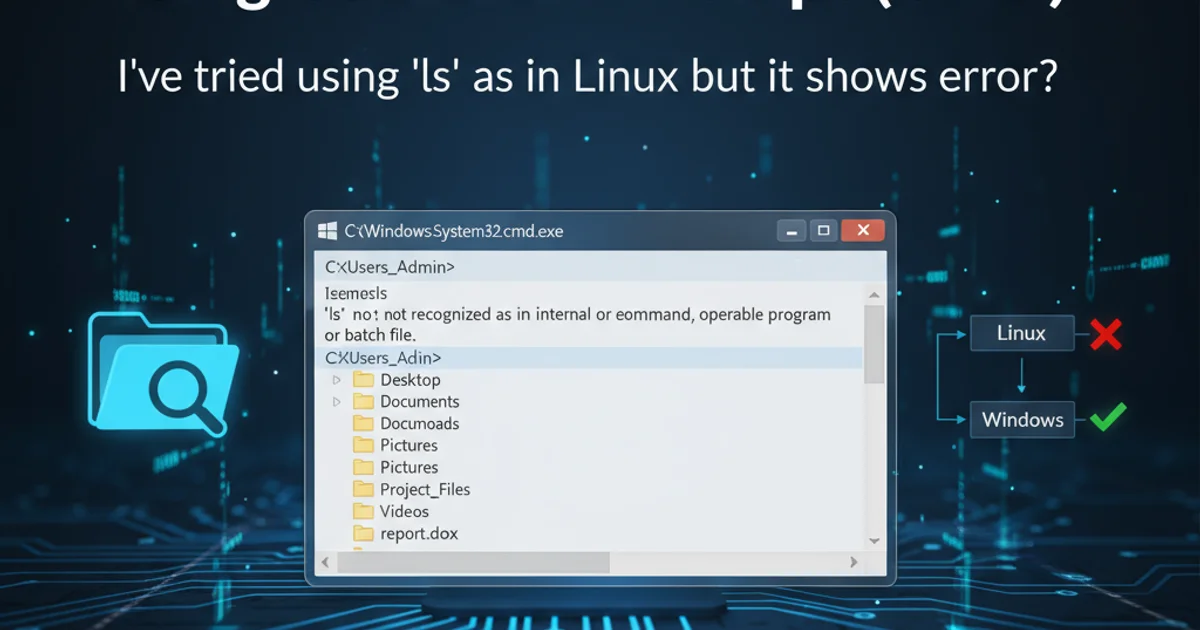
How to list files in windows using command prompt (cmd). I've tried using ' ls ' as in Linux but ...
Categories:
Listing Files in Windows Command Prompt: Beyond 'ls'
Learn the correct commands to list files and directories in Windows Command Prompt (CMD), understand their options, and see how they differ from Linux 'ls'.
If you're transitioning from a Linux or Unix-like environment to Windows, you might find yourself instinctively typing ls into the Command Prompt (CMD) to list files. However, Windows CMD uses a different set of commands for directory navigation and file listing. This article will guide you through the correct commands and their various options, helping you efficiently manage files from the Windows command line.
The 'dir' Command: Windows Equivalent of 'ls'
The primary command for listing files and directories in Windows Command Prompt is dir. It functions similarly to ls but has its own unique syntax and parameters. When you type dir and press Enter, it will display the contents of the current directory.
dir
Basic usage of the 'dir' command
Common 'dir' Command Options
The dir command offers a rich set of options to customize its output, allowing you to filter, sort, and format the listing according to your needs. Here are some of the most frequently used options:
flowchart TD
A[Start: dir command] --> B{Need specific files?}
B -->|Yes| C[Use /A attribute filter]
B -->|No| D{Need sorted output?}
D -->|Yes| E[Use /O sort order]
D -->|No| F{Need wide format?}
F -->|Yes| G[Use /W]
F -->|No| H{Need subdirectories?}
H -->|Yes| I[Use /S]
H -->|No| J[End: Display results]Decision flow for common 'dir' command options
List all files and subdirectories
dir /s
List files in wide format
dir /w
List only directories
dir /ad
List only files
dir /a-d
Sort by date/time (oldest first)
dir /od
Sort by size (smallest first)
dir /os
List hidden files
dir /ah
Understanding 'dir' Attributes (/A)
The /A switch allows you to filter files and directories based on their attributes. This is particularly useful for finding specific types of items, such as hidden files, system files, or read-only files.
dir /a:h
REM Lists hidden files and directories
dir /a:s
REM Lists system files and directories
dir /a:r
REM Lists read-only files
dir /a:d
REM Lists only directories
dir /a:-d
REM Lists only files (excludes directories)
Examples of filtering with the '/A' attribute switch
dir /a:hs would list hidden system files and directories.Practical Steps for Listing Files
Let's walk through some common scenarios for listing files in CMD.
1. Open Command Prompt
Press Win + R, type cmd, and press Enter. Alternatively, search for "Command Prompt" in the Start menu.
2. Navigate to a directory (Optional)
Use the cd (change directory) command to move to the desired location. For example, cd C:\Users\YourUsername\Documents.
3. List basic contents
Type dir and press Enter to see a simple list of files and subdirectories in the current location.
4. List all files including subdirectories
Type dir /s to recursively list all files and directories within the current directory and its subfolders.
5. List only directories
Type dir /ad to display only the subdirectories within the current path, excluding files.