Tesseract Bounding Box Problems
Categories:
Troubleshooting Tesseract Bounding Box Issues in Java

Explore common problems and solutions when extracting bounding box data with Tesseract OCR in Java, focusing on accuracy and segmentation challenges.
Tesseract OCR is a powerful engine for extracting text from images, but obtaining accurate bounding box information for individual characters, words, or lines can often be a source of frustration, especially within a Java environment. Developers frequently encounter issues such as incorrect box coordinates, missing boxes, or boxes that don't align precisely with the visual text. This article delves into the common causes of these problems and provides practical solutions to improve the reliability of Tesseract's bounding box output.
Understanding Tesseract's Bounding Box Output
Before diving into troubleshooting, it's crucial to understand how Tesseract generates bounding boxes. Tesseract performs several internal steps, including image preprocessing, layout analysis, and character recognition, each of which influences the final bounding box data. The output typically comes in various levels: page, block, paragraph, line, word, and character. The accuracy of these boxes heavily depends on the quality of the input image and the configuration of the Tesseract engine.
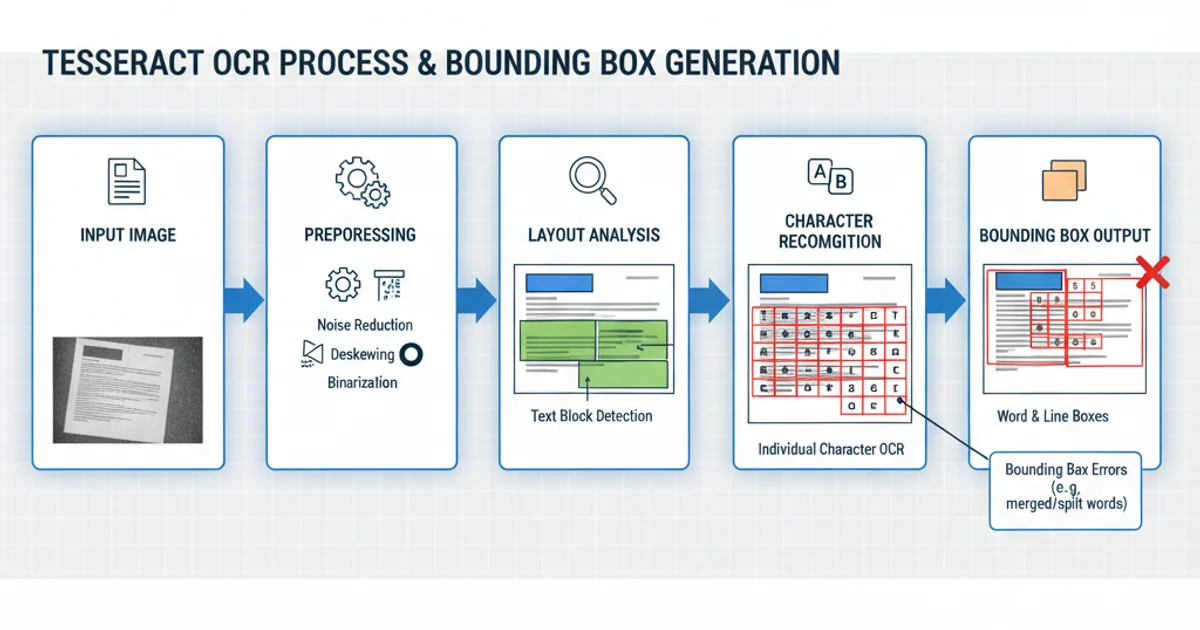
Tesseract's internal OCR process and bounding box generation.
Common Causes of Inaccurate Bounding Boxes
Several factors can lead to suboptimal bounding box results. Identifying the root cause is the first step towards a solution. These often include poor image quality, incorrect Tesseract configuration, and limitations in Tesseract's layout analysis capabilities.
1. Image Quality and Preprocessing
Low-resolution images, images with noise, skew, rotation, or inconsistent lighting can severely impact Tesseract's ability to accurately segment text and, consequently, generate correct bounding boxes. Preprocessing steps like binarization, deskewing, and noise reduction are often essential.
2. Tesseract Configuration and Parameters
Tesseract offers various configuration options, including Page Segmentation Mode (PSM) and OCR Engine Mode (OEM), which dictate how it processes the image and recognizes text. An inappropriate PSM can lead to incorrect text block detection and misaligned bounding boxes.
3. Font and Layout Challenges
Unusual fonts, highly stylized text, or complex document layouts (e.g., multi-column text, text over images, tables) can confuse Tesseract's layout analysis engine, resulting in merged or split bounding boxes.
Practical Solutions and Code Examples in Java
Let's explore how to address these issues using TessBaseAPI in Java (often via Tess4J or similar wrappers).
Solution 1: Image Preprocessing
Utilize image processing libraries (like OpenCV or java.awt.image) to clean up your images before passing them to Tesseract. Common steps include:
- Grayscale Conversion: Convert to grayscale to simplify color information.
- Binarization: Convert to black and white to enhance text contrast.
- Deskewing: Correct any rotational misalignment.
