Completely uninstall Python 3 on Mac
Categories:
Completely Uninstall Python 3 from macOS
Learn how to thoroughly remove Python 3 installations, including Homebrew, official installers, and residual files, from your Mac to resolve conflicts or start fresh.
Uninstalling Python 3 from macOS can be more complex than simply dragging an application to the trash. Python installations can come from various sources, including the official installer, Homebrew, or even pre-installed system versions (though you should never remove the system Python). This guide will walk you through the process of completely removing user-installed Python 3 versions and their associated files to ensure a clean slate, which is often necessary when troubleshooting environment issues or preparing for a new installation.
Understanding Python Installations on macOS
Before you begin, it's crucial to understand that macOS comes with its own version of Python (usually Python 2.x or a specific Python 3.x for system utilities). Do not attempt to remove the system-provided Python. Doing so can break core macOS functionalities. This guide focuses solely on removing Python versions that you, the user, have installed, typically found in /usr/local/bin, /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework, or managed by Homebrew.
Identifying the source of your Python installation is the first step. Common sources include:
- Homebrew: A popular package manager for macOS.
- Official Python.org Installer: Installs Python into
/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework. - Pyenv/Conda: Environment managers that install Python versions into specific directories, usually within your home folder.
flowchart TD
A[Start Uninstall Process] --> B{Identify Python Source?}
B -->|Homebrew| C[Uninstall Homebrew Python]
B -->|Official Installer| D[Remove Frameworks & Binaries]
B -->|Pyenv/Conda| E[Deactivate & Remove Environment]
C --> F[Clean Up Residual Files]
D --> F
E --> F
F --> G[Verify Removal]
G --> H[End]Flowchart for identifying and uninstalling Python 3 on macOS.
Step-by-Step Uninstallation Methods
The method you use to uninstall Python depends on how it was originally installed. Follow the relevant section below.
1. Uninstalling Homebrew Python
If you installed Python 3 using Homebrew, this is the cleanest method for removal. First, ensure you know which Python version Homebrew manages. Then, use the brew uninstall command.
# List all installed Python versions via Homebrew
brew list | grep python
# Uninstall a specific Python version (e.g., python@3.9)
brew uninstall python@3.9
# If you installed 'python' without a version, it usually links to the latest
brew uninstall python
# Clean up any broken symlinks or outdated files
brew cleanup
After uninstalling, Homebrew typically removes most associated files, but you might still need to check for residual files as described in the 'Cleaning Up Residual Files' section.
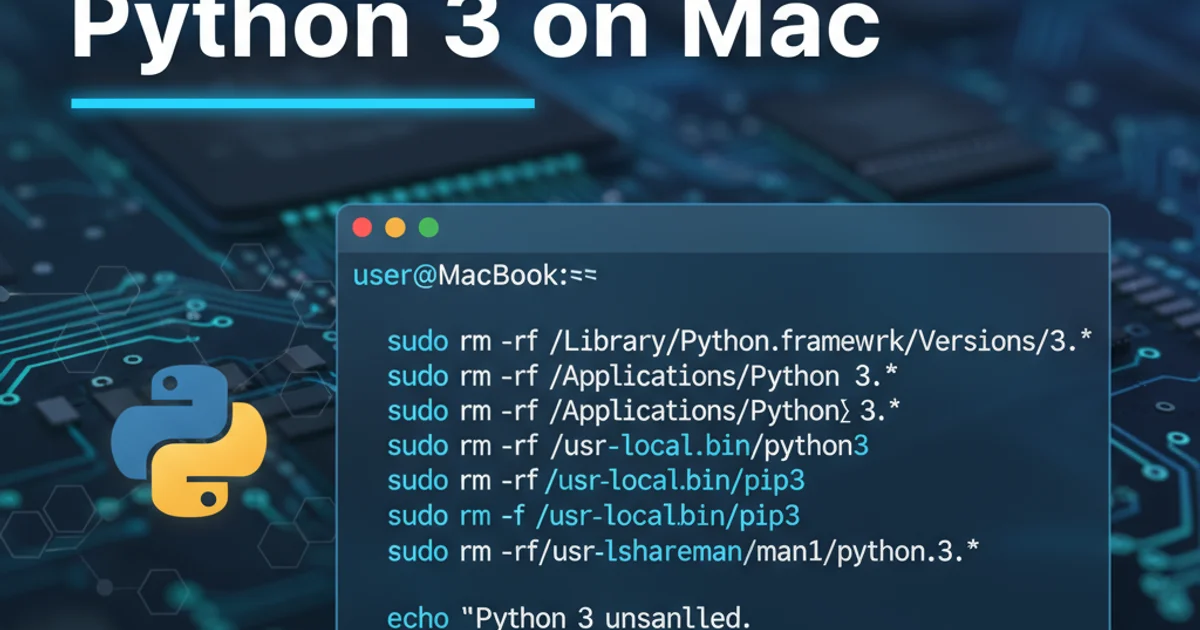
2. Uninstalling Official Python.org Installer Versions
Python versions installed via the official .pkg installer from python.org place files in /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework and create symlinks in /usr/local/bin. To remove these:
Remove the Python Framework:
sudo rm -rf /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.x # Replace '3.x' with the specific version you want to remove, e.g., 3.9, 3.10Remove Symlinks from
