chrome extension `sendResponse` does not work
sendresponse does not work with practical examples, diagrams, and best practices. Covers javascript, google-chrome-extension, messaging development techniques with visual e...Categories:
Debugging Chrome Extension sendResponse Issues
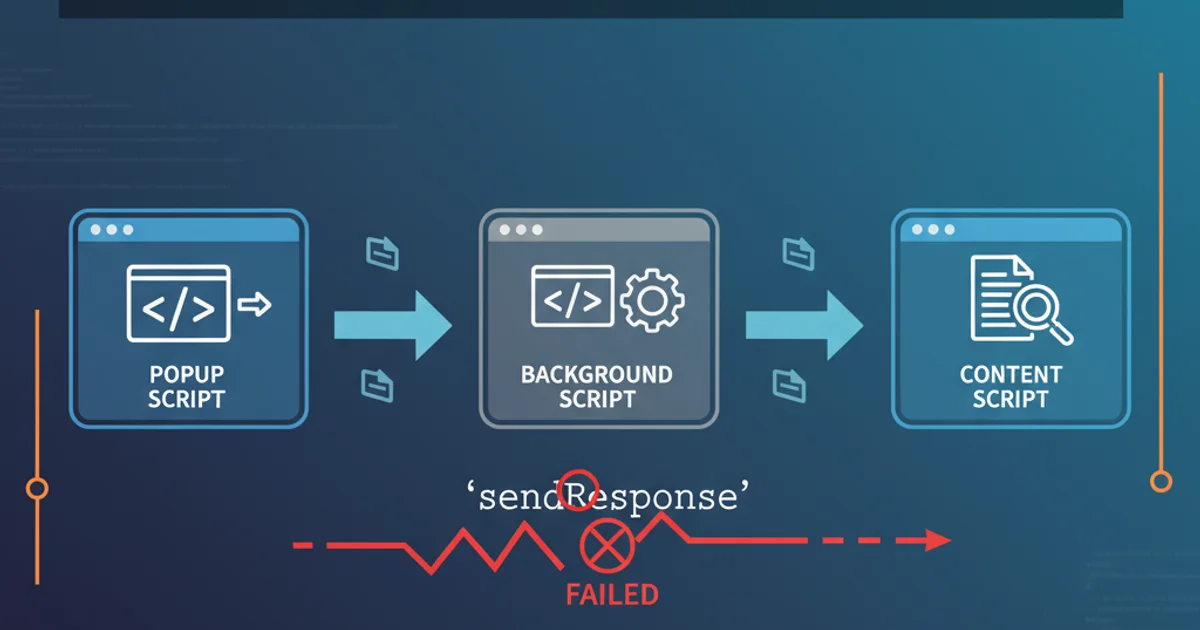
Understand common pitfalls and solutions when sendResponse fails to deliver messages in your Chrome Extensions, ensuring reliable communication between scripts.
Chrome Extensions rely heavily on message passing for communication between different parts: content scripts, background scripts, and popups. The sendResponse callback is crucial for sending data back to the script that initiated a message. However, developers often encounter scenarios where sendResponse appears not to work, leading to silent failures or unexpected behavior. This article delves into the common reasons behind these issues and provides practical solutions to ensure your extension's messaging works flawlessly.
Understanding Chrome Extension Message Passing
Before diving into sendResponse problems, it's essential to grasp the fundamentals of Chrome Extension message passing. Messages can be sent one-time or long-lived. sendResponse is primarily used with one-time requests, allowing the receiving end to send a single response back to the sender. The lifecycle of a message involves a sender, a receiver, and an optional response. If the receiver intends to respond asynchronously, it must explicitly indicate this to Chrome.
sequenceDiagram
participant Sender
participant Receiver
Sender->>Receiver: chrome.runtime.sendMessage(message)
activate Receiver
Note over Receiver: Listener processes message
alt Asynchronous Response
Receiver->>Receiver: return true (to keep port open)
Receiver-->>Sender: sendResponse(data) (later)
else Synchronous Response
Receiver-->>Sender: sendResponse(data) (immediately)
end
deactivate ReceiverSequence diagram of Chrome Extension one-time message passing with synchronous and asynchronous responses.
