What does file:///android_asset/www/index.html mean?
Categories:
Understanding file:///android_asset/www/index.html in Android Development
Explore the meaning and usage of the file:///android_asset/www/index.html URI, a common path for local web content in Android applications, particularly those built with hybrid frameworks.
If you've worked with Android applications that embed web content, especially those built using frameworks like Apache Cordova (PhoneGap) or Ionic, you've likely encountered the URI file:///android_asset/www/index.html. This path is fundamental to how these hybrid applications serve their local web assets. This article will break down what each part of this URI signifies and its role in Android app development.
Deconstructing the URI: file:///android_asset/www/index.html
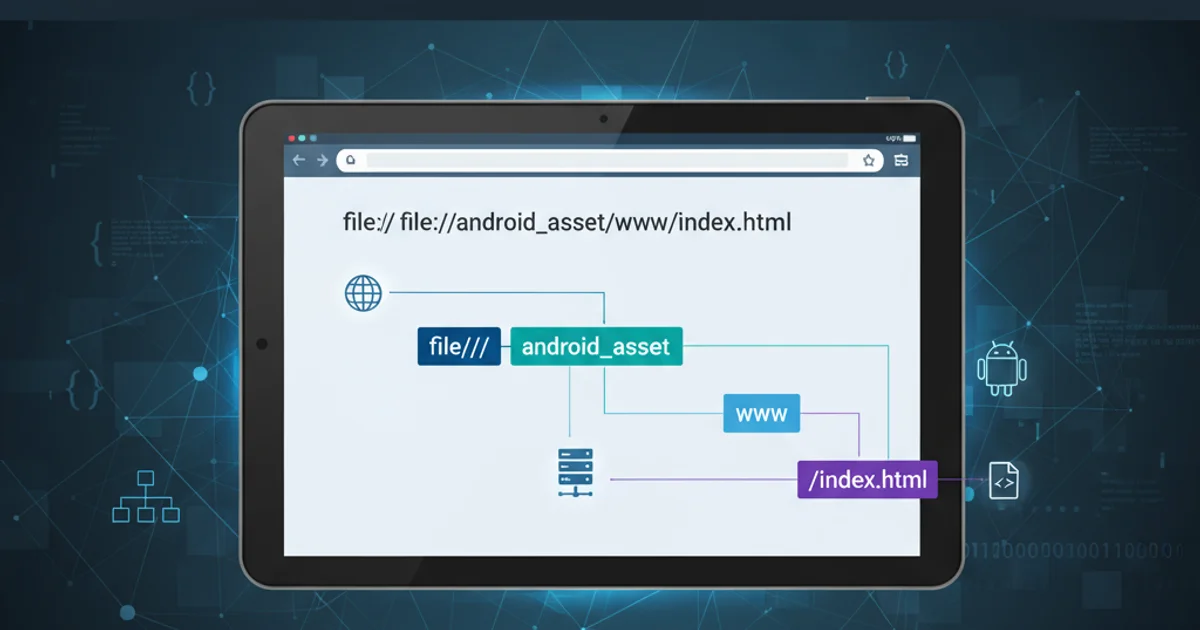
The URI file:///android_asset/www/index.html is a local file path that points to a specific resource within an Android application's package. Let's examine each component to understand its significance:
flowchart LR
A["file:///"] --> B["android_asset/"]
B --> C["www/"]
C --> D["index.html"]
A -- "Protocol for local files" --> B
B -- "Android's asset directory" --> C
C -- "Common directory for web content" --> D
D -- "Default entry point for web apps" --> E["Hybrid App Content"]Breakdown of the file:///android_asset/www/index.html URI components.
file:///: This is the standard URI scheme for local files. It indicates that the resource being accessed is a file on the local filesystem, rather than a resource over a network (likehttp://orhttps://). The three slashes are part of the standard URI syntax for local file paths.android_asset/: This is a special directory within an Android application's package. Theassetsfolder in an Android project (typically located atsrc/main/assets) is used to store raw asset files that are bundled with the application. These files are not compiled or processed by the Android build system in the same way as resources (like layouts or drawables); instead, they are included as-is. Theandroid_assetprefix in the URI tells the Android system to look for the file within thisassetsdirectory.www/: This is a conventional subdirectory often used by hybrid mobile development frameworks (like Cordova, Ionic, React Native WebView) to store all the web-related files (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, etc.) that constitute the application's user interface. While not strictly enforced by Android, it's a widely adopted practice for organizing web assets.index.html: This is the name of the specific file being requested. In web development,index.htmlis the universally recognized default entry point for a website or web application. When a WebView loads content from thewwwdirectory, it typically starts by loadingindex.html.
How it Works in Hybrid Applications
Hybrid applications leverage Android's WebView component to display web content. Instead of loading a remote URL from the internet, these applications load their entire user interface from local HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files bundled within the app itself. The file:///android_asset/www/index.html URI serves as the starting point for this local web content.
import android.webkit.WebView;
import android.webkit.WebViewClient;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
WebView myWebView = findViewById(R.id.webview);
myWebView.getSettings().setJavaScriptEnabled(true);
myWebView.setWebViewClient(new WebViewClient()); // Prevents opening links in external browser
myWebView.loadUrl("file:///android_asset/www/index.html");
}
}
Example of loading local web content into an Android WebView.
src/main/assets/www directory of your Android project. Any changes to these files require a rebuild and redeploy of the Android application.Security and Access Considerations
Accessing files via file:///android_asset/ is generally secure because these files are bundled within your application package and cannot be modified by external sources once the app is installed. However, when dealing with WebView and local files, it's crucial to be aware of potential security implications, especially if your web content interacts with native Android code via JavaScript interfaces. Always sanitize inputs and restrict access to sensitive native functions.
addJavascriptInterface) in a WebView that loads local content. Malicious JavaScript within your index.html (if compromised) could potentially access native Android features, leading to security vulnerabilities. Always ensure your web content is trusted and secure.