The difference between && and ||
Categories:
Understanding Java's Logical Operators: && vs. ||
Explore the fundamental differences between Java's logical AND (&&) and logical OR (||) operators, including short-circuiting behavior and common use cases.
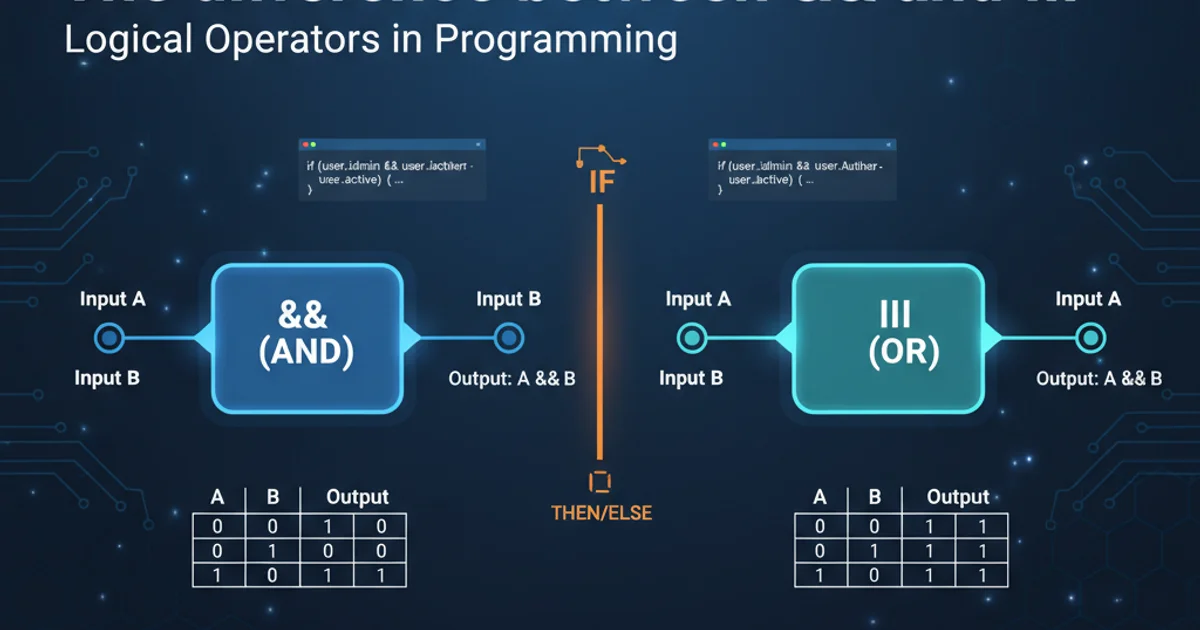
In Java, logical operators are crucial for controlling program flow based on multiple conditions. Among the most frequently used are the logical AND (&&) and logical OR (||) operators. While both combine boolean expressions, their evaluation rules and outcomes differ significantly, especially due to a feature known as 'short-circuiting'. Understanding these differences is key to writing efficient, correct, and readable Java code.
Logical AND Operator (&&)
The logical AND operator (&&) evaluates to true only if both of its operands are true. If either operand is false, the entire expression becomes false. A key characteristic of && is its 'short-circuiting' behavior: if the first operand evaluates to false, the second operand is not evaluated because the overall result is already determined to be false. This can prevent NullPointerExceptions or other runtime errors when the second operand depends on the first being true.
public class LogicalAndExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 10;
int y = 5;
// Both conditions are true
if (x > 5 && y < 10) {
System.out.println("Both conditions are true."); // This will print
}
// First condition is true, second is false
if (x > 5 && y > 10) {
System.out.println("This will not print.");
}
// First condition is false (short-circuited)
String str = null;
if (str != null && str.length() > 0) {
System.out.println("String is not null and not empty.");
} else {
System.out.println("String is null or empty."); // This will print
}
}
}
Demonstration of the logical AND (&&) operator, including short-circuiting.
flowchart TD
A[Start Evaluation]
A --> B{Is Left Operand True?}
B -->|No| C[Result: False]
B -->|Yes| D{Is Right Operand True?}
D -->|No| C
D -->|Yes| E[Result: True]Flowchart illustrating the evaluation of the logical AND (&&) operator.
false or the condition that prevents errors (like null checks) as the first operand in an && expression to maximize the benefit of short-circuiting.Logical OR Operator (||)
The logical OR operator (||) evaluates to true if at least one of its operands is true. It only evaluates to false if both operands are false. Similar to &&, || also exhibits short-circuiting behavior: if the first operand evaluates to true, the second operand is not evaluated because the overall result is already determined to be true. This can be useful for optimizing performance or preventing unnecessary computations.
public class LogicalOrExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 15;
int b = 20;
// First condition is true (short-circuited)
if (a > 10 || b < 10) {
System.out.println("At least one condition is true."); // This will print
}
// Both conditions are false
if (a < 10 || b < 15) {
System.out.println("This will not print.");
}
// Both conditions are true
if (a > 10 || b > 15) {
System.out.println("At least one condition is true (both true)."); // This will print
}
}
}
Demonstration of the logical OR (||) operator, including short-circuiting.
flowchart TD
A[Start Evaluation]
A --> B{Is Left Operand True?}
B -->|Yes| C[Result: True]
B -->|No| D{Is Right Operand True?}
D -->|No| E[Result: False]
D -->|Yes| CFlowchart illustrating the evaluation of the logical OR (||) operator.
& and |). These operators always evaluate both operands, regardless of the first operand's value. While they exist, && and || are generally preferred for boolean logic due to their efficiency and ability to prevent side effects or errors.