Pure css tree with borders
Categories:
Crafting Pure CSS Tree Structures with Borders
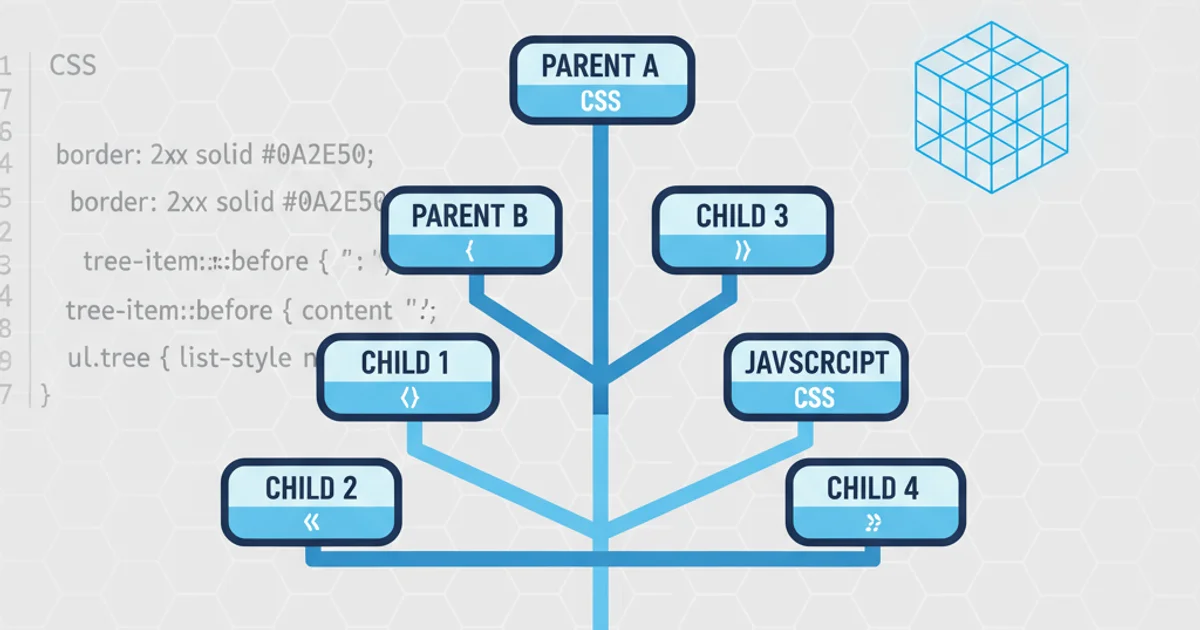
Learn how to create visually appealing and functional tree structures using only CSS, focusing on adding borders for clear hierarchy and separation.
Tree structures are a common way to represent hierarchical data, such as file systems, organizational charts, or navigation menus. While JavaScript is often used for dynamic tree manipulation, it's entirely possible to build static or semi-static tree views using pure CSS. This article will guide you through the process of creating a CSS-only tree structure, with a particular emphasis on applying borders to enhance visual clarity and define the relationships between parent and child nodes.
Basic Tree Structure with Unordered Lists
The most semantic and straightforward way to represent a tree structure in HTML is by nesting unordered lists (<ul> and <li> elements). Each <li> can contain text or another <ul> to denote a child branch. This inherent nesting provides the structural foundation we'll leverage with CSS.
<ul class="tree">
<li>Parent Node 1
<ul>
<li>Child Node 1.1</li>
<li>Child Node 1.2
<ul>
<li>Grandchild Node 1.2.1</li>
<li>Grandchild Node 1.2.2</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>Parent Node 2
<ul>
<li>Child Node 2.1</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
Basic HTML structure for a tree using nested unordered lists.
Applying Borders and Layout with CSS
To transform the nested lists into a visual tree, we'll use CSS. The key is to remove default list styling, position elements, and then strategically apply borders to create the 'branches' and 'nodes'. We'll use pseudo-elements (::before and ::after) to draw the connecting lines and borders without adding extra markup.
flowchart TD
A[HTML Structure (UL/LI)] --> B{Remove Default Styles}
B --> C{Positioning (Relative/Absolute)}
C --> D{Apply Vertical Borders (LI::before)}
D --> E{Apply Horizontal Borders (LI::after)}
E --> F[Final Pure CSS Tree]Workflow for building a pure CSS tree with borders.
.tree, .tree ul {
list-style: none;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
position: relative;
}
.tree ul {
margin-left: 20px; /* Indent child nodes */
}
.tree li {
margin: 0;
padding: 0 7px;
line-height: 20px;
border-left: 1px solid #ccc; /* Vertical line for parent */
position: relative;
}
.tree li:last-child {
border-left: none; /* Remove vertical line for last child */
}
.tree li::before {
content: '';
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: -1px; /* Adjust to align with parent border */
width: 20px;
height: 10px;
border-bottom: 1px solid #ccc; /* Horizontal line from parent */
border-left: 1px solid #ccc;
}
.tree li:first-child::before {
top: 10px; /* Adjust for first child to connect properly */
}
.tree li:last-child::before {
border-left: none; /* No vertical line for last child's connection */
}
.tree li span {
display: inline-block;
padding: 3px 8px;
border: 1px solid #999; /* Border for the node content */
border-radius: 4px;
background-color: #f9f9f9;
margin-left: 5px;
}
CSS for styling a pure CSS tree with borders.
<span> or <a> tag within the <li> to apply specific styling like borders directly to the node content, rather than the <li> itself. This also makes it easier to add hover effects or click handlers.Refining the Visuals and Interactivity
The basic CSS provides a functional tree. To enhance its appearance, you can adjust colors, line thicknesses, and spacing. For interactivity, such as expanding/collapsing nodes, you would typically introduce JavaScript. However, a pure CSS solution for collapsing can be achieved using the :has() pseudo-class (though browser support varies) or by using checkboxes and the ~ (general sibling combinator) or + (adjacent sibling combinator) selectors, which is more complex for deeply nested trees.
/* Example of styling the node content */
.tree li > span {
cursor: pointer;
transition: background-color 0.2s ease;
}
.tree li > span:hover {
background-color: #e0e0e0;
}
/* Example for a more robust border around the node text */
.tree li > a {
display: inline-block;
padding: 5px 10px;
border: 1px solid #a0a0a0;
border-radius: 5px;
text-decoration: none;
color: #333;
background-color: #fff;
margin-left: 5px;
box-shadow: 1px 1px 3px rgba(0,0,0,0.1);
}
Additional CSS for styling node content and hover effects.
border-left and border-bottom properties on ::before and ::after pseudo-elements are crucial for drawing the connecting lines. Careful positioning with top, left, width, and height ensures these lines align correctly to form the tree branches.