Which version of Python do I have installed?
Categories:
How to Check Your Python Version on Windows Server
Discover multiple reliable methods to quickly identify the Python version installed on your Windows Server, ensuring compatibility and proper environment setup.
Knowing which version of Python is installed on your system is crucial for development, deployment, and troubleshooting. Different projects may require specific Python versions, and an incorrect version can lead to unexpected errors or compatibility issues. This article provides comprehensive instructions for checking your Python version on Windows Server using various command-line tools and direct file inspection.
Method 1: Using the Command Prompt (CMD)
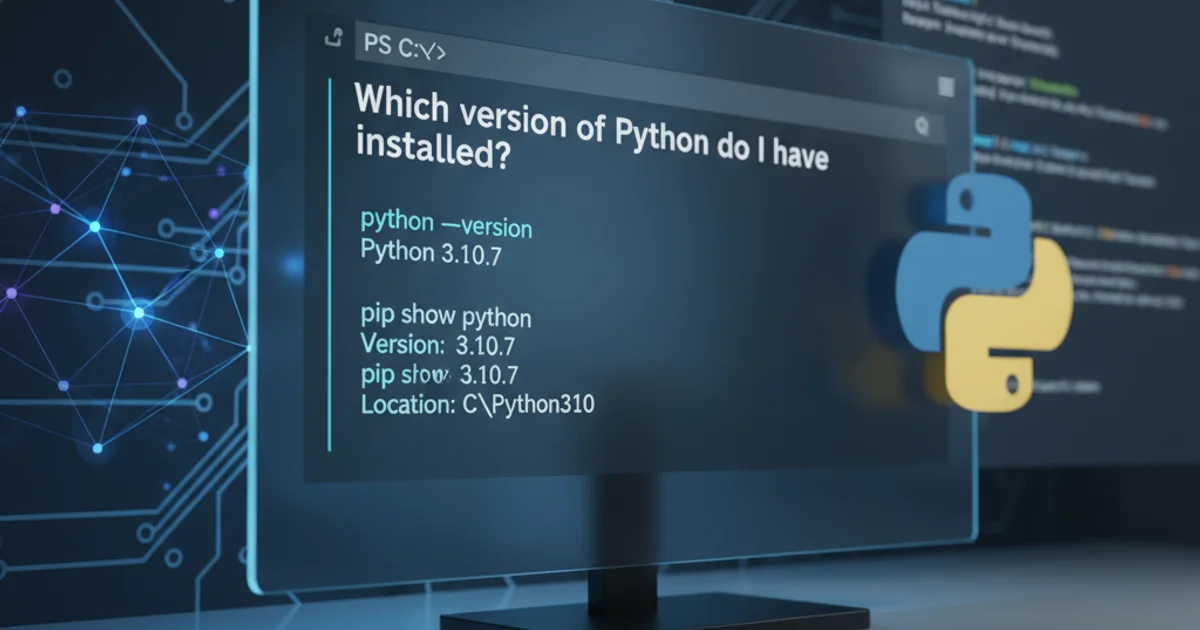
The most common and straightforward way to check your Python version is through the Command Prompt. This method works whether Python is added to your system's PATH environment variable or not, though the exact command might vary slightly.
python --version
Checking Python version using the python command.
If the python command is not recognized, it might be because Python 3 is installed and registered as python3, or it's not in your system's PATH. Try the following alternatives:
python3 --version
py --version
Alternative commands for checking Python version.
py command is the Python Launcher for Windows, which can help manage multiple Python installations and is often added to the PATH by default during installation.Method 2: Inspecting Python Executable Properties
If command-line methods fail or you need to verify the version of a specific Python executable, you can directly inspect its file properties. This is particularly useful if you have multiple Python installations or if Python is not in your system's PATH.
1. Locate the Python executable
Navigate to the directory where Python is installed. Common locations include C:\PythonXX (where XX is the version, e.g., C:\Python39) or C:\Users\YourUser\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\PythonXX.
