How to empty my destination table before inserting new records in SSIS?
Categories:
Efficiently Emptying Your Destination Table Before SSIS Inserts

Learn various methods to clear a destination table in SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) packages before loading new data, ensuring data integrity and preventing duplicates.
When working with SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS), a common requirement is to ensure that a destination table is empty before new records are inserted. This is crucial for scenarios like full data refreshes, preventing duplicate entries, or maintaining data integrity. This article explores several effective methods to achieve this, ranging from simple SQL commands to more advanced SSIS components, helping you choose the best approach for your specific needs.
Method 1: Using an 'Execute SQL Task' for TRUNCATE TABLE
The TRUNCATE TABLE statement is the fastest and most efficient way to remove all rows from a table. It deallocates the data pages used by the table, making it a metadata-only operation that is minimally logged. This method is ideal when you want to delete all records and reset identity columns, and you don't need to log individual row deletions.
1. Add an 'Execute SQL Task'
Drag and drop an 'Execute SQL Task' from the SSIS Toolbox onto your Control Flow.
2. Configure the Connection
Double-click the task to open its editor. In the 'General' page, select an OLE DB connection manager that points to your destination database.
3. Write the TRUNCATE Statement
In the 'SQLStatement' property, enter the TRUNCATE TABLE YourTableName; command. Replace YourTableName with the actual name of your destination table.
4. Precedence Constraint
Connect this 'Execute SQL Task' to your 'Data Flow Task' (or other insertion task) using a success precedence constraint, ensuring the table is truncated before data insertion begins.
TRUNCATE TABLE [dbo].[YourDestinationTable];
SQL command to truncate a table
TRUNCATE TABLE. It is a DDL operation, cannot be rolled back, and does not fire DELETE triggers. Ensure you have proper backups or are certain you want to permanently delete all data.Method 2: Using an 'Execute SQL Task' for DELETE FROM
If you need to log individual row deletions, fire DELETE triggers, or delete only a subset of data (though for emptying the entire table, TRUNCATE is usually preferred), the DELETE FROM statement is your alternative. It's slower than TRUNCATE TABLE for full table deletions but offers more flexibility.
1. Add an 'Execute SQL Task'
Similar to Method 1, add an 'Execute SQL Task' to your Control Flow.
2. Configure the Connection
Set up the OLE DB connection manager to your destination database.
3. Write the DELETE Statement
In the 'SQLStatement' property, enter DELETE FROM YourTableName;. If you need to delete specific rows, you can add a WHERE clause, e.g., DELETE FROM YourTableName WHERE SomeColumn = 'SomeValue';.
4. Precedence Constraint
Connect this task to your data insertion task with a success precedence constraint.
DELETE FROM [dbo].[YourDestinationTable];
-- Or for conditional deletion:
-- DELETE FROM [dbo].[YourDestinationTable] WHERE LoadDate < GETDATE();
SQL command to delete all rows from a table
DELETE FROM might cause transaction log issues, consider deleting data in batches within a loop or using TRUNCATE if applicable.Method 3: Using a 'Data Flow Task' with a 'Destination' Component
While less common for simply emptying a table, some destination components in a 'Data Flow Task' offer options to truncate or delete rows before loading. This is typically found in OLE DB Destination or SQL Server Destination components.
1. Add a 'Data Flow Task'
Drag a 'Data Flow Task' onto your Control Flow.
2. Add a 'Destination' Component
Inside the 'Data Flow Task', add an 'OLE DB Destination' or 'SQL Server Destination' component.
3. Configure the Destination
Double-click the destination component. On the 'Connection Manager' page, select your destination table.
4. Enable Table Lock/Truncation
For 'OLE DB Destination', go to the 'Table or view' dropdown. If you select 'Table or view - fast load', you'll see a checkbox for 'Table lock' and 'Check constraint'. Below that, there's often an option like 'Keep identity' and 'Truncate table'. Check 'Truncate table' if available and desired. Note that this option's availability and exact wording can vary based on the destination type and version.
