What is the difference between baud rate and bit rate?
Categories:
Baud Rate vs. Bit Rate: Understanding Serial Communication Speed
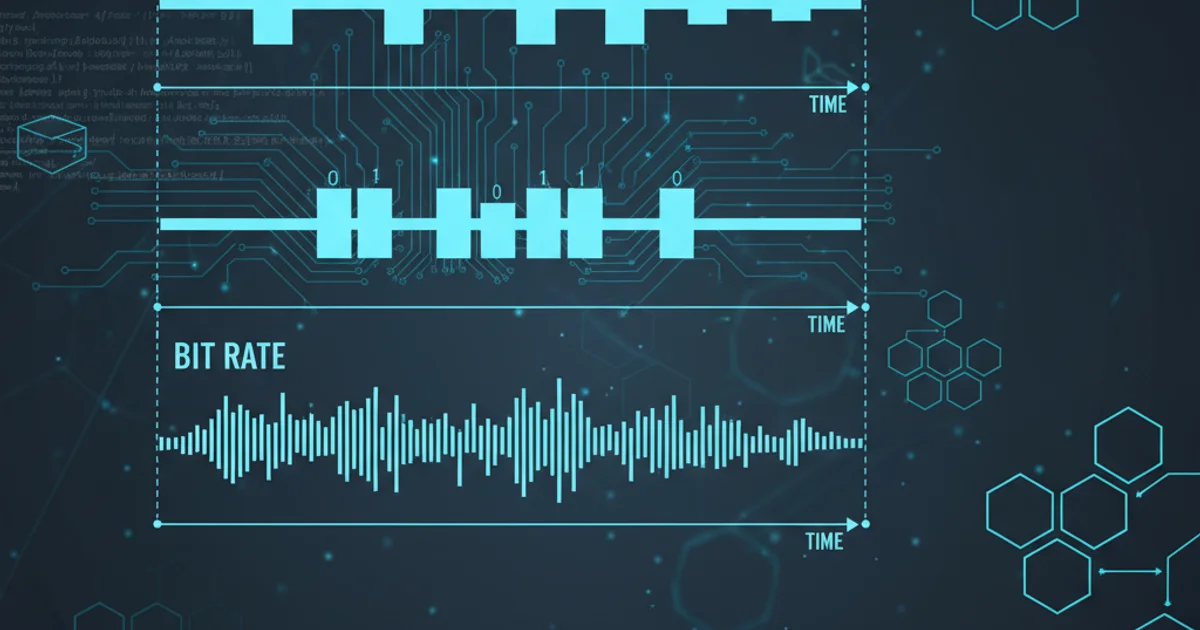

Demystify the common confusion between baud rate and bit rate in serial communication, especially in the context of microcontrollers and UART. Learn how these terms relate to data transfer speed and signal changes.
When working with serial communication, particularly with microcontrollers and protocols like UART, two terms frequently arise: baud rate and bit rate. While often used interchangeably, they represent distinct concepts crucial for understanding how data is transmitted. This article will clarify the difference, explain their significance, and provide practical examples.
What is Bit Rate?
The bit rate refers to the number of individual bits (binary digits, 0s or 1s) transmitted per second. It is a direct measure of the actual data throughput. The unit for bit rate is bits per second (bps). In most modern digital communication systems, especially those using simple encoding schemes, the bit rate is often the primary metric for data transfer speed. For example, if you're sending a stream of 1s and 0s directly, the bit rate tells you how many of those 1s and 0s are being sent every second.
What is Baud Rate?
The baud rate (named after Émile Baudot, inventor of the Baudot code) refers to the number of signal changes, or symbol changes, that occur on the transmission medium per second. A 'symbol' is a distinct signal event that can represent one or more bits. The unit for baud rate is bauds.
In the simplest case, where each signal change represents exactly one bit (e.g., a voltage change from low to high represents a '1', and high to low represents a '0'), the baud rate and bit rate are equal. However, with more advanced modulation techniques, a single symbol can encode multiple bits. For instance, if a system uses four distinct voltage levels, each level (symbol) can represent two bits (00, 01, 10, 11). In such a scenario, the bit rate would be twice the baud rate.
flowchart TD
A[Data Source] --> B{Encoding Process}
B --> C[Modulator]
C --> D[Transmission Medium]
D --> E[Demodulator]
E --> F{Decoding Process}
F --> G[Data Destination]
subgraph "Bit Rate"
B -- "Bits/second" --> C
end
subgraph "Baud Rate"
C -- "Symbols/second" --> D
end
style B fill:#f9f,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style F fill:#f9f,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style C fill:#ccf,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style E fill:#ccf,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style D fill:#afa,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2pxFlowchart illustrating the relationship between bit rate and baud rate in a communication system.
