How to Get the HTTP Post data in C#?
Categories:
Mastering HTTP POST Data Retrieval in C# ASP.NET
Learn various techniques to effectively retrieve and process HTTP POST data in C# ASP.NET applications, covering form data, JSON, and raw body content.
Retrieving HTTP POST data is a fundamental task in web development, especially when building interactive applications that handle user input, API requests, or file uploads. In C# ASP.NET, there are several ways to access this data, depending on its format (e.g., form-urlencoded, JSON, raw body). This article will guide you through the most common scenarios and provide practical code examples to help you effectively process incoming POST requests.
Understanding HTTP POST Data Formats
Before diving into the code, it's crucial to understand the different ways data can be sent via an HTTP POST request. The Content-Type header of the request plays a vital role in determining how the data is structured and, consequently, how you should retrieve it in your C# application. The most common content types for POST requests include:
application/x-www-form-urlencoded: Standard for HTML form submissions. Data is sent as key-value pairs, URL-encoded.multipart/form-data: Used for HTML forms that include file uploads. Data is sent as a series of parts, each with its ownContent-Type.application/json: Increasingly common for API requests, where data is sent as a JSON string.text/plainorapplication/octet-stream: For sending raw text or binary data.
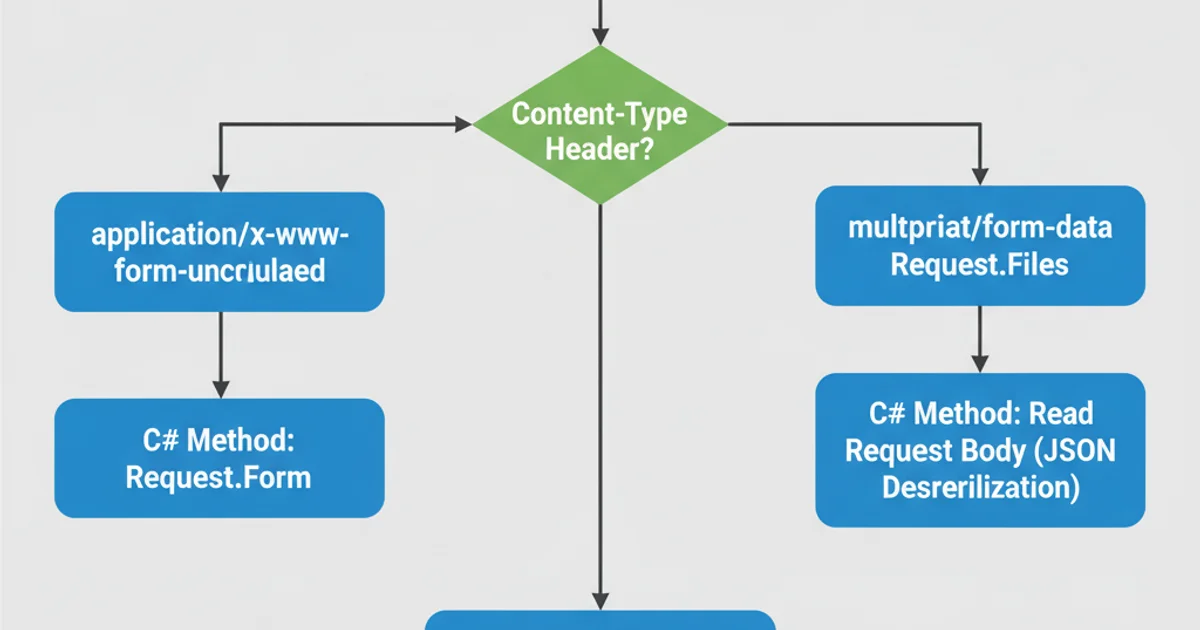
Decision flow for handling different HTTP POST content types in ASP.NET.
