Converting bytes to megabytes
Categories:
Understanding and Converting Bytes to Megabytes

Demystify digital storage units by learning how to accurately convert bytes to megabytes, understanding the difference between base-2 and base-10 systems.
In the world of computing, understanding how digital storage is measured is fundamental. From the smallest file to the largest hard drive, data is quantified using units like bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, and gigabytes. While the conversion might seem straightforward, a common point of confusion arises from the use of both base-2 (binary) and base-10 (decimal) systems. This article will clarify these concepts and provide practical methods for converting bytes to megabytes.
The Basics: Bytes and Their Multiples
At its core, a byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. A bit is the smallest unit of data, representing a binary value of either 0 or 1. Larger units are formed by multiples of bytes. Historically, and in many computing contexts, these multiples are based on powers of 2 (binary system). However, for marketing and general usage, especially with storage manufacturers, powers of 10 (decimal system) are often used, leading to discrepancies.
flowchart TD
A[Bit] --> B[8 Bits = 1 Byte]
B --> C["1024 Bytes = 1 Kilobyte (KiB)"]
C --> D["1024 Kilobytes = 1 Megabyte (MiB)"]
D --> E["1024 Megabytes = 1 Gigabyte (GiB)"]
style A fill:#f9f,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style B fill:#bbf,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style C fill:#bbf,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style D fill:#bbf,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style E fill:#bbf,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2pxBinary (Base-2) Data Unit Hierarchy
Base-2 vs. Base-10: The Kilobyte Conundrum
The primary source of confusion stems from the two different interpretations of prefixes like 'kilo', 'mega', and 'giga'.
Base-2 (Binary) System: In computing, a kilobyte (KB or KiB) is traditionally 1024 bytes (2^10 bytes). A megabyte (MB or MiB) is 1024 kilobytes (2^20 bytes). This system is used by operating systems and software to report file sizes and memory.
Base-10 (Decimal) System: In the International System of Units (SI), 'kilo' means 1,000, 'mega' means 1,000,000, and so on. Storage manufacturers often use this system, where 1 kilobyte (KB) = 1,000 bytes, and 1 megabyte (MB) = 1,000,000 bytes. This is why a '1TB' hard drive might show up as '931GB' in your operating system.
Converting Bytes to Megabytes
Regardless of the system, the conversion process involves division. The key is to know which conversion factor to use (1000 or 1024).
Using Base-2 (Binary) Conversion (1024-based)
This is the most common conversion for understanding file sizes and memory in operating systems.
- Bytes to Kilobytes (KiB): Divide the number of bytes by 1024.
Bytes / 1024 = Kilobytes (KiB) - Kilobytes (KiB) to Megabytes (MiB): Divide the number of kilobytes by 1024.
Kilobytes (KiB) / 1024 = Megabytes (MiB)
Combining these, to convert bytes directly to megabytes (MiB):
Bytes / (1024 * 1024) = Megabytes (MiB)
Bytes / 1,048,576 = Megabytes (MiB)
Using Base-10 (Decimal) Conversion (1000-based)
This conversion is typically used by storage manufacturers.
- Bytes to Kilobytes (KB): Divide the number of bytes by 1000.
Bytes / 1000 = Kilobytes (KB) - Kilobytes (KB) to Megabytes (MB): Divide the number of kilobytes by 1000.