/usr/local/bin:# List Python-related symlinks in /usr/local/bin ls -l /usr/local/bin | grep python # Remove specific symlinks (e.g., python3, pip3, idle3, pydoc3, 2to3) sudo rm -f /usr/local/bin/python3.x sudo rm -f /usr/local/bin/pip3.x # Repeat for any other symlinks pointing to the removed frameworkRemove Python Applications (IDLE, Python Launcher): These are usually found in
/Applications/Python 3.x. Drag the folder to the Trash.sudo rm -rf /Applications/Python\ 3.x
3. Uninstalling Pyenv or Conda Environments
If you're using pyenv or conda (Anaconda/Miniconda), you should manage Python versions through their respective commands. These tools typically install Python versions within your user directory, making them easier to remove without affecting system-wide installations.
For Pyenv:
# List installed versions pyenv versions # Uninstall a specific version (e.g., 3.9.1) pyenv uninstall 3.9.1For Conda (Anaconda/Miniconda):
# List environments conda env list # Remove a specific environment (e.g., myenv) conda env remove --name myenv # To completely remove Anaconda/Miniconda # 1. Remove the installation directory (e.g., ~/opt/anaconda3 or ~/miniconda3) rm -rf ~/opt/anaconda3 # 2. Remove paths from your shell configuration (.bash_profile, .zshrc, etc.) # 3. Remove hidden files and folders rm -rf ~/.condarc ~/.conda ~/.continuum
Cleaning Up Residual Files
Even after using the above methods, some residual files, such as pip packages, .bash_profile or .zshrc entries, and cached files, might remain. It's good practice to clean these up.
Remove
pippackages: If you had apipinstallation associated with the Python version you removed, its packages might still be present. Whilepipitself is usually removed with the Python version, you can manually check and remove any lingering package directories.# Check common pip package locations ls -l /usr/local/lib/python3.x/site-packages ls -l ~/Library/Python/3.x/lib/python/site-packages # Manually remove directories if found (use with caution) # sudo rm -rf /usr/local/lib/python3.x/site-packagesCheck Shell Configuration Files: Open your shell's configuration file (
~/.bash_profile,~/.zshrc,~/.profile) and remove anyPATHentries or aliases that point to the uninstalled Python version. Save the file and thensourceit or restart your terminal.# Example of what to look for and remove export PATH="/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.x/bin:${PATH}"Remove Python Cache Directories:
sudo rm -rf ~/Library/Caches/pip sudo rm -rf ~/.python_history
sudo rm -rf. This command permanently deletes files and directories without confirmation. Double-check your paths before executing to avoid accidental data loss or damaging your macOS installation.Verifying Complete Removal
After performing the uninstallation steps, verify that Python 3 has been removed from your system's PATH.
Check Python version:
python3 --versionIf it returns
command not foundor shows a different, unexpected version (e.g., the system Python), it's a good sign. If it still shows the version you intended to remove, revisit the steps, especially checking yourPATHenvironment variable.Check
whichcommand:which python3 which pip3These commands should ideally return nothing or point to the system Python (e.g.,
/usr/bin/python3), not a user-installed version.
pyenv or conda. These tools allow you to manage multiple Python versions and virtual environments easily, preventing conflicts and making future uninstallation much simpler.