Getting the bounding box of the recognized words using python-tesseract
Categories:
Extracting Bounding Boxes for Words with Python-Tesseract
Learn how to use Python-Tesseract to not only recognize text but also retrieve the precise bounding box coordinates for each detected word, enabling advanced OCR applications.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is a technology that enables the conversion of different types of documents, such as scanned paper documents, PDF files, or images captured by a digital camera, into editable and searchable data. While basic OCR provides the recognized text, many advanced applications require more granular information, specifically the location of each recognized word or character on the original image. This article will guide you through using python-tesseract to achieve this, focusing on word-level bounding box extraction.
Understanding Tesseract's Output Formats
Tesseract, the OCR engine behind python-tesseract, can output recognized text in various formats. Beyond plain text, it offers structured data that includes bounding box information. This is crucial for tasks like highlighting text in an image, creating interactive PDFs, or performing layout analysis. The image_to_data() function in python-tesseract is specifically designed for this purpose, providing a detailed breakdown of recognized components.
flowchart TD
A[Input Image] --> B{Tesseract OCR Engine}
B --> C["image_to_data() function"]
C --> D["Pandas DataFrame Output"]
D --> E{"Extract Bounding Box Data"}
E --> F["Word Coordinates (left, top, width, height)"]
E --> G["Confidence Score"]
E --> H["Recognized Text"]
F --> I["Further Processing (e.g., Drawing Boxes)"]Flowchart of Tesseract's data extraction process for bounding boxes.
Prerequisites and Setup
Before diving into the code, ensure you have Tesseract OCR installed on your system and the pytesseract library installed in your Python environment. You'll also need OpenCV (cv2) for image loading and manipulation, and Pillow (PIL) for image handling with pytesseract.
1. Install Tesseract OCR Engine
Download and install Tesseract from its official GitHub page or via your system's package manager. For Windows, consider installers like UB-Mannheim's. Remember to add Tesseract to your system's PATH environment variable.
2. Install Python Libraries
Use pip to install the necessary Python packages: pip install pytesseract opencv-python Pillow.
3. Verify Installation
Run tesseract --version in your terminal to confirm Tesseract is installed. In Python, try import pytesseract to ensure the library is accessible.
Extracting Word Bounding Boxes
The pytesseract.image_to_data() function is the key to obtaining detailed OCR results, including bounding box information. It returns a dictionary that can be easily converted into a Pandas DataFrame for better readability and manipulation. Each row in this DataFrame corresponds to a recognized component (page, block, paragraph, line, word), and includes its text, confidence score, and bounding box coordinates.
import cv2
import pytesseract
from PIL import Image
# Path to your Tesseract executable (change if necessary)
# pytesseract.pytesseract.tesseract_cmd = r'C:\Program Files\Tesseract-OCR\tesseract.exe'
def get_word_bounding_boxes(image_path):
# Load the image using OpenCV
img = cv2.imread(image_path)
if img is None:
print(f"Error: Could not load image from {image_path}")
return
# Convert the image to RGB (Tesseract expects RGB or grayscale)
rgb_img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# Use image_to_data to get detailed OCR results
# output_type=pytesseract.Output.DICT returns a dictionary
data = pytesseract.image_to_data(rgb_img, output_type=pytesseract.Output.DICT)
n_boxes = len(data['level'])
for i in range(n_boxes):
# Level 5 corresponds to words
if data['level'][i] == 5:
text = data['text'][i]
conf = int(data['conf'][i])
# Filter out empty text and low confidence results
if text.strip() and conf > 60: # Adjust confidence threshold as needed
x, y, w, h = data['left'][i], data['top'][i], data['width'][i], data['height'][i]
# Draw bounding box on the image
cv2.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# Put text label (optional)
cv2.putText(img, text, (x, y - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 255), 1)
print(f"Word: '{text}', Confidence: {conf}, Bounding Box: (x={x}, y={y}, w={w}, h={h})")
# Display the image with bounding boxes
cv2.imshow('Detected Words', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# Example usage:
# Make sure you have an image file named 'sample.png' in the same directory
# or provide a full path to your image.
# get_word_bounding_boxes('sample.png')
Python code to extract word-level bounding boxes and draw them on an image.
