How can I compile a PLSQL package
Categories:
How to Compile a PL/SQL Package in Oracle Databases
Learn the essential methods for compiling PL/SQL packages using SQL*Plus, SQL Developer, and Toad, ensuring your database objects are valid and ready for execution.
Compiling PL/SQL packages is a fundamental task for any Oracle developer or DBA. Whether you're deploying new code, fixing bugs, or refreshing dependencies, understanding the various compilation methods is crucial. A successful compilation ensures that your package's syntax is correct, its dependencies are resolved, and it's ready to be executed within the Oracle database environment. This article will guide you through the most common ways to compile PL/SQL packages.
Understanding PL/SQL Package Compilation
A PL/SQL package is a schema object that groups logically related PL/SQL types, variables, constants, subprograms (procedures and functions), and cursors. When you compile a package, the Oracle database parses its code, checks for syntax errors, resolves references to other database objects, and stores the compiled code in the data dictionary. If any errors are found, the compilation fails, and the package becomes invalid. It's important to address all compilation errors before the package can be used.
flowchart TD
A[Start Compilation] --> B{Package Source Code Available?}
B -- No --> C[Load Source Code]
B -- Yes --> D[Parse Code & Check Syntax]
D --> E{Syntax Errors?}
E -- Yes --> F[Report Errors & Invalidate Package]
E -- No --> G[Resolve Dependencies]
G --> H{Dependency Issues?}
H -- Yes --> F
H -- No --> I[Store Compiled Code]
I --> J[Mark Package Valid]
J --> K[End Compilation]PL/SQL Package Compilation Workflow
Compilation Methods
There are several ways to compile PL/SQL packages, each suitable for different scenarios and preferences. We'll cover the most common tools: SQL*Plus, Oracle SQL Developer, and Toad for Oracle.
USER_ERRORS or ALL_ERRORS data dictionary views after compilation to review any warnings or errors, especially if the package status is INVALID.1. Using SQL*Plus
SQL*Plus is Oracle's command-line interface and is ideal for scripting and automated deployments. To compile a package, you typically use the ALTER PACKAGE ... COMPILE statement or execute the source file directly.
2. Compile Package Body
To compile only the package body, use the ALTER PACKAGE <package_name> COMPILE BODY; command. This is useful when only the implementation has changed and the package specification remains the same.
3. Compile Package Specification
To compile only the package specification, use the ALTER PACKAGE <package_name> COMPILE SPECIFICATION; command. This is less common as changes to the specification often require recompilation of the body and dependent objects.
4. Compile Entire Package
To compile both the specification and body, use ALTER PACKAGE <package_name> COMPILE;. This is the most common approach when making changes to either part of the package.
5. Execute Source File
Alternatively, you can execute the .sql file containing your package source code using @<file_path>. This will create or replace the package and compile it automatically.
ALTER PACKAGE my_package COMPILE;
ALTER PACKAGE my_package COMPILE PACKAGE;
ALTER PACKAGE my_package COMPILE SPECIFICATION;
ALTER PACKAGE my_package COMPILE BODY;
-- Example of executing a source file
@/path/to/my_package.sql
SQLPlus commands for compiling a PL/SQL package.*
1. Using Oracle SQL Developer
Oracle SQL Developer provides a rich graphical interface for database development. Compiling packages here is intuitive.
2. Navigate to Packages
In the Connections navigator, expand your connection, then expand 'Packages'.
3. Select and Compile
Right-click on the desired package (or its specification/body) and select 'Compile'. SQL Developer will show compilation results in the 'Compiler Log' tab.
4. Compile with Debug
You can also choose 'Compile for Debug' if you intend to step through the code using the debugger.
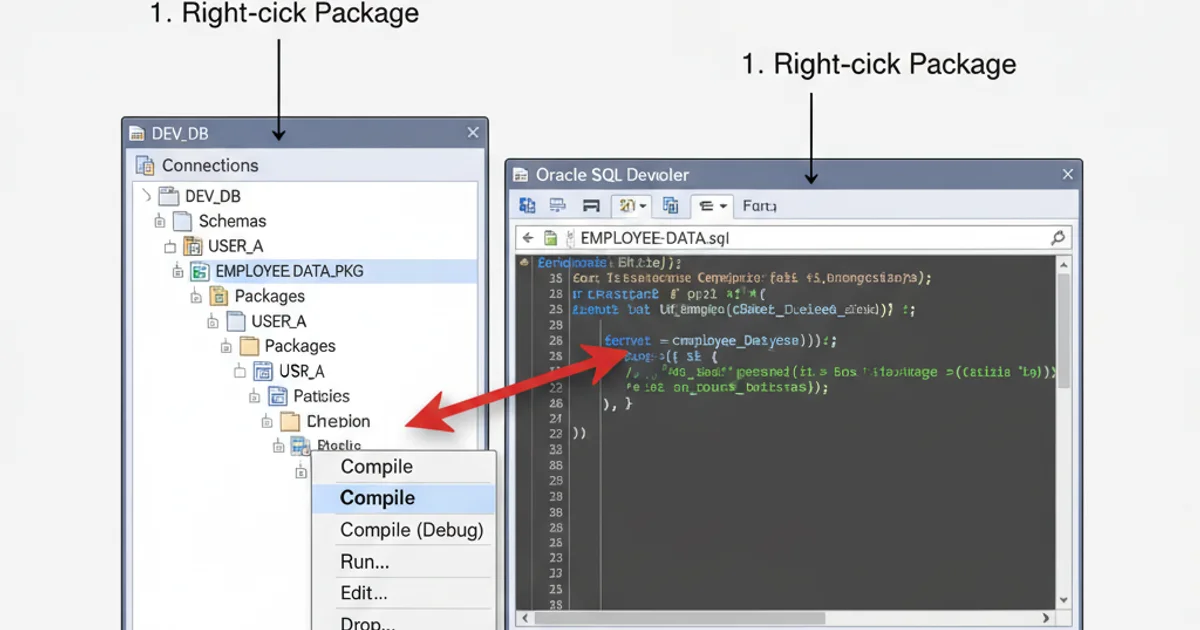
Compiling a package in Oracle SQL Developer.
1. Using Toad for Oracle
Toad is another popular third-party tool for Oracle development, offering similar functionality to SQL Developer.
2. Open Schema Browser
Go to 'Database' -> 'Schema Browser' or press F10.
3. Locate Package
Select 'Packages' from the object type dropdown. Find your package in the list.
4. Compile Package
Right-click on the package name and select 'Compile' or 'Compile Invalid Objects'. Toad will display compilation messages in the 'Output' window.
Checking Package Status and Errors
After attempting to compile, it's essential to verify the package's status and review any errors. You can do this using SQL queries against the data dictionary views.
SELECT object_name, object_type, status
FROM user_objects
WHERE object_name = 'MY_PACKAGE';
SELECT line, position, text
FROM user_errors
WHERE name = 'MY_PACKAGE'
AND type = 'PACKAGE'
ORDER BY line, position;
Checking package status and compilation errors.
A status of VALID indicates a successful compilation. If the status is INVALID, the USER_ERRORS view will provide details on why the compilation failed, including line numbers and error messages, which are crucial for debugging.