glibc, glib and gnulib
Categories:
Understanding glibc, GLib, and GNU Libc: A Comprehensive Guide

Navigate the often-confused landscape of C libraries: glibc, GLib, and GNU Libc. This guide clarifies their distinct roles, functionalities, and typical use cases in software development.
In the world of C and C++ programming, especially within the Linux ecosystem, you'll frequently encounter terms like glibc, GLib, and GNU Libc. While they sound similar and are often used interchangeably by mistake, they refer to distinct projects with different purposes and functionalities. This article aims to demystify these three critical components, explaining what each one is, what it does, and how they relate (or don't relate) to each other.
GNU C Library (glibc / GNU Libc)
The GNU C Library, commonly known as glibc or GNU Libc, is the GNU Project's implementation of the standard C library. It provides the core functionality that nearly all C programs rely on, offering a vast collection of functions for fundamental operations. These include input/output (I/O), string manipulation, memory management, mathematical computations, and system calls that interface with the operating system kernel. glibc is a foundational component of most Linux distributions and is essential for running virtually any program compiled for these systems.
glibc is not just for C programs; C++ programs also link against it for their standard library functions, as do programs written in many other languages that compile down to native code.#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char *str = malloc(10);
if (str == NULL) {
perror("malloc failed");
return 1;
}
strcpy(str, "Hello");
printf("%s, World!\n", str);
free(str);
return 0;
}
A simple C program using glibc functions like malloc, strcpy, and printf.
GLib: The GLib Utility Library
GLib is a separate, high-level utility library that provides core application building blocks for projects like GTK+ and GNOME. Unlike glibc, which is a low-level C standard library implementation, GLib offers more abstract data types, object and type systems, thread management, event loops, and robust utility functions. It's designed to be cross-platform and provides a consistent API across different operating systems, making it easier to write portable applications. GLib is often used in conjunction with glibc, as GLib itself relies on the underlying C standard library for its basic operations.
flowchart TD
A[Application] --> B["GLib (High-level utilities)"]
B --> C["glibc (C Standard Library)"]
C --> D["Linux Kernel (System Calls)"]
style A fill:#f9f,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style B fill:#bbf,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style C fill:#bfb,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style D fill:#ffb,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2pxRelationship between an application, GLib, glibc, and the Linux Kernel.
#include <glib.h>
int main() {
GList *list = NULL;
list = g_list_append(list, "Hello");
list = g_list_append(list, "World");
for (GList *l = list; l != NULL; l = l->next) {
g_print("%s ", (char*)l->data);
}
g_print("\n");
g_list_free(list);
return 0;
}
Example using GLib's GList data structure and g_print function.
Key Differences and Use Cases
The primary distinction lies in their scope and abstraction level. glibc is the fundamental layer providing direct access to system resources and standard C functions. It's a mandatory dependency for almost all native executables on Linux. GLib, on the other hand, is an application development toolkit that builds upon glibc (and other system libraries) to offer more advanced, object-oriented, and cross-platform features. You would choose glibc for low-level system programming or when writing simple C utilities, while GLib is preferred for building complex, portable applications, especially those with graphical user interfaces (GUIs) or requiring sophisticated data structures and concurrency management.
glibc as the engine of a car, providing the core power and mechanics. GLib would then be the car's advanced infotainment system, climate control, and power windows – features that enhance the user experience and build upon the engine's capabilities.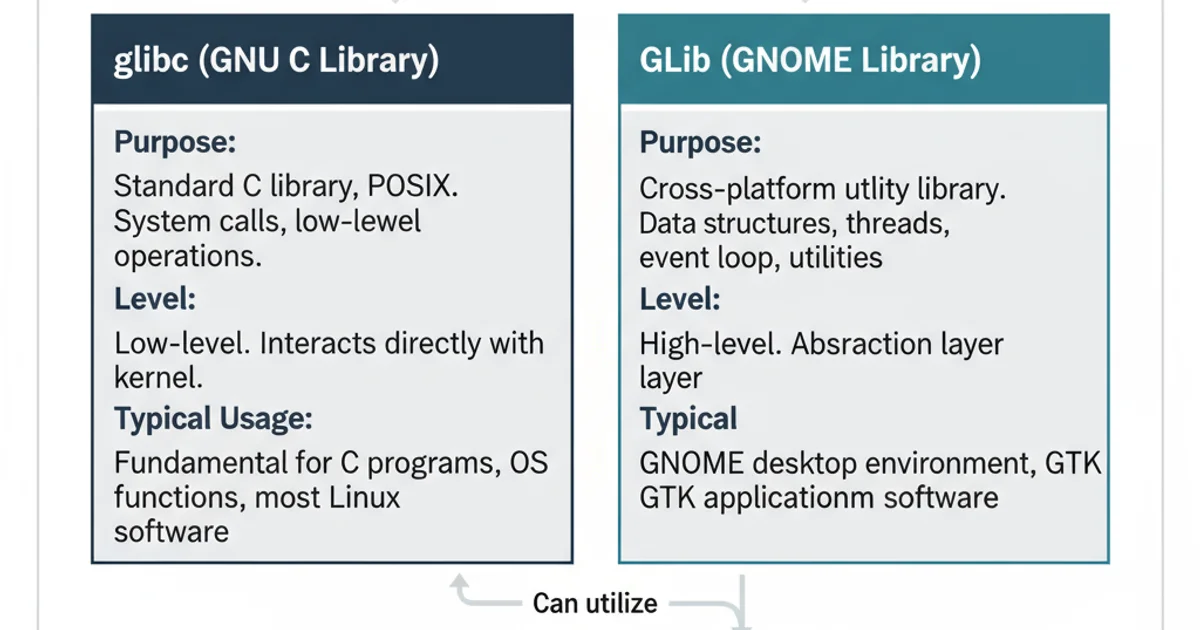
A summary of the distinctions between glibc and GLib.