- Noise Reduction: Apply filters to remove speckles or artifacts.
import net.sourceforge.tess4j.Tesseract;
import net.sourceforge.tess4j.ITesseract;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.io.File;
public class ImagePreprocessor {
public static BufferedImage preprocessImage(BufferedImage originalImage) {
// Example: Convert to grayscale and then binarize
BufferedImage grayImage = new BufferedImage(
originalImage.getWidth(), originalImage.getHeight(), BufferedImage.TYPE_BYTE_GRAY);
grayImage.getGraphics().drawImage(originalImage, 0, 0, null);
BufferedImage binarizedImage = new BufferedImage(
grayImage.getWidth(), grayImage.getHeight(), BufferedImage.TYPE_BYTE_BINARY);
for (int y = 0; y < grayImage.getHeight(); y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < grayImage.getWidth(); x++) {
int rgb = grayImage.getRGB(x, y);
int red = (rgb >> 16) & 0xFF;
// Simple thresholding for binarization
int newPixel = (red < 128) ? 0xFF000000 : 0xFFFFFFFF; // Black or White
binarizedImage.setRGB(x, y, newPixel);
}
}
return binarizedImage;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File imageFile = new File("path/to/your/scanned_document.png");
BufferedImage original = ImageIO.read(imageFile);
BufferedImage preprocessed = preprocessImage(original);
ImageIO.write(preprocessed, "png", new File("path/to/preprocessed_document.png"));
System.out.println("Image preprocessed and saved.");
// Now use Tesseract with the preprocessed image
ITesseract tesseract = new Tesseract();
tesseract.setDatapath("/path/to/tessdata");
// ... further Tesseract configuration and OCR
}
}
Basic image preprocessing (grayscale and binarization) in Java.
Solution 2: Optimizing Tesseract Configuration
Experiment with different Page Segmentation Modes (PSM) to find the one that best suits your document layout. The PSM parameter tells Tesseract how to interpret the page layout. Common values include:
PSM_AUTO(3): Automatic page segmentation (default).PSM_SINGLE_BLOCK(6): Assume a single uniform block of text.PSM_SINGLE_LINE(7): Treat the image as a single text line.PSM_SINGLE_WORD(8): Treat the image as a single word.PSM_SINGLE_CHAR(10): Treat the image as a single character.
Also, ensure your tessdata path is correctly set and that you are using appropriate language data files.
import net.sourceforge.tess4j.Tesseract;
import net.sourceforge.tess4j.ITesseract;
import net.sourceforge.tess4j.TesseractException;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.List;
import net.sourceforge.tess4j.Word;
public class TesseractConfigExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ITesseract tesseract = new Tesseract();
tesseract.setDatapath("/path/to/tessdata"); // Path to your tessdata directory
tesseract.setLanguage("eng"); // Set language (e.g., English)
// Experiment with different PSM values
// For a single block of text, try PSM_SINGLE_BLOCK (6)
// For a single line, try PSM_SINGLE_LINE (7)
tesseract.setPageSegMode(6); // Example: Assume a single uniform block of text
File imageFile = new File("path/to/your/image.png");
BufferedImage image = ImageIO.read(imageFile);
try {
// Get bounding box data for words
List<Word> words = tesseract.getWords(image, ITesseract.RenderedFormat.TEXT);
for (Word word : words) {
System.out.println("Word: " + word.getText() + ", Bounding Box: " + word.getBoundingBox());
}
// You can also get character bounding boxes using a different method or iterating through words
// For character level, you might need to process the image region for each word again with PSM_SINGLE_CHAR
} catch (TesseractException e) {
System.err.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Configuring Tesseract's Page Segmentation Mode (PSM) in Java.
Solution 3: Post-processing Bounding Box Data
Sometimes, Tesseract's output might be slightly off. You can implement post-processing logic to refine the bounding boxes. This could involve:
- Merging adjacent boxes: If Tesseract splits a single word or character into multiple boxes.
- Filtering small boxes: Removing spurious boxes that are too small to contain meaningful text.
- Adjusting coordinates: Applying minor offsets based on observed patterns of inaccuracy.
This often requires custom logic based on the specific characteristics of your documents.
1. Step 1: Prepare Your Image
Ensure your input image is as clean as possible. Convert to grayscale, apply binarization, and correct any skew or rotation. Use image processing tools to enhance contrast and reduce noise.
2. Step 2: Configure Tesseract
Initialize your Tesseract instance. Set the datapath and language. Crucially, experiment with different setPageSegMode() values (e.g., 3, 6, 7, 8, 10) to match your document's layout. For character-level boxes, PSM_SINGLE_CHAR (10) might be necessary on cropped regions.
3. Step 3: Extract Bounding Boxes
Use tesseract.getWords() or similar methods to retrieve Word objects, which contain text and bounding box information. For character-level data, you might need to iterate through words and re-OCR small regions with a character-specific PSM.
4. Step 4: Visualize and Refine
Draw the extracted bounding boxes onto the original image using Java's Graphics2D to visually inspect accuracy. Based on observations, apply post-processing logic (merging, filtering, adjusting) to correct any remaining inaccuracies.