How does `scp` differ from `rsync`?
scp differ from rsync? with practical examples, diagrams, and best practices. Covers rsync, scp development techniques with visual explanations.Categories:
SCP vs. Rsync: Choosing the Right Tool for Remote File Transfers
Explore the key differences between scp and rsync for transferring files over SSH, understanding their strengths, weaknesses, and optimal use cases.
When it comes to transferring files securely between Unix-like systems, scp (Secure Copy Protocol) and rsync (remote synchronization) are two of the most commonly used command-line utilities. Both leverage SSH for secure communication, but they operate on fundamentally different principles, leading to distinct advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the most efficient and appropriate tool for your specific file transfer needs.
SCP: Simplicity and Direct Copying
scp is a straightforward command-line utility for copying files and directories between hosts on a network. It uses SSH for data transfer and authentication, providing the same level of security as SSH itself. Think of scp as a secure version of the cp command, extended for remote operations. It's ideal for simple, one-time transfers where you need to copy entire files or directories without much concern for bandwidth optimization or incremental updates.
# Copy a single file from local to remote
scp /path/to/local/file.txt user@remote_host:/path/to/remote/
# Copy a directory recursively from remote to local
scp -r user@remote_host:/path/to/remote/directory /path/to/local/
Basic scp commands for file and directory transfers.
flowchart TD
A[Local Machine] -->|SSH Connection| B(Remote Machine)
B --> C[Remote File System]
A -- "Copy Entire File" --> CConceptual flow of scp transferring an entire file.
scp is simple, it re-transfers entire files even if only a small portion has changed. This can be inefficient for large files or slow network connections.Rsync: Efficiency Through Delta Transfer
rsync is a more advanced and versatile utility designed for efficient file synchronization. Its key innovation is the "delta transfer algorithm," which detects and transfers only the differences between files. This makes rsync exceptionally efficient for updating files that already exist on the destination, especially over slow links or for large datasets where only minor changes have occurred. rsync can also be used for local file copying, acting as a powerful cp replacement with advanced features like progress indicators, deletion of extraneous files, and more.
# Synchronize a directory from local to remote (archive mode, verbose, progress)
rsync -avP /path/to/local/directory/ user@remote_host:/path/to/remote/
# Synchronize a directory from remote to local, deleting extraneous files on local
rsync -av --delete user@remote_host:/path/to/remote/directory/ /path/to/local/
Common rsync commands for synchronization and deletion.
flowchart TD
A[Local File] -->|Hash/Checksum Comparison| B{Files Identical?}
B -- No --> C[Calculate Delta]
C --> D[Transfer Delta Only]
D --> E[Remote File Updated]
B -- Yes --> F[No Transfer Needed]The delta transfer mechanism of rsync.
--delete option in rsync, especially when synchronizing from a source to a destination. It will remove files on the destination that are not present on the source, which can lead to data loss if used incorrectly.Key Differences and Use Cases
The choice between scp and rsync largely depends on your specific requirements. Here's a summary of their core distinctions and when to use each:
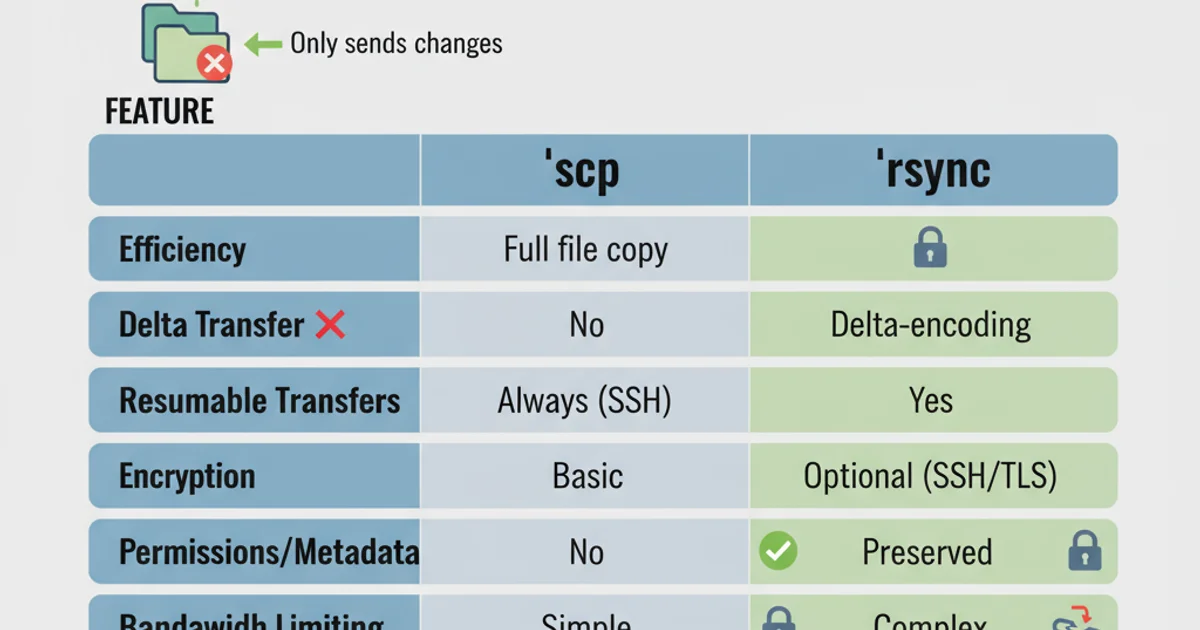
Comparison of scp and rsync features.
When to use scp:
- Simple, one-off transfers: When you just need to copy a file or a directory once and don't anticipate future updates.
- Minimalistic environments: On systems where
rsyncmight not be installed or where you need the absolute simplest command. - Transferring new files: If all files are new to the destination,
scp's performance might be comparable torsyncfor the initial transfer, asrsyncstill incurs overhead for checksumming.
When to use rsync:
- Synchronizing directories: For keeping two directories identical, especially across multiple transfers.
- Large files with small changes: When transferring large files that have only minor modifications,
rsync's delta transfer saves significant bandwidth and time. - Slow or unreliable networks: Its ability to resume transfers and optimize bandwidth makes it superior in challenging network conditions.
- Automated backups:
rsyncis a staple for scripting backup solutions due to its efficiency and robust options. - Preserving file attributes:
rsyncoffers more granular control over preserving permissions, ownership, timestamps, and symbolic links.