How can I enable the Windows Server Task Scheduler History recording?
Categories:
Enable Task Scheduler History in Windows Server
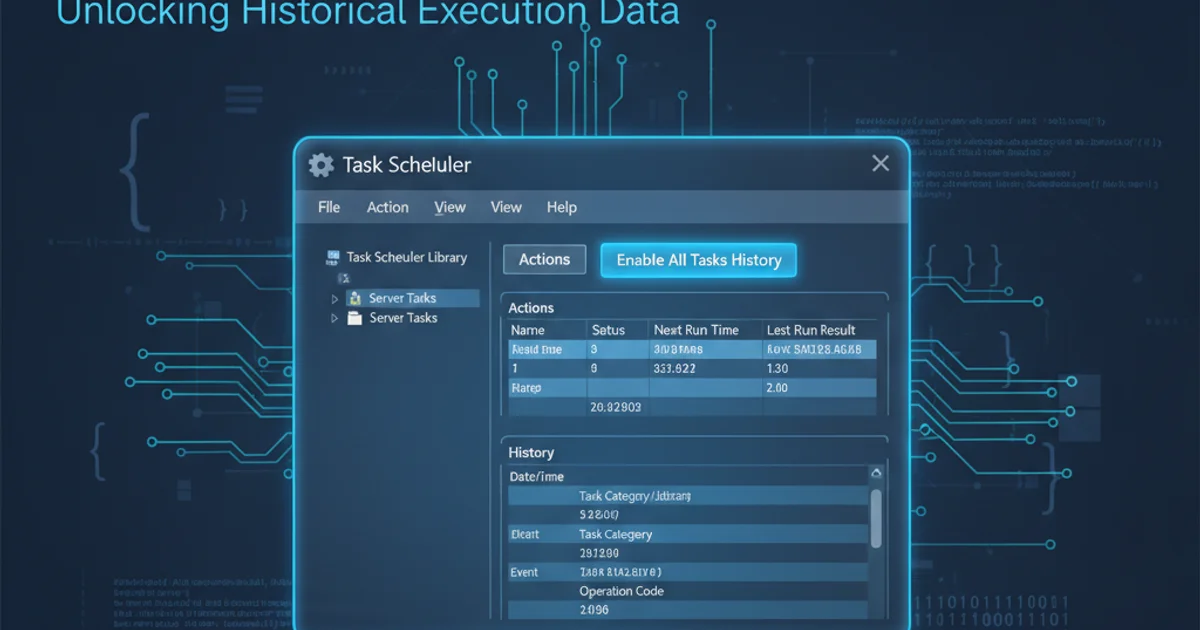
Learn how to activate and view the operational history for scheduled tasks in Windows Server, crucial for troubleshooting and auditing.
The Windows Task Scheduler is a powerful tool for automating administrative tasks and running applications at specific times or in response to events. However, by default, the 'History' tab for scheduled tasks is often disabled, making it difficult to track when tasks ran, whether they succeeded or failed, and what errors occurred. Enabling this history is a critical step for effective troubleshooting and auditing of your automated processes.
Understanding Task Scheduler History
The Task Scheduler History provides a detailed log of all events related to a scheduled task, including its creation, modification, execution attempts, success or failure status, and any associated error messages. This information is invaluable for diagnosing issues, verifying task execution, and maintaining system health. Without it, you're left guessing why a task didn't run as expected.
flowchart TD
A[Task Scheduler Service] --> B{Task Triggered?}
B -- Yes --> C[Task Execution Attempt]
C -- Success --> D[Log Success Event]
C -- Failure --> E[Log Failure Event]
D --> F[History Log]
E --> F[History Log]
B -- No --> G[Wait for Trigger]
G --> BSimplified flow of Task Scheduler history logging
Enabling Task History via Task Scheduler Console
The most straightforward method to enable Task Scheduler History is directly through the Task Scheduler console. This setting applies globally to all tasks managed by the scheduler on that server. Once enabled, you will start seeing events populate the 'History' tab for each task.
1. Open Task Scheduler
Press Win + R, type taskschd.msc, and press Enter.
2. Navigate to Actions Pane
In the Task Scheduler window, locate the 'Actions' pane on the right-hand side.
