How can I convert String to Int?
Categories:
Mastering String to Integer Conversion in C#
Learn the robust and safe methods for converting string representations of numbers into integer types in C#, covering int.Parse(), Convert.ToInt32(), and int.TryParse().
Converting a string to an integer is a common task in C# development, especially when dealing with user input, configuration files, or data retrieved from external sources. However, this operation isn't always straightforward due to the potential for invalid input. C# provides several methods to handle this conversion, each with its own use cases and error handling characteristics. This article will guide you through the most common and safest approaches.
Understanding the Core Methods
C# offers three primary methods for converting a string to an integer: int.Parse(), Convert.ToInt32(), and int.TryParse(). While they all achieve the same goal, their behavior when encountering invalid input differs significantly, which is crucial for writing robust applications.
flowchart TD
A[Start: String Input] --> B{Is Input Valid Integer Format?}
B -- Yes --> C[int.Parse() / Convert.ToInt32()]
C --> D[Result: Integer Value]
B -- No --> E{Error Handling Strategy?}
E -- Throw Exception --> F[int.Parse() / Convert.ToInt32()]
F --> G[Error: FormatException]
E -- Avoid Exception --> H[int.TryParse()]
H --> I{Conversion Successful?}
I -- Yes --> D
I -- No --> J[Result: Default Value (0) + Error Handling]Decision flow for choosing a string to integer conversion method.
1. Using int.Parse()
The int.Parse() method is a direct way to convert a string to its integer equivalent. It's suitable when you are absolutely certain that the input string is in a valid integer format. If the string is null, empty, or contains non-numeric characters (other than a sign or valid culture-specific decimal separator), int.Parse() will throw an exception.
string validString = "123";
string invalidString = "abc";
string nullString = null;
try
{
int number1 = int.Parse(validString);
Console.WriteLine($"Successfully parsed: {number1}"); // Output: Successfully parsed: 123
// This will throw a FormatException
// int number2 = int.Parse(invalidString);
// This will throw an ArgumentNullException
// int number3 = int.Parse(nullString);
}
catch (FormatException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error: Invalid format. {ex.Message}");
}
catch (ArgumentNullException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error: Input string is null. {ex.Message}");
}
catch (OverflowException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error: Number is too large or too small for an int. {ex.Message}");
}
Example of int.Parse() with valid and invalid inputs.
int.Parse() with caution. It's best suited for scenarios where input validation has already occurred, or where an exception is the expected and desired way to handle invalid data.2. Using Convert.ToInt32()
The Convert.ToInt32() method, part of the System.Convert class, offers similar functionality to int.Parse(). It also converts a string to a 32-bit signed integer. The key difference is its handling of null input: Convert.ToInt32(null) returns 0 instead of throwing an ArgumentNullException. For non-numeric strings, it behaves like int.Parse() and throws a FormatException.
string validString = "456";
string invalidString = "xyz";
string nullString = null;
try
{
int number1 = Convert.ToInt32(validString);
Console.WriteLine($"Successfully converted: {number1}"); // Output: Successfully converted: 456
int number2 = Convert.ToInt32(nullString);
Console.WriteLine($"Converted null to: {number2}"); // Output: Converted null to: 0
// This will throw a FormatException
// int number3 = Convert.ToInt32(invalidString);
}
catch (FormatException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error: Invalid format. {ex.Message}");
}
catch (OverflowException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error: Number is too large or too small for an int. {ex.Message}");
}
Example of Convert.ToInt32() handling valid, null, and invalid inputs.
Convert.ToInt32() can also convert other numeric types (like double, decimal) to int, performing appropriate rounding or truncation. For string conversion, its main advantage over int.Parse() is its null handling.3. Using int.TryParse() (The Recommended Approach)
For most real-world scenarios, int.TryParse() is the safest and most recommended method for string to integer conversion. It attempts to convert the string and returns a boolean indicating success or failure, without throwing an exception. The converted integer value is returned via an out parameter.
