converting 'describe' into 'create table' in MySQL?
Converting MySQL DESCRIBE Output to CREATE TABLE Statements
Learn how to transform the output of MySQL's DESCRIBE command into a CREATE TABLE statement, enabling easy table recreation or migration.
The DESCRIBE (or DESC) command in MySQL is incredibly useful for quickly inspecting the structure of an existing table. It provides details like column names, data types, nullability, default values, and key information. However, if you need to recreate that table, perhaps in a different database or as part of a migration script, simply viewing the DESCRIBE output isn't enough. You need a CREATE TABLE statement.
This article will guide you through various methods to convert the information obtained from DESCRIBE into a fully functional CREATE TABLE statement, ranging from simple SQL commands to more advanced scripting techniques.
Using SHOW CREATE TABLE for Direct Generation
The most straightforward and recommended way to get a CREATE TABLE statement for an existing table is to use the SHOW CREATE TABLE command. This command directly outputs the exact SQL statement that was used to create the table, including all column definitions, indexes, foreign keys, and table options (like engine and character set).
SHOW CREATE TABLE your_table_name;
Example of using SHOW CREATE TABLE
The output of SHOW CREATE TABLE will typically have two columns: Table and Create Table. The Create Table column will contain the full CREATE TABLE statement. You can then copy and paste this statement to recreate the table elsewhere.
SHOW CREATE TABLE over trying to manually construct a CREATE TABLE statement from DESCRIBE output. SHOW CREATE TABLE captures all nuances, including indexes, foreign keys, and table-level options, which DESCRIBE does not fully expose.Extracting Information from information_schema.COLUMNS
While SHOW CREATE TABLE is ideal, there might be scenarios where you need to programmatically construct CREATE TABLE statements, perhaps with modifications, or when you only have access to information_schema. The information_schema.COLUMNS table provides detailed metadata about all columns in all tables across your MySQL instance. You can query this table to gather the necessary information to build a CREATE TABLE statement.
SELECT
COLUMN_NAME,
COLUMN_TYPE,
IS_NULLABLE,
COLUMN_DEFAULT,
EXTRA
FROM
information_schema.COLUMNS
WHERE
TABLE_SCHEMA = 'your_database_name' AND TABLE_NAME = 'your_table_name'
ORDER BY
ORDINAL_POSITION;
Querying information_schema.COLUMNS for table metadata
From this output, you would then need to manually or programmatically piece together the CREATE TABLE statement. This approach is more complex and error-prone than SHOW CREATE TABLE because it doesn't directly provide index definitions, foreign key constraints, or table options. It's generally used when you need fine-grained control over the column definitions or when SHOW CREATE TABLE is not an option.
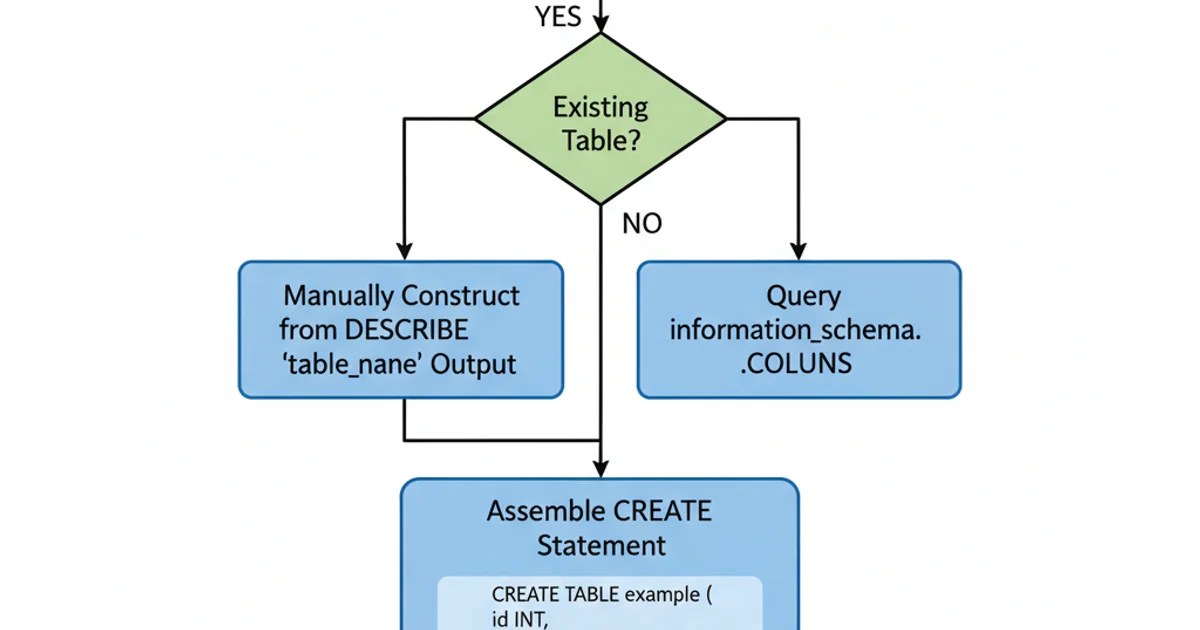
Workflow for generating CREATE TABLE statements
Using mysqldump for Database Schema Export
For exporting entire database schemas or specific tables, mysqldump is the go-to utility. It generates SQL statements that can recreate the database structure (and optionally data). This is particularly useful for backups, migrations, or setting up development environments.
mysqldump -u your_username -p your_database_name your_table_name --no-data > create_table_script.sql
Using mysqldump to export only the table schema
The --no-data option ensures that only the CREATE TABLE statements (and other schema-related statements like CREATE DATABASE if applicable) are included in the output file, without any INSERT statements for the data. This provides a robust and complete CREATE TABLE statement, including all constraints and options, similar to SHOW CREATE TABLE but for one or more tables at once.
mysqldump, ensure you have the necessary permissions to access the database. Also, be mindful of sensitive data if you omit --no-data and are exporting to an insecure location.