2. Right-click on python.exe
Find the python.exe file (or pythonw.exe for the GUI version) and right-click on it.
3. Select 'Properties'
From the context menu, choose 'Properties'.
4. Go to the 'Details' tab
In the Properties window, click on the 'Details' tab. The 'Product version' field will display the installed Python version.
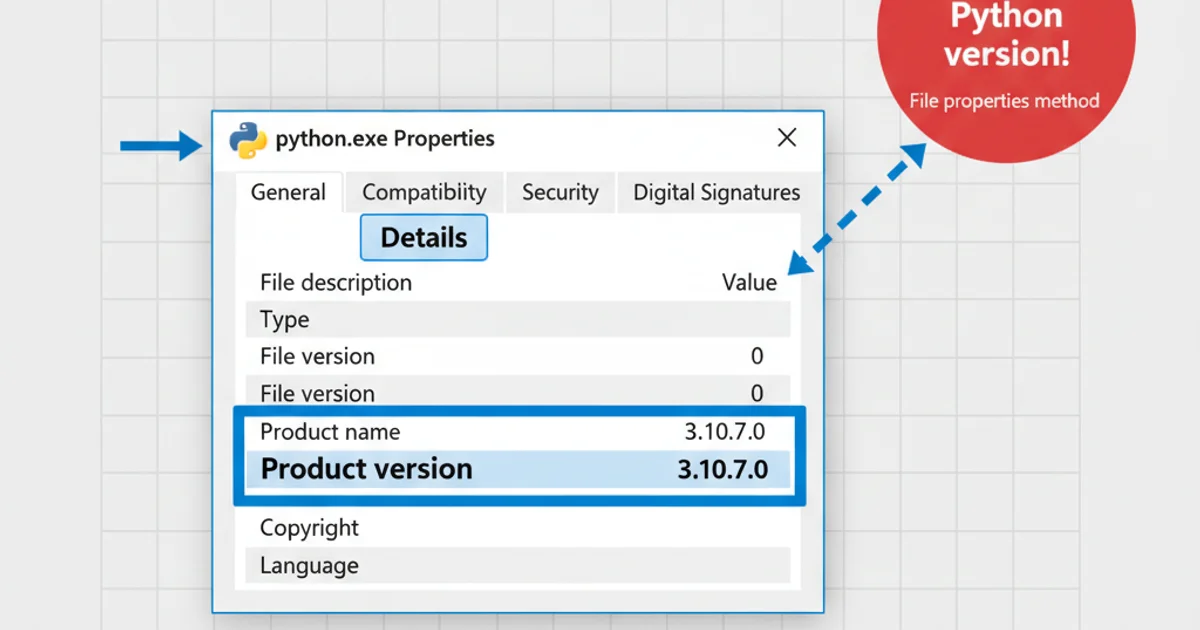
Checking Python version via file properties.
Method 3: Using Python's sys Module
You can also run a small Python script to programmatically determine the version. This method is reliable as it directly queries the Python interpreter itself.
import sys
print(sys.version)
Python script to print the installed version.
To execute this, you can either save it as a .py file and run it, or execute it directly from the command line:
python -c "import sys; print(sys.version)"
Executing Python code directly from the command line.
flowchart TD
A[Start] --> B{Open Command Prompt}
B --> C{Try `python --version`}
C --"Command not found"--> D{Try `python3 --version`}
D --"Command not found"--> E{Try `py --version`}
E --"Still not found"--> F[Locate python.exe]
F --> G{Right-click -> Properties -> Details}
G --> H[Check 'Product version']
C --"Version displayed"--> I[End]
D --"Version displayed"--> I
E --"Version displayed"--> I
H --> IFlowchart of methods to check Python version.
sys.version provides a detailed string including the version number, build date, and compiler information. If you only need the major.minor.patch version, you can use sys.version_info.