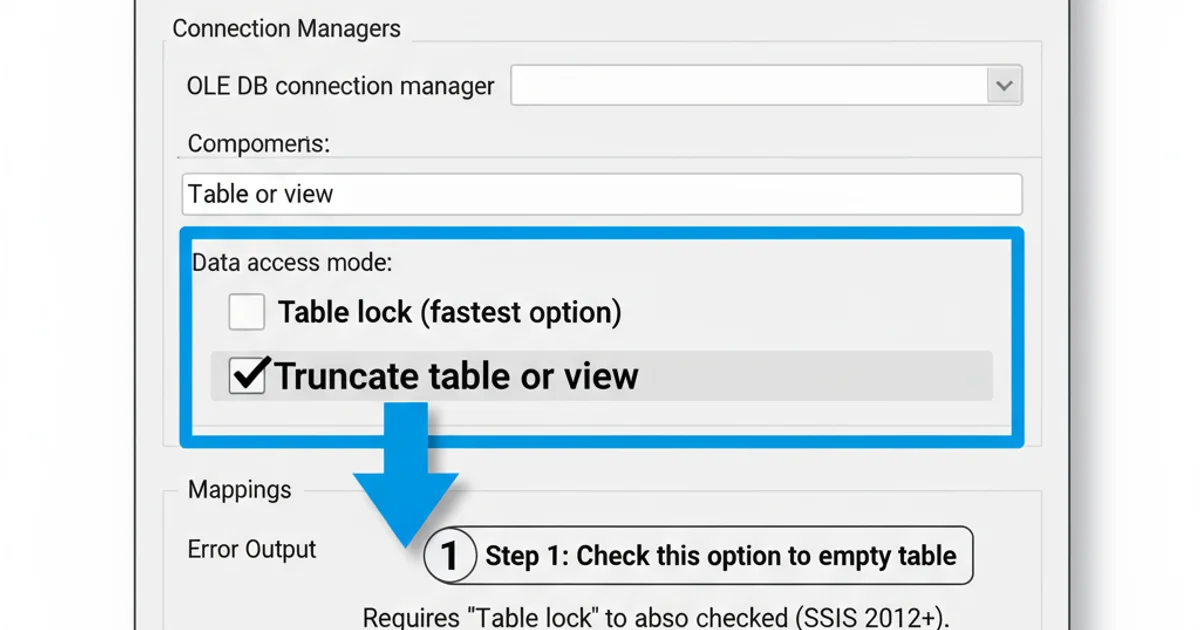
Configuring 'Truncate table' in OLE DB Destination (SSIS 2012+)
Choosing the Right Method
The best method depends on your specific requirements:
TRUNCATE TABLE(Execute SQL Task): Best for full table refreshes where speed is critical, identity columns need to be reset, and you don't need to log individual deletions or fire triggers.DELETE FROM(Execute SQL Task): Use when you need to fire DELETE triggers, log individual deletions, or delete only a subset of data. It's slower for full table deletions.- Destination Component 'Truncate table' option: Convenient for simple full table refreshes when available within your chosen destination component, integrating the operation directly into the data flow.
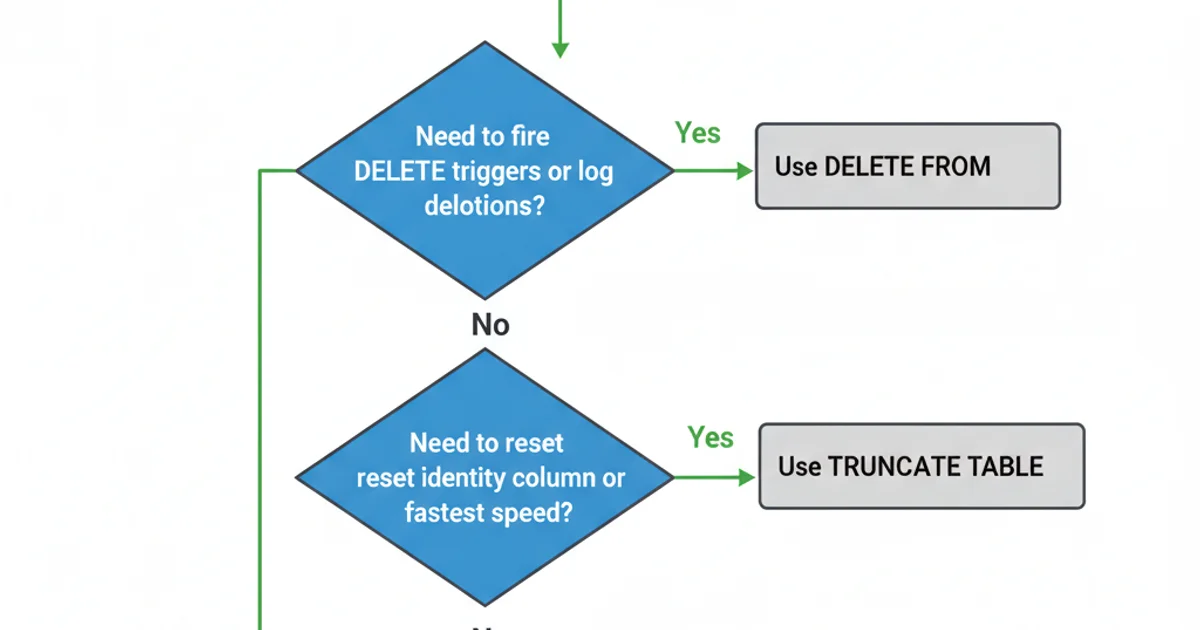
Decision flow for choosing a table emptying method in SSIS