What are differences between INSERT and UPDATE in MySQL?
INSERT vs. UPDATE in MySQL: Understanding the Core Differences
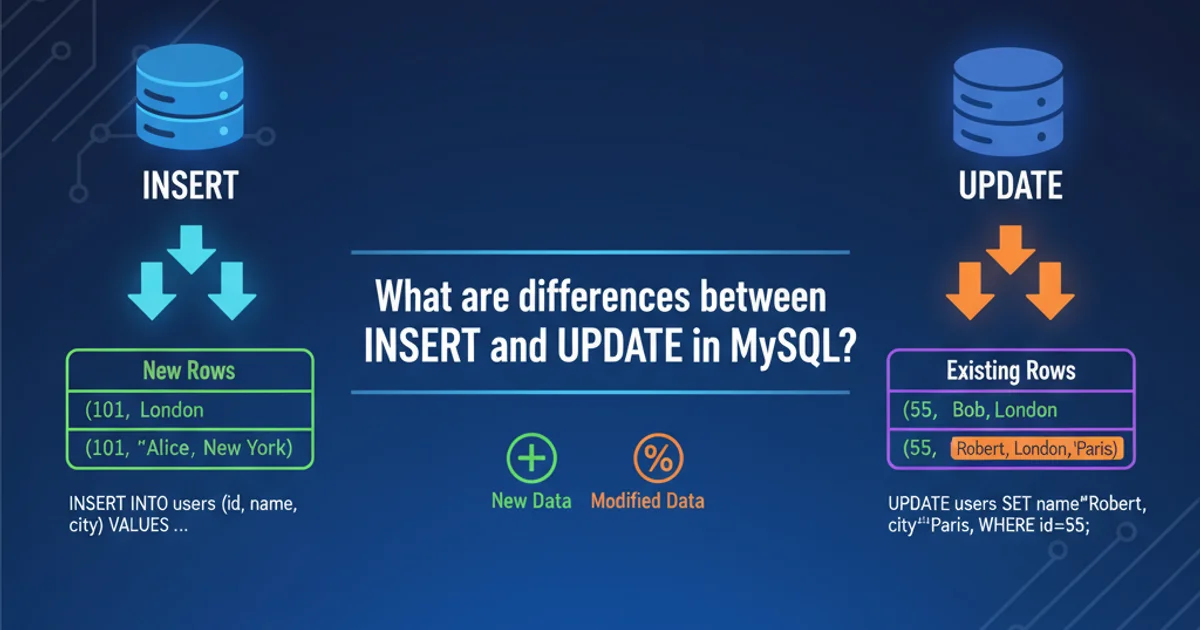
Explore the fundamental distinctions between the SQL INSERT and UPDATE statements in MySQL, including their use cases, syntax, and impact on data.
In MySQL, INSERT and UPDATE are two of the most frequently used Data Manipulation Language (DML) statements. While both are used to modify data within a database, they serve distinct purposes. Understanding when to use each is crucial for efficient and correct database management. This article will delve into the specifics of INSERT for adding new records and UPDATE for modifying existing ones, providing clear examples and best practices.
The INSERT Statement: Adding New Data
The INSERT statement is used to add one or more new rows (records) into a table. When you use INSERT, you are creating entirely new entries in your database. This is typically done when you have new information that doesn't yet exist in any table. You can insert data into all columns or specify a subset of columns, letting the database handle defaults for the rest.
INSERT INTO Customers (CustomerID, FirstName, LastName, Email)
VALUES (1, 'John', 'Doe', 'john.doe@example.com');
Basic INSERT statement to add a single row.
INSERT INTO Products (ProductName, Price)
VALUES
('Laptop', 1200.00),
('Mouse', 25.00),
('Keyboard', 75.00);
INSERT statement to add multiple rows at once.
INSERT will fail.The UPDATE Statement: Modifying Existing Data
The UPDATE statement is used to modify existing rows in a table. Unlike INSERT, UPDATE does not create new records; it changes the values of columns in rows that already exist. The WHERE clause is critical with UPDATE to specify which rows should be modified. Without a WHERE clause, the UPDATE statement will affect all rows in the table, which can lead to unintended data loss or corruption.
UPDATE Customers
SET Email = 'john.new.email@example.com'
WHERE CustomerID = 1;
Basic UPDATE statement to modify a single row's email address.
UPDATE Products
SET Price = Price * 1.10
WHERE Category = 'Electronics';
UPDATE statement to increase the price of all 'Electronics' products by 10%.
WHERE clause with UPDATE unless you explicitly intend to modify every row in the table. Forgetting it can have severe consequences for your data integrity.Key Differences and Use Cases
The core difference lies in their fundamental action: INSERT adds new data, while UPDATE changes existing data. This distinction dictates their respective use cases. INSERT is for initial data population or adding new events/entities. UPDATE is for correcting errors, reflecting changes in status, or modifying attributes of existing entities.
flowchart TD
A[Start]
A --> B{Is data new?}
B -- Yes --> C[Use INSERT statement]
C --> D[Add new row(s) to table]
B -- No --> E[Use UPDATE statement]
E --> F{Which rows to modify?}
F -- Specific rows --> G[Apply WHERE clause]
F -- All rows --> H[No WHERE clause (Caution!)]
G --> I[Modify existing row(s) in table]
H --> I
D --> J[End]
I --> JDecision flow for choosing between INSERT and UPDATE.
Consider a scenario where you're managing an e-commerce database:
- New Customer Registration: When a new user signs up, you would use
INSERTto add their details to theCustomerstable. - Customer Address Change: If an existing customer moves, you would use
UPDATEto change their address in theCustomerstable. - Adding a New Product: When a new item is stocked,
INSERTis used to add it to theProductstable. - Product Price Adjustment: If the price of an existing product changes,
UPDATEis used to modify itsPricein theProductstable.
INSERT ... ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE or REPLACE INTO.