&& (AND) and || (OR) in IF statements
Categories:
Mastering Conditional Logic: && (AND) and || (OR) in IF Statements
Unlock the power of complex decision-making in your code by effectively using logical AND (&&) and OR (||) operators within IF statements. This guide covers syntax, behavior, and best practices.
Conditional statements are the backbone of any programming language, allowing your code to make decisions based on various conditions. While simple if statements check a single condition, real-world applications often require evaluating multiple conditions simultaneously. This is where logical operators && (AND) and || (OR) become indispensable. Understanding how to combine these operators effectively is crucial for writing robust and efficient code.
The Logical AND Operator (&&)
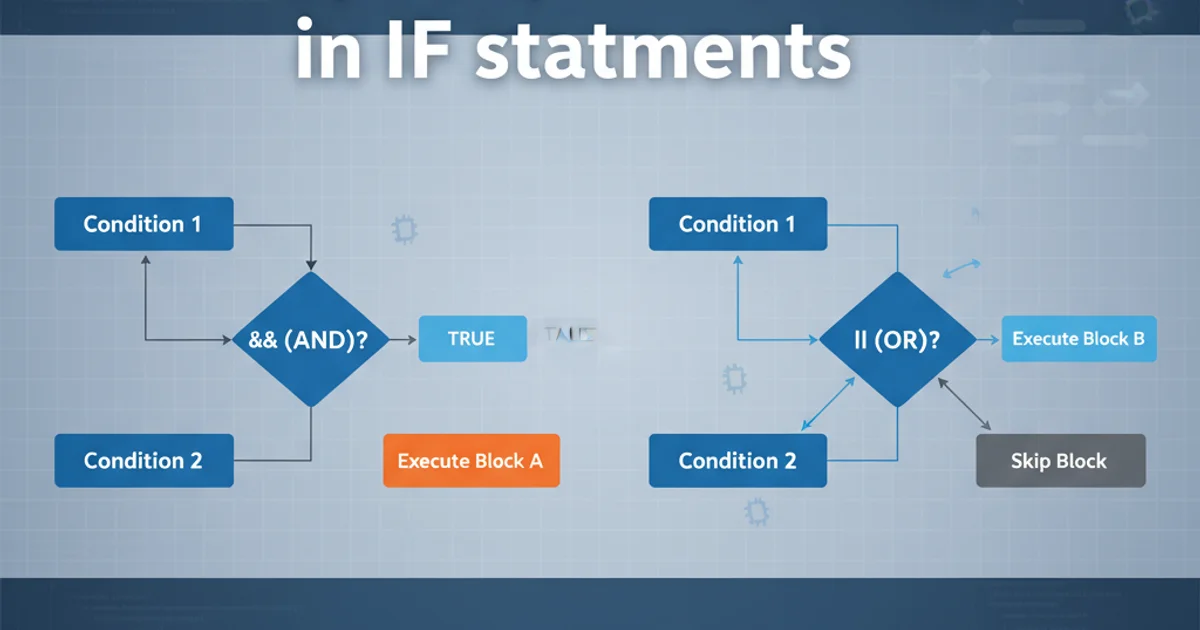
The logical AND operator (&&) evaluates to true only if all the conditions it connects are true. If even one condition is false, the entire expression becomes false. This operator is often used when multiple criteria must be met for a certain block of code to execute. It exhibits 'short-circuiting' behavior, meaning if the first condition is false, the subsequent conditions are not evaluated, as the overall result is already determined to be false.
int age = 25;
boolean hasLicense = true;
if (age >= 18 && hasLicense) {
System.out.println("Eligible to drive.");
} else {
System.out.println("Not eligible to drive.");
}
// Example with short-circuiting
String name = null;
if (name != null && name.length() > 0) {
System.out.println("Name is not empty.");
} else {
System.out.println("Name is null or empty.");
}
Java example demonstrating the logical AND (&&) operator.
flowchart TD
A[Start] --> B{Is Age >= 18?}
B -- No --> D[Not Eligible]
B -- Yes --> C{Has License?}
C -- No --> D[Not Eligible]
C -- Yes --> E[Eligible to Drive]
D --> F[End]
E --> F[End]Flowchart illustrating the logic of the AND (&&) operator.
