How to generate random strings in Python?
Categories:
Mastering Random String Generation in Python

Learn various Python techniques to generate random strings for passwords, tokens, and unique identifiers, from basic alphanumeric sequences to cryptographically secure options.
Generating random strings is a common requirement in many programming tasks, such as creating temporary passwords, unique identifiers, session tokens, or test data. Python offers several modules and approaches to achieve this, ranging from simple character selection to cryptographically secure methods. This article will guide you through the most effective ways to generate random strings in Python, explaining the use cases and security considerations for each.
Basic Random String Generation with random and string modules
For most non-security-sensitive applications, Python's built-in random and string modules provide a straightforward way to generate random strings. The string module offers convenient constants for common character sets (e.g., string.ascii_letters, string.digits, string.punctuation), while the random module provides functions like random.choice() to pick elements from a sequence and random.sample() for selecting multiple unique elements.
import random
import string
def generate_random_string(length):
characters = string.ascii_letters + string.digits + string.punctuation
random_string = ''.join(random.choice(characters) for i in range(length))
return random_string
# Example usage:
print(f"Random string (10 chars): {generate_random_string(10)}")
print(f"Random string (20 chars): {generate_random_string(20)}")
Generating a random string using random.choice() and string constants.
characters variable to include or exclude specific character types based on your requirements. For example, to generate an alphanumeric string, use string.ascii_letters + string.digits.Generating Cryptographically Secure Random Strings
When generating strings for security-sensitive purposes like passwords, API keys, or session tokens, it's crucial to use a cryptographically secure random number generator (CSPRNG). The random module is generally not suitable for these cases as its pseudo-random number generator might be predictable. Python's secrets module, introduced in Python 3.6, is specifically designed for generating cryptographically strong random numbers and strings.
flowchart TD
A[Start]
A --> B{"Security Requirement?"}
B -->|Low (e.g., test data)| C[Use `random` module]
B -->|High (e.g., passwords, tokens)| D[Use `secrets` module]
C --> E[Combine `string` constants & `random.choice()`]
D --> F[Use `secrets.token_hex()` or `secrets.token_urlsafe()`]
E --> G[Output Random String]
F --> G
G --> H[End]Decision flow for choosing between random and secrets modules.
import secrets
import string
def generate_secure_random_string(length):
alphabet = string.ascii_letters + string.digits + string.punctuation
secure_string = ''.join(secrets.choice(alphabet) for i in range(length))
return secure_string
def generate_token_hex(length):
# Each byte becomes two hex digits, so length/2 bytes needed
return secrets.token_hex(length // 2)
def generate_token_urlsafe(length):
# Base64 encoding, roughly 4/3 times the byte length
return secrets.token_urlsafe(length // 4 * 3)
# Example usage:
print(f"Secure random string (16 chars): {generate_secure_random_string(16)}")
print(f"Hex token (32 chars): {generate_token_hex(32)}")
print(f"URL-safe token (24 chars): {generate_token_urlsafe(24)}")
Generating cryptographically secure random strings and tokens using the secrets module.
random.seed() with a predictable seed for security-sensitive applications, as this can make your 'random' strings easily guessable. The secrets module handles seeding securely.Understanding secrets.token_hex() and secrets.token_urlsafe()
The secrets module also provides specialized functions for generating tokens:
secrets.token_hex(nbytes): Generates a random text string in hexadecimal. Each byte of randomness results in two hexadecimal digits. So,secrets.token_hex(16)will produce a 32-character hex string.secrets.token_urlsafe(nbytes): Generates a random URL-safe text string, containing[A-Za-z0-9_-]. It uses Base64 encoding, so the length of the output string will be roughly 1.3 times the number of bytes requested. This is ideal for use in URLs or file names.
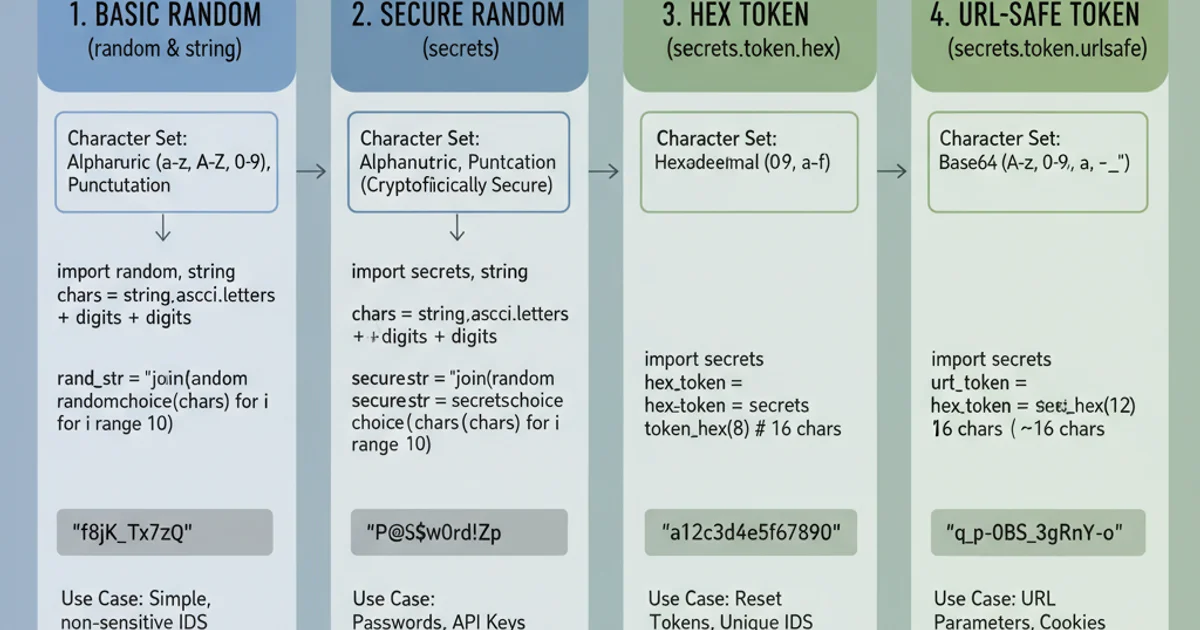
Different methods yield different string characteristics and are suited for specific purposes.