Laravel 4 Call to undefined method create()
Categories:
Resolving 'Call to undefined method create()' in Laravel 4

Understand and fix the common 'Call to undefined method create()' error when working with Eloquent models in Laravel 4, focusing on proper model instantiation and usage.
The 'Call to undefined method create()' error is a frequent stumbling block for developers new to Laravel 4, particularly when interacting with Eloquent ORM. This error typically arises when you attempt to call the static create() method on an instance of a model, rather than on the model class itself. Understanding the distinction between static and instance methods is crucial for effective Eloquent usage.
Understanding the 'create()' Method in Eloquent
In Laravel's Eloquent ORM, the create() method is a static method designed to quickly create and save a new record in your database. It expects an associative array of attributes that correspond to your table columns. This method handles both the instantiation of a new model and its persistence to the database in a single call. Because it's a static method, it must be called directly on the model class, not on an object instance of that class.
<?php
// Correct usage: Calling create() statically on the User model class
$user = User::create([
'name' => 'John Doe',
'email' => 'john.doe@example.com',
'password' => Hash::make('secret')
]);
// Incorrect usage (will throw 'Call to undefined method create()')
$userInstance = new User();
$userInstance->create([
'name' => 'Jane Doe',
'email' => 'jane.doe@example.com',
'password' => Hash::make('anothersecret')
]);
Illustrating correct and incorrect usage of Eloquent's create() method.
Common Causes and Solutions
The primary reason for this error is attempting to call create() on a model instance. Let's look at a typical scenario and its resolution.
<?php
// Scenario: You have a User model and a controller method
// app/models/User.php
class User extends Eloquent {
protected $fillable = ['name', 'email', 'password'];
}
// app/controllers/UserController.php
class UserController extends BaseController {
public function store() {
// INCORRECT: Instantiating the model first
$user = new User();
// This line will cause the error: Call to undefined method User::create()
$user->create(Input::all());
// CORRECT: Calling create() statically on the model class
$user = User::create(Input::all());
return Redirect::to('users')->with('message', 'User created successfully!');
}
}
Example of the error in a controller and its fix.
$fillable or $guarded property correctly set. Without $fillable, mass assignment via create() will be blocked, potentially leading to MassAssignmentException or silently failing to save data.Alternative: Manual Model Instantiation and Saving
If you need to perform actions on the model instance before saving, or prefer a more explicit approach, you can manually instantiate the model, assign attributes, and then call the save() method. The save() method is an instance method, meaning it's called on an object of the model.
<?php
// Manual instantiation and saving
$user = new User();
$user->name = Input::get('name');
$user->email = Input::get('email');
$user->password = Hash::make(Input::get('password'));
$user->save(); // This is an instance method, called on $user object
// This approach is useful if you need to manipulate the model object
// or perform validations before saving.
Using new Model() and save() for explicit control.
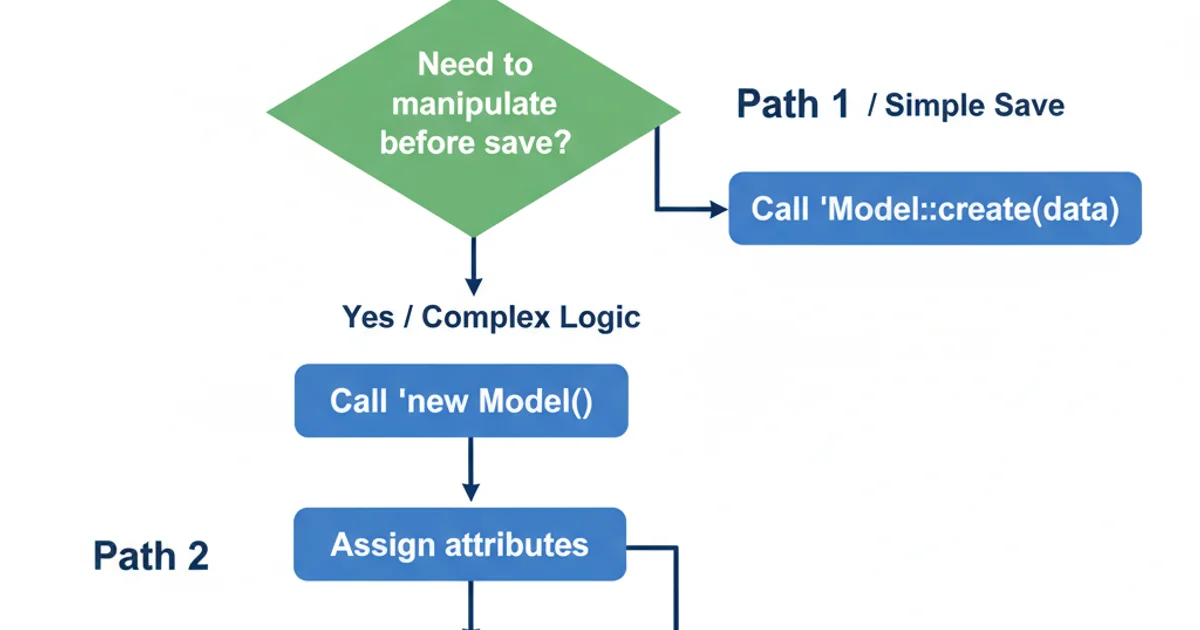
Flowchart: Eloquent Model Creation Methods