AngularJS - Find Element with attribute
Categories:
AngularJS: Efficiently Finding Elements by Attribute

Discover various methods to locate DOM elements in AngularJS applications based on their attributes, enhancing your ability to manipulate and interact with the UI.
In AngularJS, interacting with the DOM is often abstracted away by directives and data binding. However, there are scenarios where you need to directly access or manipulate DOM elements based on specific attributes. This article explores several robust techniques for finding elements by attribute within your AngularJS applications, ranging from native JavaScript methods to AngularJS-specific approaches.
Understanding the Need for Element Selection
While AngularJS encourages a declarative approach where directives handle most DOM manipulation, direct element selection becomes necessary for tasks like integrating with third-party libraries that require DOM references, performing complex animations, or implementing custom UI behaviors that fall outside standard directive capabilities. Selecting elements by attribute is a common pattern, especially when dealing with custom directives or specific data attributes.
Method 1: Using Native JavaScript querySelector / querySelectorAll
The most straightforward and performant way to find elements by attribute is by leveraging native JavaScript's querySelector and querySelectorAll methods. These methods accept CSS selectors, allowing you to target elements based on their attributes, classes, IDs, and more. This approach is generally recommended for its speed and broad browser support.
// Find the first element with a specific attribute
var element = document.querySelector('[my-custom-attribute]');
console.log(element);
// Find all elements with a specific attribute
var elements = document.querySelectorAll('[data-id="123"]');
elements.forEach(function(el) {
console.log(el);
});
// Find elements with an attribute containing a specific value
var partialMatch = document.querySelectorAll('[class*="ng-"]');
partialMatch.forEach(function(el) {
console.log(el);
});
Examples of using querySelector and querySelectorAll to find elements by attribute.
querySelector or querySelectorAll, remember that these methods operate on the entire document by default. For better performance and scope, consider calling them on a specific parent element if you know the element's general location, e.g., parentElement.querySelector('[attribute]').Method 2: AngularJS angular.element (JQLite)
AngularJS provides its own lightweight wrapper around DOM elements called angular.element, often referred to as JQLite. While not as feature-rich as full jQuery, it offers a subset of jQuery's functionalities, including element selection. You can use angular.element with CSS selectors to find elements by attribute. This is particularly useful when you're already working within an AngularJS context and want to maintain a consistent API.
angular.module('myApp', [])
.controller('MyController', function($scope, $element) {
// Assuming $element is the current element of the directive/controller
// Find elements within the current controller's scope
var specificElement = $element.find('[my-data-attribute="value"]');
console.log(specificElement);
// Find all elements with a specific attribute within the document
var allElements = angular.element(document).find('[another-attribute]');
console.log(allElements);
// Using a more complex selector
var complexSelection = angular.element(document.querySelector('.container')).find('div[ng-if]');
console.log(complexSelection);
});
Using angular.element and its find method to locate elements by attribute.
angular.element is convenient, it's important to note that its find() method only works on descendants of the current element. If you need to search the entire document, you'll need to start your selection from angular.element(document) or use native document.querySelector.Method 3: Custom Directives for Attribute-Based Logic
For scenarios where you frequently need to interact with elements based on a specific attribute, creating a custom directive is often the most 'AngularJS-idiomatic' approach. Directives allow you to encapsulate DOM manipulation logic and reuse it across your application. You can define a directive that matches a specific attribute and then perform actions within its link function.
angular.module('myApp', [])
.directive('myHighlightAttribute', function() {
return {
restrict: 'A', // Attribute directive
link: function(scope, element, attrs) {
// The 'element' parameter is the DOM element with this attribute
// 'attrs' contains all attributes on this element
if (attrs.myHighlightAttribute === 'true') {
element.css('background-color', 'yellow');
}
console.log('Element with myHighlightAttribute:', element[0]);
console.log('Value of myHighlightAttribute:', attrs.myHighlightAttribute);
}
};
});
Defining a custom attribute directive to act on elements with my-highlight-attribute.
To use this directive, you would simply add the attribute to your HTML element:
<div my-highlight-attribute="true">
This div will be highlighted.
</div>
<span my-highlight-attribute="false">
This span will not be highlighted.
</span>
HTML usage of the myHighlightAttribute directive.
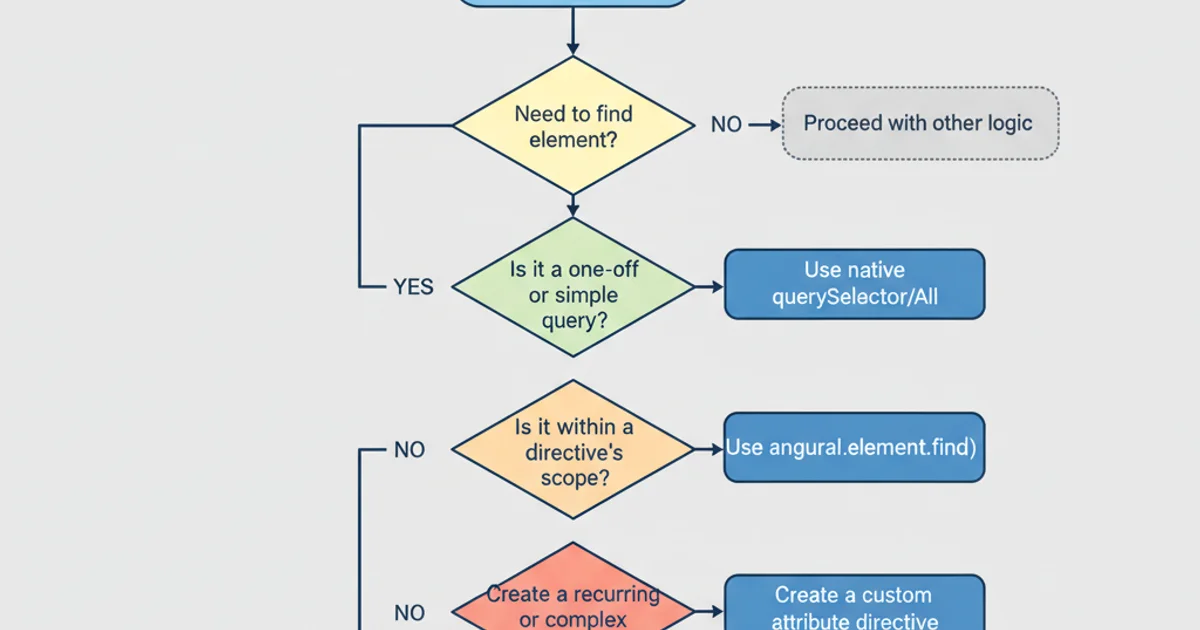
Decision flow for choosing an element selection method.