3. Enable All Tasks History
Click on 'Enable All Tasks History'. If it says 'Disable All Tasks History', it means it's already enabled.
4. Verify History Tab
Select any scheduled task in the middle pane and click on the 'History' tab at the bottom. You should now see events listed (new events will appear after tasks run).
Enabling Task History via Group Policy (GPO)
For domain-joined servers or environments where you need to manage this setting across multiple machines, Group Policy is the preferred method. This ensures consistent configuration and can be applied to Organizational Units (OUs) containing your servers.
1. Open Group Policy Management Editor
On a Domain Controller or a machine with RSAT installed, open gpmc.msc (Group Policy Management Console).
2. Create or Edit a GPO
Navigate to the desired OU, right-click, and select 'Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here...' or edit an existing GPO.
3. Edit the GPO
Right-click the GPO and select 'Edit'.
4. Navigate to Task Scheduler Settings
Go to Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Task Scheduler.
5. Enable Task History Policy
Find the setting 'Turn On Task Scheduler History' (or similar, depending on Windows Server version). Double-click it, select 'Enabled', and click 'Apply' then 'OK'.
6. Update Group Policy
On the target server(s), run gpupdate /force in an elevated command prompt to apply the new policy settings.
Verifying History and Event Viewer Integration
Once enabled, the Task Scheduler History events are actually stored in the Windows Event Log. Specifically, they are found under Applications and Services Logs -> Microsoft -> Windows -> TaskScheduler -> Operational. This integration allows for advanced filtering, forwarding, and centralized logging solutions.
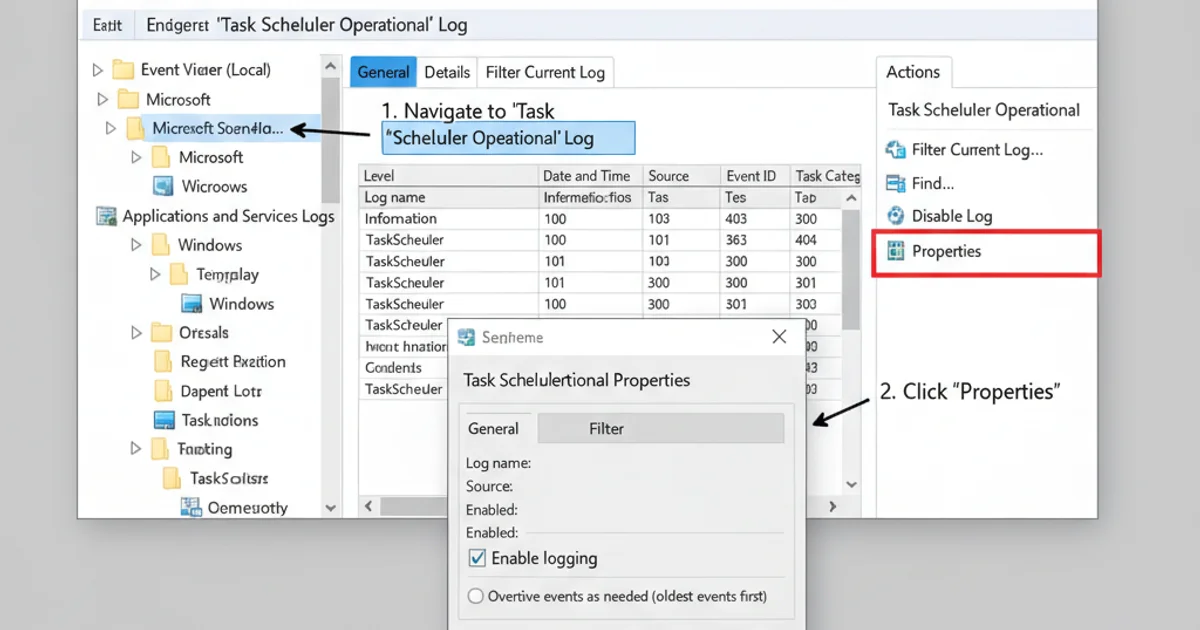
Task Scheduler events are logged in the Event Viewer under the Operational log.
By enabling Task Scheduler History, you gain crucial visibility into the execution of your automated tasks, transforming a 'black box' into a transparent and manageable system. This is a fundamental practice for any administrator managing Windows Server environments.