundary Representation (B-Rep)
Boundary Representation (B-Rep) defines a 3D object by its enclosing surfaces or boundaries. Instead of describing the entire volume of an object, B-Rep focuses on the topological and geometric information of its faces, edges, and vertices. The object's volume is implicitly defined by these boundaries. For example, a cube is defined by its six faces, twelve edges, and eight vertices. Each face is a surface (e.g., a planar surface), each edge is a curve (e.g., a straight line), and each vertex is a point.
B-Rep models are highly accurate and are the standard for solid modeling in most professional CAD systems. They allow for complex shapes and precise calculations of properties like volume and surface area. However, a pure B-Rep model typically does not retain the history of its creation. If you want to modify a feature, you often have to delete and recreate the affected geometry, which can be time-consuming and error-prone for complex designs.
flowchart TD
A[Start with basic primitive] --> B{Define Faces, Edges, Vertices}
B --> C[Combine with Boolean Operations]
C --> D[Resulting Solid Model (B-Rep)]
D --"No direct history"--> E[Modify by re-editing boundaries]Simplified B-Rep modeling workflow
Parametric Representation
Parametric modeling, often referred to as 'feature-based' or 'history-based' modeling, takes a different approach. Instead of just storing the final geometry, it stores the sequence of operations (features) and their associated parameters that led to the creation of the model. Each feature (e.g., an extrusion, a hole, a fillet) is defined by parameters (e.g., depth of extrusion, diameter of hole, fillet radius) and relationships (e.g., a hole is concentric with a cylinder).
The key advantage of parametric modeling is its editability. Because the design intent is captured in the feature tree, you can go back and modify any parameter or feature in the history, and the model will automatically update. This makes design iterations much faster and less prone to errors. Most modern CAD software, like SolidWorks, Fusion 360, and Inventor, are primarily parametric modelers, though they often use B-Rep as the underlying geometric kernel to store the final shape.
flowchart TD
A[Start Sketch (Parameters)] --> B{Extrude (Parameter: Depth)}
B --> C{Add Hole (Parameters: Diameter, Location)}
C --> D{Apply Fillet (Parameter: Radius)}
D --> E[Resulting Solid Model]
E --"Retains History"--> F[Modify any parameter in history]
F --> ESimplified Parametric modeling workflow
Key Differences and Hybrid Approaches
The main distinction lies in how design intent and modifications are handled. B-Rep is about the 'what' (the final shape), while parametric modeling is about the 'how' (the steps and parameters to create the shape). Most modern CAD systems employ a hybrid approach, using a B-Rep kernel for geometric calculations and display, while layering a parametric feature tree on top to manage design history and intent. This allows users to benefit from both the robustness of B-Rep and the flexibility of parametric editing.
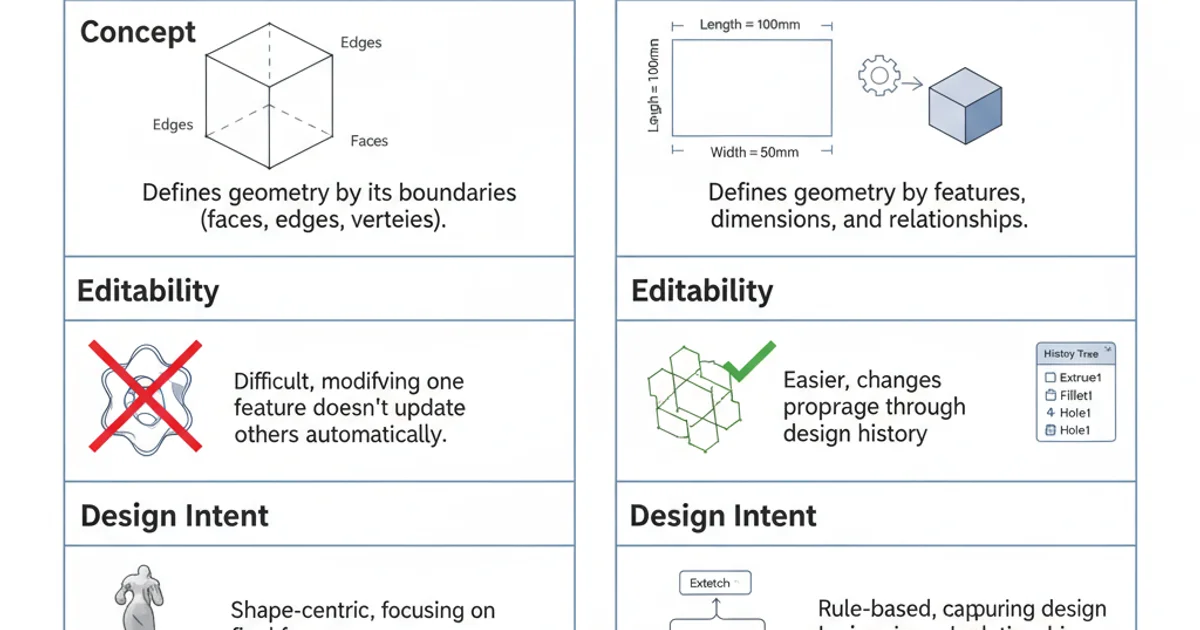
Comparison of B-Rep and Parametric Modeling
Understanding these representations is fundamental to mastering CAD. While B-Rep provides the geometric foundation, parametric modeling empowers designers with unparalleled flexibility and control over their designs, making it the dominant paradigm in modern product development.