string validString = "789";
string invalidString = "hello";
string emptyString = "";
string largeString = "9999999999999999999"; // Exceeds int.MaxValue
int result;
// Valid conversion
if (int.TryParse(validString, out result))
{
Console.WriteLine($"TryParse successful: {result}"); // Output: TryParse successful: 789
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"TryParse failed for '{validString}'");
}
// Invalid conversion
if (int.TryParse(invalidString, out result))
{
Console.WriteLine($"TryParse successful: {result}");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"TryParse failed for '{invalidString}'. Result is default: {result}"); // Output: TryParse failed for 'hello'. Result is default: 0
}
// Empty string conversion
if (int.TryParse(emptyString, out result))
{
Console.WriteLine($"TryParse successful: {result}");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"TryParse failed for empty string. Result is default: {result}"); // Output: TryParse failed for empty string. Result is default: 0
}
// Overflowing string conversion
if (int.TryParse(largeString, out result))
{
Console.WriteLine($"TryParse successful: {result}");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"TryParse failed for '{largeString}' (overflow). Result is default: {result}"); // Output: TryParse failed for '9999999999999999999' (overflow). Result is default: 0
}
Demonstration of int.TryParse() handling various inputs gracefully.
int.TryParse() is ideal for user input or data from external sources where the format is not guaranteed. It prevents application crashes and allows for graceful error handling without the overhead of try-catch blocks.Choosing the Right Method
The choice of method depends on your specific requirements for error handling and the expected quality of the input string.
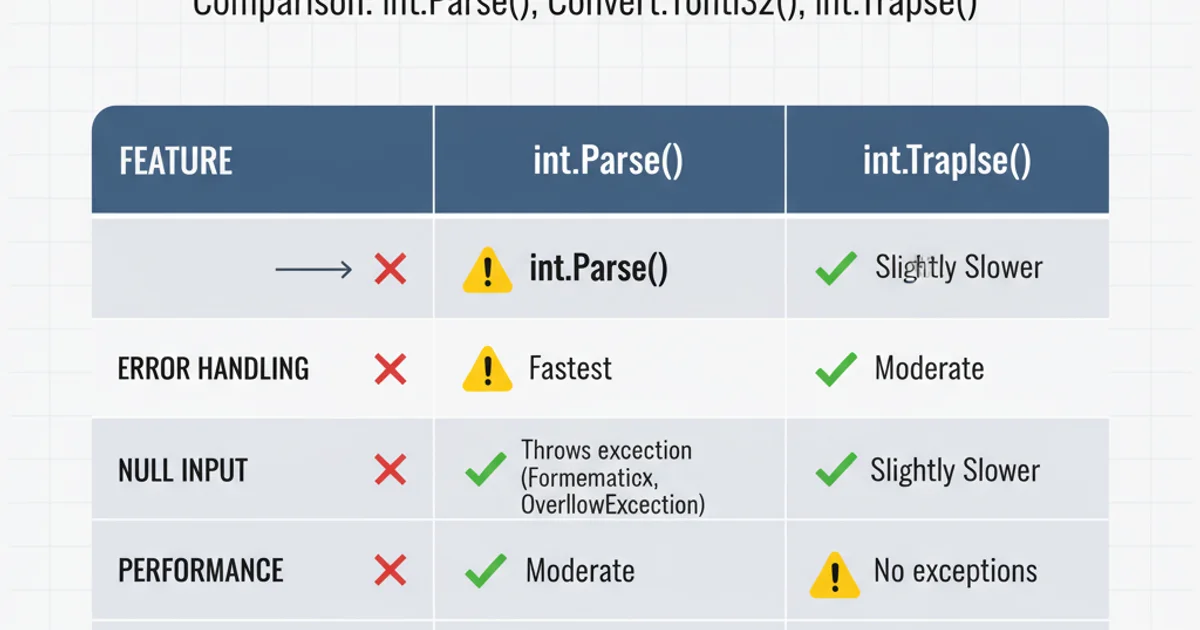
Comparison of String to Int Conversion Methods
1. Step 1: Assess Input Reliability
Determine how reliable your string input is. Is it guaranteed to be a valid integer, or could it come from user input, files, or network streams where errors are possible?
2. Step 2: Decide on Error Handling
If an invalid input should halt execution or is an exceptional circumstance, int.Parse() or Convert.ToInt32() (with try-catch) might be acceptable. If you need to gracefully handle invalid input and continue execution, int.TryParse() is the superior choice.
3. Step 3: Implement the Chosen Method
Based on your assessment, implement the appropriate conversion method. Always prioritize int.TryParse() for robustness in most application scenarios.