Common Reasons for sendResponse Failure
Several factors can cause sendResponse to fail or not be received. Understanding these is key to effective debugging.
1. Forgetting to Return true for Asynchronous Responses
This is by far the most common reason for sendResponse not working. If your message listener performs an asynchronous operation (e.g., an API call, setTimeout, or any Promise-based operation) before calling sendResponse, Chrome will close the message channel before your asynchronous code has a chance to execute the callback. To prevent this, you must return true from your onMessage listener function. This tells Chrome to keep the message channel open, indicating that sendResponse will be called later.
// Incorrect: sendResponse will likely fail if fetchData is async
chrome.runtime.onMessage.addListener((request, sender, sendResponse) => {
if (request.action === "getData") {
fetchData().then(data => {
sendResponse({ data: data });
});
}
});
// Correct: Returning true keeps the channel open
chrome.runtime.onMessage.addListener((request, sender, sendResponse) => {
if (request.action === "getData") {
fetchData().then(data => {
sendResponse({ data: data });
});
return true; // IMPORTANT: Indicate asynchronous response
}
});
Correctly handling asynchronous sendResponse by returning true.
2. Calling sendResponse More Than Once
The sendResponse callback is designed for a one-time response. Calling it multiple times for a single message will result in an error (e.g., "The message port closed before a response was received.") or simply subsequent calls being ignored. If you need to send multiple messages, consider using long-lived connections (chrome.runtime.connect) instead of one-time messages.
// Incorrect: Calling sendResponse twice
chrome.runtime.onMessage.addListener((request, sender, sendResponse) => {
if (request.action === "initial") {
sendResponse({ status: "received" });
// ... some other logic ...
sendResponse({ status: "completed" }); // This will fail or be ignored
}
});
Example of incorrectly calling sendResponse multiple times.
3. Listener Not Registered or Unregistered Prematurely
Ensure that your chrome.runtime.onMessage.addListener is properly registered and remains active for the lifetime of the script that needs to receive messages. For background scripts, this means it should be at the top level of your background.js file. For content scripts, it should be in a file injected into the page. If a script unregisters its listener or terminates before a message arrives, sendResponse will have no active port to respond to.
4. Sender Not Expecting a Response
When sending a message, if you expect a response, you must provide a callback function as the last argument to chrome.runtime.sendMessage (or chrome.tabs.sendMessage). If no callback is provided, Chrome assumes no response is expected, and the sendResponse from the receiver will effectively be ignored or lead to an error on the receiving side if return true was used unnecessarily.
// Sender not expecting a response (no callback)
chrome.runtime.sendMessage({ action: "doSomething" });
// Sender expecting a response (with callback)
chrome.runtime.sendMessage({ action: "getData" }, (response) => {
if (chrome.runtime.lastError) {
console.error("Error receiving response:", chrome.runtime.lastError.message);
return;
}
console.log("Received data:", response.data);
});
Sending messages with and without an expected response callback.
chrome.runtime.lastError in your sendMessage callback. This object provides valuable debugging information if the message or response fails.5. Message Channel Closing Due to Script Termination
If the script that sent the message (e.g., a popup script) closes before the sendResponse is called, the response will never be received. Similarly, if a content script is injected into a page that navigates away or refreshes, its message listeners and any pending sendResponse calls will be terminated.
6. Incorrect Manifest Permissions or Host Permissions
While less directly related to sendResponse itself, incorrect permissions can prevent scripts from communicating effectively. For instance, a content script might not be able to send messages to a background script if its host permissions are not correctly defined, or if the background script lacks necessary permissions to perform an action requested by the content script. Always double-check your manifest.json.
{
"manifest_version": 3,
"name": "My Extension",
"version": "1.0",
"permissions": [
"activeTab",
"storage"
],
"host_permissions": [
"<all_urls>"
],
"background": {
"service_worker": "background.js"
},
"content_scripts": [
{
"matches": ["<all_urls>"],
"js": ["content.js"]
}
]
}
Example manifest.json with relevant permissions for message passing.