sql query to return differences between two tables
Finding Differences Between Two SQL Tables
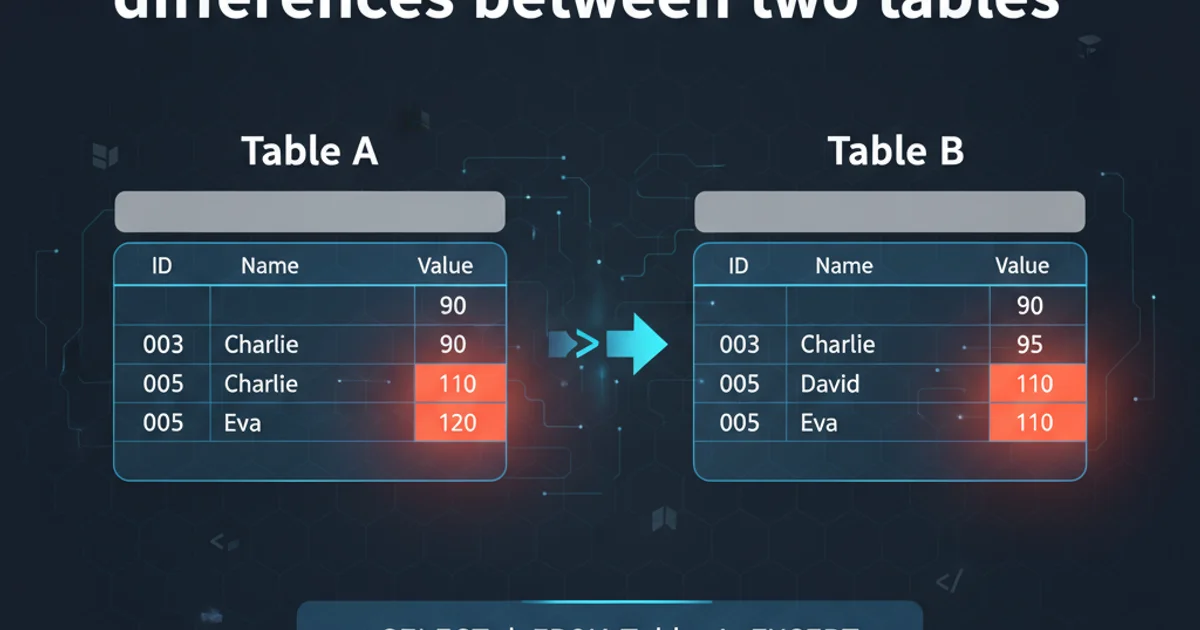
Learn various SQL techniques to identify and retrieve rows that exist in one table but not another, or rows with differing values between two tables. This guide covers EXCEPT, NOT EXISTS, LEFT JOIN, and FULL OUTER JOIN methods.
Comparing two tables to find differences is a common task in database management, data migration, and data synchronization. Whether you need to identify new records, missing records, or records with changed values, SQL provides several powerful constructs to achieve this. This article will explore different SQL query patterns, focusing on their use cases and performance characteristics, particularly within SQL Server environments.
Identifying Rows Unique to One Table (EXCEPT Operator)
The EXCEPT operator is a straightforward way to return all distinct rows from the first query that are not output by the second query. It's ideal for finding rows present in TableA but not in TableB, assuming both tables have compatible column structures (same number of columns and compatible data types).
SELECT Column1, Column2, Column3
FROM TableA
EXCEPT
SELECT Column1, Column2, Column3
FROM TableB;
Using EXCEPT to find rows in TableA not present in TableB
EXCEPT operator implicitly performs a DISTINCT operation on the result set. If you need to include duplicate rows, you might need to use other methods like NOT EXISTS or LEFT JOIN.Finding Missing Rows Using NOT EXISTS
The NOT EXISTS clause is a flexible and often performant way to find rows in one table that do not have a corresponding match in another table based on a specified condition. This method is particularly useful when you need to compare specific columns or when the tables have different structures but share a common key.
SELECT A.Column1, A.Column2
FROM TableA A
WHERE NOT EXISTS (
SELECT 1
FROM TableB B
WHERE A.PrimaryKey = B.PrimaryKey
);
Using NOT EXISTS to find rows in TableA that do not exist in TableB based on PrimaryKey
flowchart TD
A[Start Query: SELECT from TableA]
B{For each row in TableA}
C{Check if PrimaryKey exists in TableB}
D{NOT EXISTS condition met?}
E[Include row from TableA in result]
F[End Query]
A --> B
B --> C
C --> D
D -- Yes --> E
D -- No --> B
E --> B
B -- All rows processed --> FFlowchart of the NOT EXISTS logic for finding differences
Identifying Differences with LEFT JOIN and NULL Checks
A LEFT JOIN combined with a WHERE clause checking for NULL values in the right table's columns is another common technique. This approach is versatile for finding rows that exist in the left table but not in the right, and can also be extended to find rows with differing values.
SELECT A.*
FROM TableA A
LEFT JOIN TableB B ON A.PrimaryKey = B.PrimaryKey
WHERE B.PrimaryKey IS NULL;
Using LEFT JOIN to find rows in TableA not present in TableB
Finding All Differences (FULL OUTER JOIN)
When you need to find rows that are unique to TableA, unique to TableB, and rows that exist in both but have differing values, a FULL OUTER JOIN is the most comprehensive approach. This method returns all rows from both tables, pairing them where the join condition is met, and showing NULL for unmatched columns.
SELECT
ISNULL(A.PrimaryKey, B.PrimaryKey) AS Key,
A.Column1 AS TableA_Column1,
B.Column1 AS TableB_Column1,
A.Column2 AS TableA_Column2,
B.Column2 AS TableB_Column2
FROM TableA A
FULL OUTER JOIN TableB B ON A.PrimaryKey = B.PrimaryKey
WHERE A.PrimaryKey IS NULL OR B.PrimaryKey IS NULL -- Rows unique to either table
OR A.Column1 <> B.Column1 OR A.Column2 <> B.Column2; -- Rows with differing values
Using FULL OUTER JOIN to find all types of differences between two tables
FULL OUTER JOIN, be mindful of NULL values. The comparison A.Column <> B.Column will evaluate to UNKNOWN if either A.Column or B.Column is NULL. Use (A.Column <> B.Column OR (A.Column IS NULL AND B.Column IS NOT NULL) OR (A.Column IS NOT NULL AND B.Column IS NULL)) for robust NULL-safe comparisons.