What is the difference between OpenAI and ChatOpenAI in LangChain?
Categories:
OpenAI vs. ChatOpenAI in LangChain: Understanding the Differences
Explore the key distinctions between LangChain's OpenAI and ChatOpenAI classes, and learn when to use each for your LLM applications.
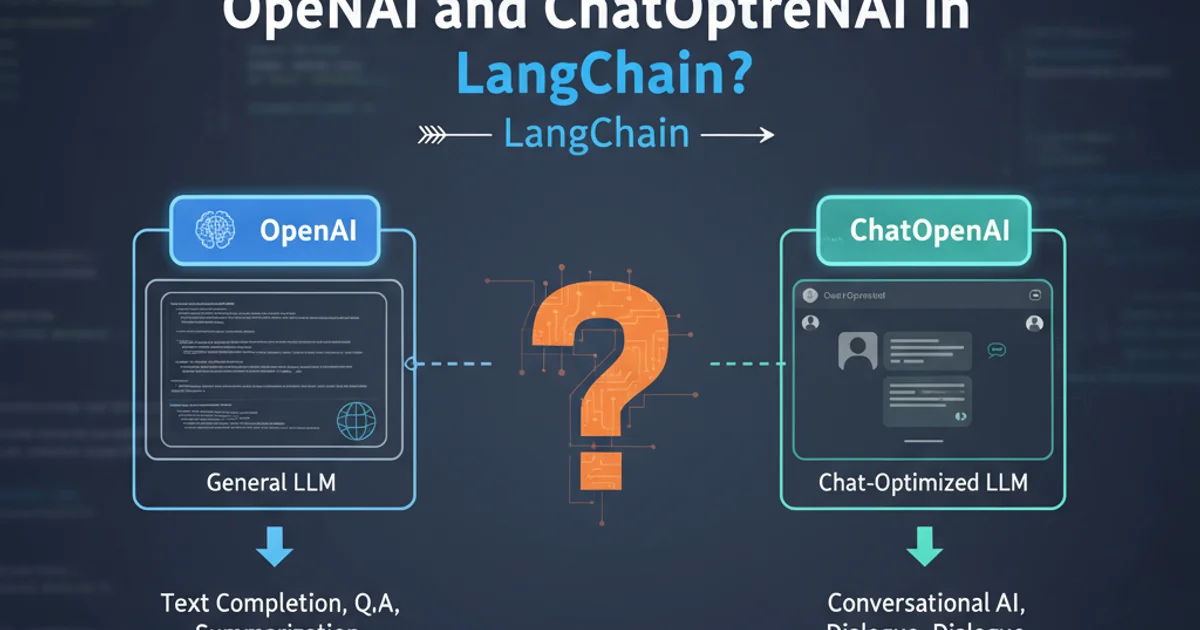
LangChain provides powerful abstractions for interacting with Large Language Models (LLMs). When working with OpenAI models, you'll primarily encounter two classes: OpenAI and ChatOpenAI. While both facilitate communication with OpenAI's API, they are designed for different types of interactions and leverage distinct underlying API endpoints. Understanding their differences is crucial for building efficient and effective LLM applications.
The Core Distinction: Completions vs. Chat Completions
The fundamental difference between OpenAI and ChatOpenAI lies in the OpenAI API endpoints they interact with. OpenAI is designed for the older 'Completions' API, which typically takes a single string prompt and returns a completed string. ChatOpenAI, on the other hand, is built for the newer 'Chat Completions' API, which is optimized for multi-turn conversations and accepts a list of 'messages' as input, returning a message as output.
flowchart TD
A[LangChain Application]
subgraph OpenAI Class
B[OpenAI Class]
B --> C{Completions API}
C --> D[String Prompt]
D --> E[String Completion]
end
subgraph ChatOpenAI Class
F[ChatOpenAI Class]
F --> G{Chat Completions API}
G --> H[List of Messages]
H --> I[Message Response]
end
A --> B
A --> FArchitectural overview of how LangChain's OpenAI and ChatOpenAI classes interact with different OpenAI API endpoints.
OpenAI Class: Text Completions
The OpenAI class in LangChain is a wrapper around OpenAI's legacy 'Completions' API. It's best suited for tasks where you provide a single, often long, text prompt and expect a single text completion. This includes tasks like text generation, summarization, translation, or code generation where the context is primarily contained within the initial prompt. It typically uses models like text-davinci-003 (though newer chat models can also be used, they are less optimized for this endpoint).
from langchain_openai import OpenAI
llm = OpenAI(model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo-instruct", temperature=0.7)
prompt = "Write a short poem about a cat."
response = llm.invoke(prompt)
print(response)
Example of using the OpenAI class for a text completion task.