The Logical OR Operator (||)
In contrast to &&, the logical OR operator (||) evaluates to true if at least one of the conditions it connects is true. The entire expression is false only if all connected conditions are false. Like &&, || also short-circuits: if the first condition is true, the subsequent conditions are not evaluated because the overall result is already true. This is useful when you want to execute code if any of several possible conditions are met.
String dayOfWeek = "Sunday";
boolean isHoliday = false;
if (dayOfWeek.equals("Saturday") || dayOfWeek.equals("Sunday") || isHoliday) {
System.out.println("It's a weekend or a holiday!");
} else {
System.out.println("It's a weekday.");
}
// Another example
int score = 95;
if (score > 90 || score == 100) {
System.out.println("Excellent score!");
}
Java example demonstrating the logical OR (||) operator.
flowchart TD
A[Start] --> B{Is Day Saturday?}
B -- Yes --> E[Weekend/Holiday]
B -- No --> C{Is Day Sunday?}
C -- Yes --> E[Weekend/Holiday]
C -- No --> D{Is it a Holiday?}
D -- Yes --> E[Weekend/Holiday]
D -- No --> F[Weekday]
E --> G[End]
F --> G[End]Flowchart illustrating the logic of the OR (||) operator.
Combining AND and OR Operators
You can combine && and || operators to create highly complex conditional logic. When doing so, remember that && has higher precedence than ||. This means && operations are evaluated before || operations, similar to how multiplication is evaluated before addition in mathematics. You can use parentheses () to explicitly control the order of evaluation and improve readability, ensuring your conditions are grouped as intended.
int temperature = 25;
boolean isRaining = true;
boolean hasUmbrella = false;
// Without parentheses: (temperature > 20 && isRaining) || hasUmbrella
if (temperature > 20 && isRaining || hasUmbrella) {
System.out.println("Consider taking an umbrella or staying indoors.");
} else {
System.out.println("Weather seems fine.");
}
// With explicit parentheses for clarity: (temperature > 20 && isRaining) || hasUmbrella
if ((temperature > 20 && isRaining) || hasUmbrella) {
System.out.println("Consider taking an umbrella or staying indoors (explicit).");
} else {
System.out.println("Weather seems fine (explicit).");
}
// Different logic with parentheses: temperature > 20 && (isRaining || hasUmbrella)
if (temperature > 20 && (isRaining || hasUmbrella)) {
System.out.println("It's warm, and either raining or you have an umbrella.");
} else {
System.out.println("Conditions not met for this specific logic.");
}
Java example combining AND and OR operators, demonstrating precedence and parentheses.
() to explicitly define the order of operations when combining && and ||. This not only prevents unexpected behavior due to operator precedence but also significantly improves the readability and maintainability of your code for yourself and others.Best Practices for Conditional Statements
Writing clear and efficient conditional logic is a skill that improves with practice. Here are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Keep conditions concise: Avoid overly long and complex single
ifstatements. If a condition becomes too convoluted, consider breaking it down into smaller, named boolean variables or helper methods. - Use parentheses for clarity: Even if operator precedence would yield the correct result, explicit parentheses make your intentions clear.
- Leverage short-circuiting: Understand how
&&and||short-circuit. This can be used to preventNullPointerExceptions(e.g.,if (obj != null && obj.method())) or to optimize performance by placing less expensive or more likely-to-be-false conditions first in an&&chain, and less expensive or more likely-to-be-true conditions first in an||chain. - Avoid redundant checks: Don't check conditions that are already implied by previous checks in a chain.
- Test thoroughly: Complex conditional logic can be prone to errors. Ensure you write comprehensive unit tests that cover all possible true/false combinations of your conditions.