data dictionary returned by image_to_data() contains keys like level, page_num, block_num, par_num, line_num, word_num, left, top, width, height, conf, and text. The level key indicates the hierarchy (1=page, 2=block, 3=paragraph, 4=line, 5=word). Filtering by level == 5 ensures you're processing individual words.Interpreting the Output
The image_to_data() function provides coordinates relative to the top-left corner of the image. The left and top values represent the x and y coordinates of the top-left corner of the bounding box, while width and height define its dimensions. The conf (confidence) score indicates how certain Tesseract is about the recognition, ranging from 0 to 100. Filtering by confidence can help remove spurious detections.
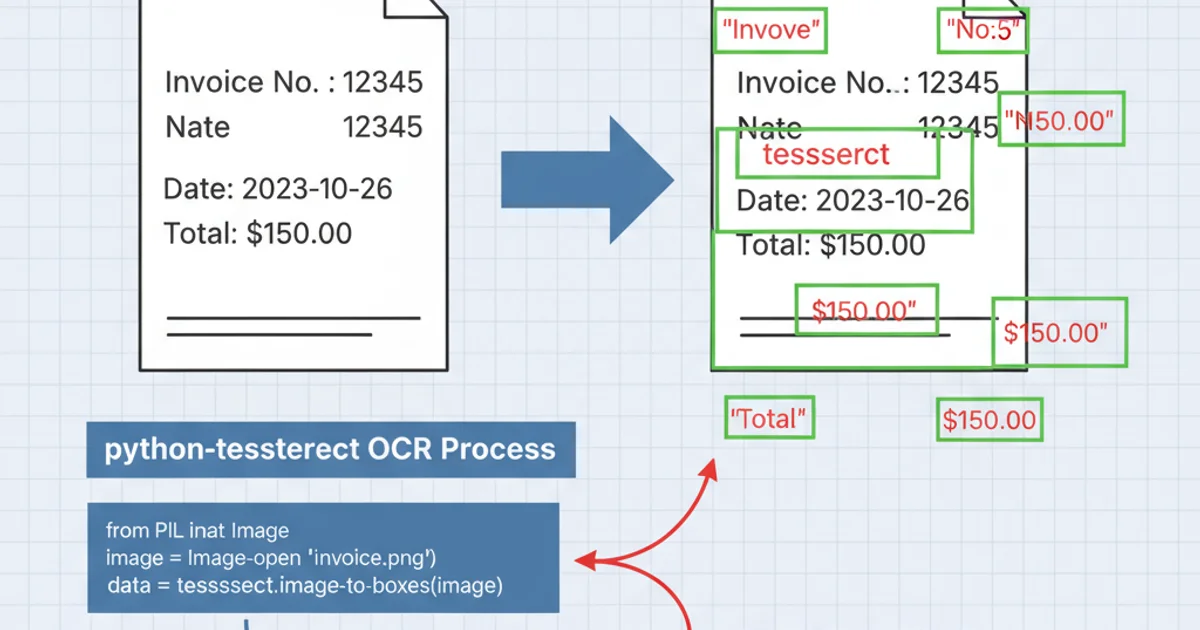
An example of an image with word-level bounding boxes drawn using the provided Python script.
Advanced Considerations and Best Practices
For more robust OCR, consider pre-processing your images. This can include resizing, binarization, noise reduction, and deskewing. Tesseract's performance is highly dependent on image quality. Additionally, for specific languages, ensure you have the corresponding language data packs installed and specify the language using the lang parameter in pytesseract.image_to_data().
image_to_data() can sometimes return empty strings or very low confidence scores for non-text regions or poorly recognized words. Always include checks for text.strip() and conf values to filter out unreliable results, especially when drawing boxes or performing further analysis.