What's the difference between F5 refresh and Shift+F5 in Google Chrome browser?
Categories:
F5 vs. Shift+F5 in Chrome: Understanding Browser Refresh Mechanisms

Explore the subtle yet significant differences between a standard F5 refresh and a hard refresh (Shift+F5) in Google Chrome, and learn when to use each for effective troubleshooting and development.
In web development and even general browsing, you often encounter situations where a webpage doesn't display the latest content or behaves unexpectedly. Your first instinct might be to hit the refresh button or press F5. However, Google Chrome (and most modern browsers) offers a more powerful refresh option: Shift+F5 (or Ctrl+Shift+R on Windows/Linux, Cmd+Shift+R on Mac). While both actions reload the page, they do so with a crucial difference in how they handle cached resources. Understanding this distinction is key to effectively troubleshooting web issues and ensuring you're always viewing the most current version of a site.
The Standard Refresh (F5)
When you press F5 (or click the refresh icon in the browser's address bar), Google Chrome performs a standard refresh. This action reloads the current page, but it primarily uses cached versions of resources (like images, stylesheets, and JavaScript files) that it deems fresh enough. The browser checks with the server to see if the main HTML document has changed, and if so, it fetches the new HTML. For other resources, it relies on HTTP caching headers (like Cache-Control and Expires) to determine if a cached copy can be used without re-downloading. This approach is designed to save bandwidth and speed up page loading times, as the browser doesn't have to re-download every single asset on the page.
flowchart TD
A[User presses F5] --> B{Browser checks cache for resources?}
B -->|Yes, if fresh| C[Serve from cache]
B -->|No, if stale or no-cache| D[Request from server]
D --> E[Server responds with resource]
E --> F[Display page with mixed cached/new resources]Flowchart of a standard F5 refresh in Google Chrome.
The Hard Refresh (Shift+F5 / Ctrl+Shift+R)
A hard refresh, triggered by Shift+F5 (or Ctrl+Shift+R on Windows/Linux, Cmd+Shift+R on Mac), is a more aggressive form of reloading. When you perform a hard refresh, Chrome bypasses its local cache entirely for the current page. It forces the browser to re-download all resources (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, etc.) directly from the web server, ignoring any cached versions it might have. This is particularly useful when you suspect that cached files are causing display issues, or when you're a developer and want to ensure you're seeing the absolute latest changes to your code without any caching interference.
flowchart TD
A[User presses Shift+F5] --> B{Browser ignores cache?}
B -->|Yes, always| C[Request ALL resources from server]
C --> D[Server responds with ALL resources]
D --> E[Display page with ALL new resources]Flowchart of a hard refresh (Shift+F5) in Google Chrome.
F12). With DevTools open, right-clicking the refresh icon in the address bar reveals additional refresh options, including 'Hard Reload' and 'Empty Cache and Hard Reload', which is the most thorough option for clearing all cached data for the current site.When to Use Which Refresh Type
Choosing between a standard and hard refresh depends on the situation:
Use F5 (Standard Refresh) when:
- A page is stuck or unresponsive, and you just need to reload it quickly.
- You expect the content to be updated, but you don't suspect caching issues with static assets.
- You want to save bandwidth and load the page as fast as possible.
Use Shift+F5 (Hard Refresh) when:
- You've made changes to a website's CSS, JavaScript, or images, and the changes aren't appearing.
- A webpage is displaying old or incorrect information, even after a regular refresh.
- You're troubleshooting a layout or functionality issue that might be caused by stale cached files.
- You want to ensure you're viewing the absolute latest version of a page, bypassing all local caching.
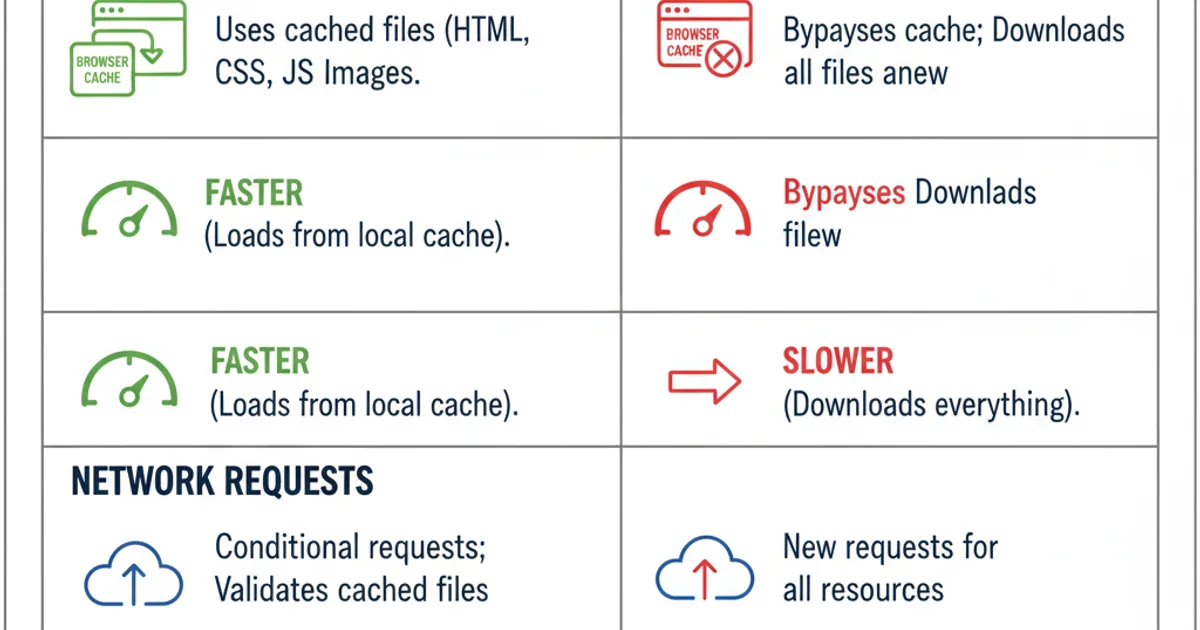
Key differences between F5 and Shift+F5 refresh actions.
In summary, while F5 is your everyday refresh, Shift+F5 is your go-to tool for ensuring you're working with the freshest possible version of a webpage, making it an indispensable shortcut for web developers and power users alike.