ChatOpenAI Class: Conversational AI
The ChatOpenAI class is the recommended choice for building conversational applications. It leverages the 'Chat Completions' API, which is specifically designed for multi-turn interactions. Instead of a single string, you pass a list of 'messages', each with a role (e.g., 'system', 'user', 'assistant'). This structure allows the model to maintain context across turns, making it ideal for chatbots, virtual assistants, and interactive agents. Models like gpt-3.5-turbo and gpt-4 are optimized for this API.
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, SystemMessage, AIMessage
chat_model = ChatOpenAI(model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0.7)
messages = [
SystemMessage(content="You are a helpful AI assistant."),
HumanMessage(content="What is the capital of France?")
]
response = chat_model.invoke(messages)
print(response.content)
Example of using the ChatOpenAI class for a conversational turn.
ChatOpenAI is the preferred and more powerful choice due to its optimization for conversational contexts and access to the latest chat-optimized models.Key Differences Summarized
Here's a quick comparison of the main characteristics:
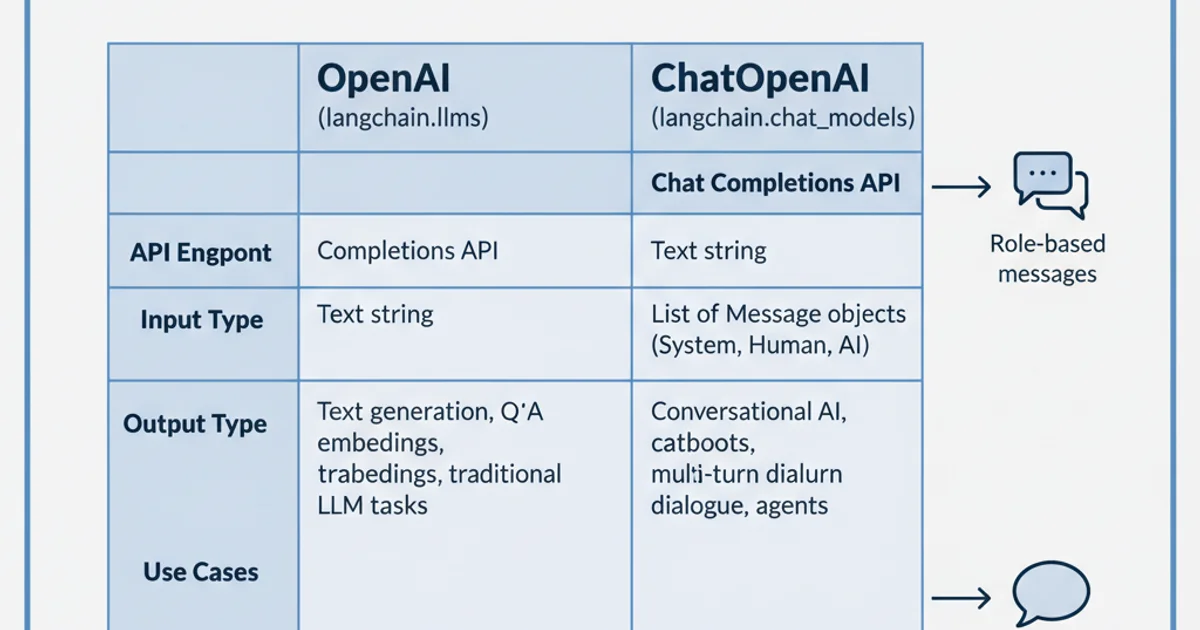
Comparison of OpenAI and ChatOpenAI classes.
When to Use Which
Choosing between OpenAI and ChatOpenAI depends on your specific use case:
Use
OpenAIwhen:- You need to perform simple, single-turn text generation tasks.
- Your application primarily involves completing a given text prompt.
- You are working with older models specifically designed for the Completions API (e.g.,
text-davinci-003).
Use
ChatOpenAIwhen:- You are building a chatbot, virtual assistant, or any conversational AI.
- Your application requires multi-turn interactions and maintaining conversation history.
- You want to leverage the latest and most capable OpenAI models (e.g.,
gpt-3.5-turbo,gpt-4). - You need to define system-level instructions or roles for the AI.
OpenAI class, it's generally not recommended as it bypasses the conversational optimizations of the Chat Completions API and might lead to suboptimal performance or unexpected behavior for chat-specific tasks.