Retrieving Form Data (application/x-www-form-urlencoded)
When an HTML form is submitted with the default enctype (or application/x-www-form-urlencoded), the data is accessible through the Request.Form collection in ASP.NET. This collection provides a convenient way to get individual form fields by their name attribute.
using System.Web.Mvc;
public class HomeController : Controller
{
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult SubmitForm()
{
// Access individual form fields by name
string username = Request.Form["username"];
string email = Request.Form["email"];
string message = Request.Form["message"];
// You can also iterate through all form keys
foreach (string key in Request.Form.Keys)
{
string value = Request.Form[key];
// Log or process key-value pair
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine($"{key}: {value}");
}
// Process the data...
ViewBag.Message = $"Received: Username={username}, Email={email}, Message={message}";
return View("Success");
}
}
Example of retrieving form data using Request.Form in an ASP.NET MVC controller.
Request.Form to prevent security vulnerabilities like XSS and SQL injection.Retrieving JSON Data (application/json)
For API endpoints or modern web applications, data is often sent as a JSON payload in the request body. To retrieve this, you need to read the raw request body and then deserialize the JSON string into a C# object. This typically involves using StreamReader to read the Request.InputStream and a JSON deserializer like Newtonsoft.Json or System.Text.Json.
using System.IO;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using Newtonsoft.Json; // Requires NuGet package: Newtonsoft.Json
public class Product
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
}
public class ApiController : Controller
{
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult CreateProduct()
{
Product product = null;
using (StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(Request.InputStream))
{
string jsonContent = reader.ReadToEnd();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(jsonContent))
{
product = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<Product>(jsonContent);
}
}
if (product != null)
{
// Process the product object
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine($"Received Product: Id={product.Id}, Name={product.Name}, Price={product.Price}");
return Json(new { success = true, message = "Product created successfully" });
}
else
{
return Json(new { success = false, message = "Invalid JSON data" });
}
}
}
Example of reading and deserializing JSON data from the request body in ASP.NET MVC.
public IActionResult CreateProduct([FromBody] Product product).Retrieving File Uploads (multipart/form-data)
When an HTML form includes file input fields and its enctype is set to multipart/form-data, files are sent as part of the POST request. ASP.NET provides the Request.Files collection to access these uploaded files. Each file is represented by an HttpPostedFileBase object (or IFormFile in ASP.NET Core).
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using System.IO;
public class UploadController : Controller
{
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult UploadFile()
{
if (Request.Files.Count > 0)
{
HttpPostedFileBase file = Request.Files[0]; // Get the first uploaded file
if (file != null && file.ContentLength > 0)
{
// Get file name and extension
string fileName = Path.GetFileName(file.FileName);
string fileExtension = Path.GetExtension(fileName);
// Define a path to save the file (e.g., in App_Data or a dedicated uploads folder)
string path = Path.Combine(Server.MapPath("~/App_Data/Uploads"), fileName);
// Ensure the directory exists
Directory.CreateDirectory(Path.GetDirectoryName(path));
// Save the file to the server
file.SaveAs(path);
ViewBag.Message = $"File '{fileName}' uploaded successfully to {path}";
return View("Success");
}
}
ViewBag.Message = "No file uploaded or file was empty.";
return View("Error");
}
}
Example of handling file uploads using Request.Files in ASP.NET MVC.
Retrieving Raw Request Body (General Purpose)
For scenarios where the Content-Type is not one of the common types (e.g., text/plain, application/octet-stream, or a custom type), you might need to read the raw request body directly. This is similar to reading JSON, but without the deserialization step.
using System.IO;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using System.Text;
public class RawDataController : Controller
{
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult ProcessRawData()
{
string rawContent;
using (StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(Request.InputStream, Encoding.UTF8))
{
rawContent = reader.ReadToEnd();
}
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(rawContent))
{
// Log or process the raw content
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine($"Received Raw Data: {rawContent}");
return Content($"Raw data received: {rawContent}", "text/plain");
}
else
{
return Content("No raw data received.", "text/plain");
}
}
}
Example of reading the raw request body for generic content types.
Request.InputStream. Encoding.UTF8 is a common and safe choice, but verify it matches the client's Content-Type header if specified.