The Relationship: Bit Rate = Baud Rate × Bits per Symbol
The fundamental relationship between bit rate and baud rate is given by the formula:
Bit Rate = Baud Rate × Number of Bits per Symbol
- If 1 symbol = 1 bit: Then Bit Rate = Baud Rate. This is common in simple serial communication like UART, where each voltage level change typically represents one bit.
- If 1 symbol > 1 bit: Then Bit Rate > Baud Rate. This occurs in more complex modulation schemes (e.g., QAM in modems) where multiple bits are encoded into a single signal change. For example, if a symbol can represent 2 bits, then a 2400 baud modem would have a bit rate of 4800 bps.
Practical Implications for Microcontrollers (UART)
When configuring a UART peripheral on a microcontroller, you typically set the baud rate. This setting determines the rate at which the UART hardware will sample the incoming signal or generate outgoing signal changes. Since UART commonly uses a simple encoding where one symbol equals one bit, setting the baud rate to, say, 9600 means that 9600 bits per second will be transmitted or received. Both the transmitting and receiving devices must agree on the same baud rate for successful communication.
#include <Arduino.h>
void setup() {
// Initializes serial communication at 9600 baud
// For UART, this also means 9600 bits per second (bps)
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("UART communication initialized at 9600 baud.");
}
void loop() {
// Your main code here
// Data sent via Serial.write() or Serial.print() will adhere to the 9600 baud rate
}
Arduino example setting UART baud rate
Summary of Differences
To summarize the key distinctions:
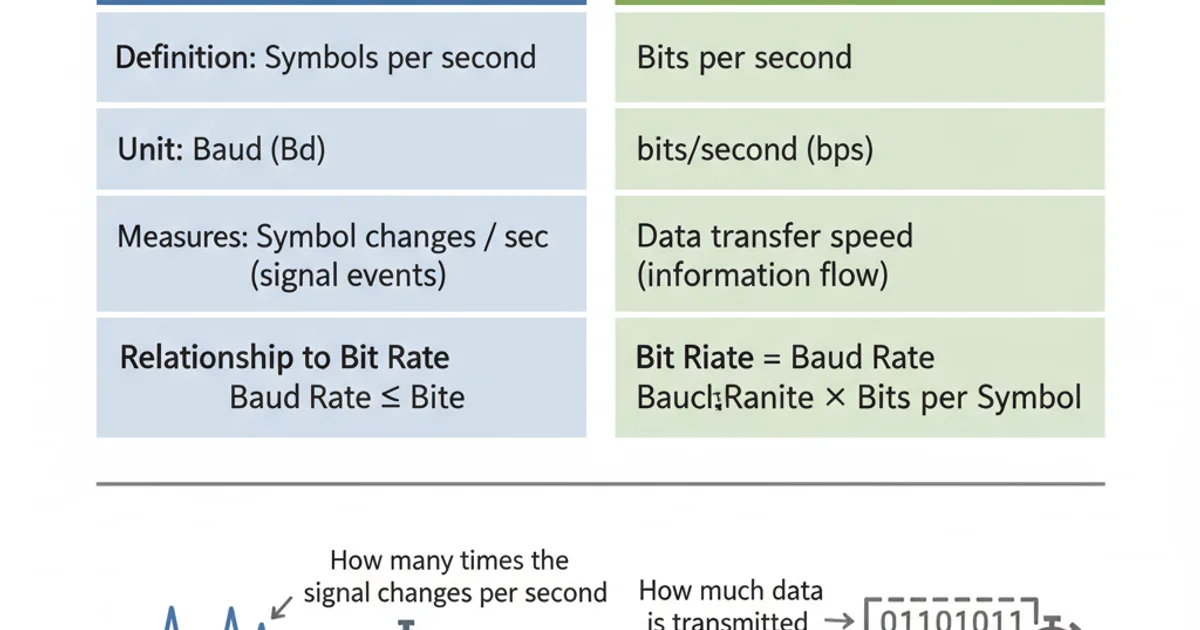
Comparison of Baud Rate and Bit Rate
Understanding the difference between baud rate and bit rate is fundamental for anyone working with serial communication. While they often coincide in simple systems like microcontroller UART, recognizing their distinct meanings is crucial for troubleshooting and for delving into more complex communication protocols.