Kilobytes (KB) / 1000 = Megabytes (MB)
Combining these, to convert bytes directly to megabytes (MB):
Bytes / (1000 * 1000) = Megabytes (MB)
Bytes / 1,000,000 = Megabytes (MB)
Python
Base-2 (Binary) Conversion
def bytes_to_mebibytes(bytes_value): return bytes_value / (1024 * 1024)
Base-10 (Decimal) Conversion
def bytes_to_megabytes_decimal(bytes_value): return bytes_value / (1000 * 1000)
Example usage:
file_size_bytes = 5242880 # 5 MB (binary) print(f"{file_size_bytes} bytes is {bytes_to_mebibytes(file_size_bytes):.2f} MiB")
storage_size_bytes = 5000000 # 5 MB (decimal) print(f"{storage_size_bytes} bytes is {bytes_to_megabytes_decimal(storage_size_bytes):.2f} MB")
JavaScript
// Base-2 (Binary) Conversion function bytesToMebibytes(bytesValue) { return bytesValue / (1024 * 1024); }
// Base-10 (Decimal) Conversion function bytesToMegabytesDecimal(bytesValue) { return bytesValue / (1000 * 1000); }
// Example usage:
const fileSizeBytes = 5242880; // 5 MB (binary)
console.log(${fileSizeBytes} bytes is ${bytesToMebibytes(fileSizeBytes).toFixed(2)} MiB);
const storageSizeBytes = 5000000; // 5 MB (decimal)
console.log(${storageSizeBytes} bytes is ${bytesToMegabytesDecimal(storageSizeBytes).toFixed(2)} MB);
Java
// Base-2 (Binary) Conversion public static double bytesToMebibytes(long bytesValue) { return (double) bytesValue / (1024 * 1024); }
// Base-10 (Decimal) Conversion public static double bytesToMegabytesDecimal(long bytesValue) { return (double) bytesValue / (1000 * 1000); }
// Example usage: long fileSizeBytes = 5242880L; // 5 MB (binary) System.out.printf("%d bytes is %.2f MiB%n", fileSizeBytes, bytesToMebibytes(fileSizeBytes));
long storageSizeBytes = 5000000L; // 5 MB (decimal) System.out.printf("%d bytes is %.2f MB%n", storageSizeBytes, bytesToMegabytesDecimal(storageSizeBytes));
Practical Application: Why the Difference Matters
The difference between base-2 and base-10 conversions can lead to confusion and perceived discrepancies in storage capacity. For example, a hard drive advertised as 1 terabyte (1,000,000,000,000 bytes) will be reported by an operating system (which uses base-2) as approximately 0.909 TiB (terabytes in binary), or 931 GiB (gigabytes in binary). This is not a defect, but a difference in measurement standards.
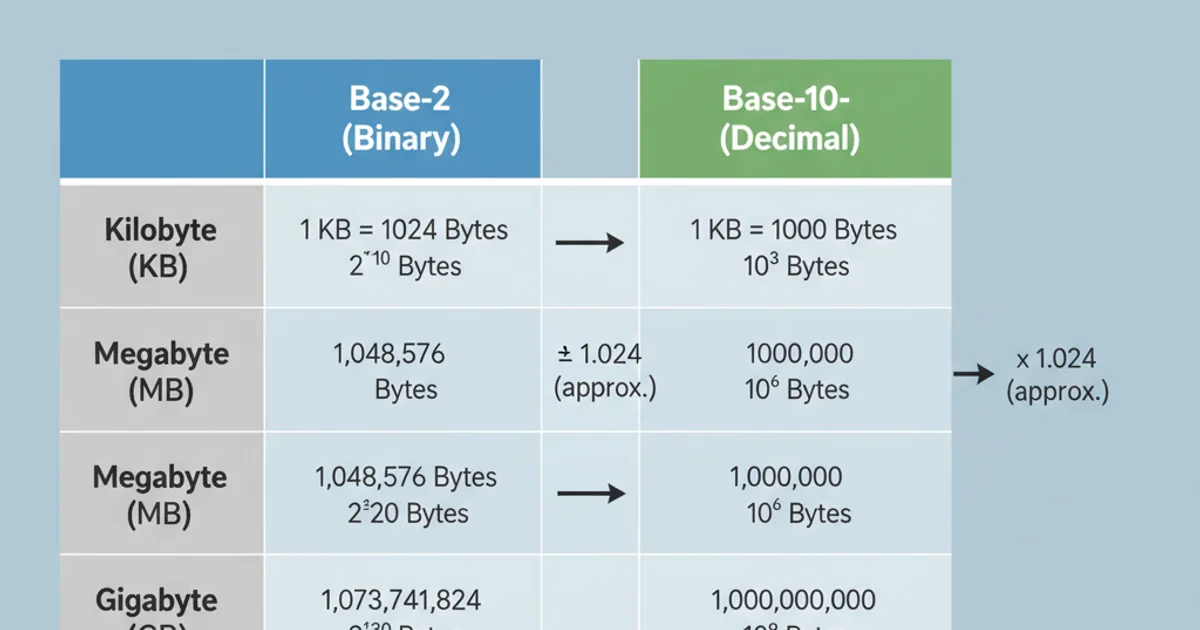
Comparison of Base-2 (Binary) vs. Base-10 (Decimal) Units
By understanding these two systems and the appropriate conversion factors, you can accurately interpret digital storage measurements and avoid common misunderstandings. Whether you're a developer, a system administrator, or just a curious user, this knowledge is invaluable for navigating the digital landscape.