Create a two dimensional string array anArray[2][2]
Categories:
Creating a Two-Dimensional String Array in Java
Learn how to declare, initialize, and manipulate 2D string arrays in Java, including practical examples for common use cases.
Two-dimensional arrays, often referred to as matrices or tables, are fundamental data structures in programming. In Java, they allow you to store collections of elements in a grid-like format, organized by rows and columns. This article will guide you through the process of creating and working with a two-dimensional array specifically designed to hold String objects, such as anArray[2][2].
Understanding Two-Dimensional Arrays
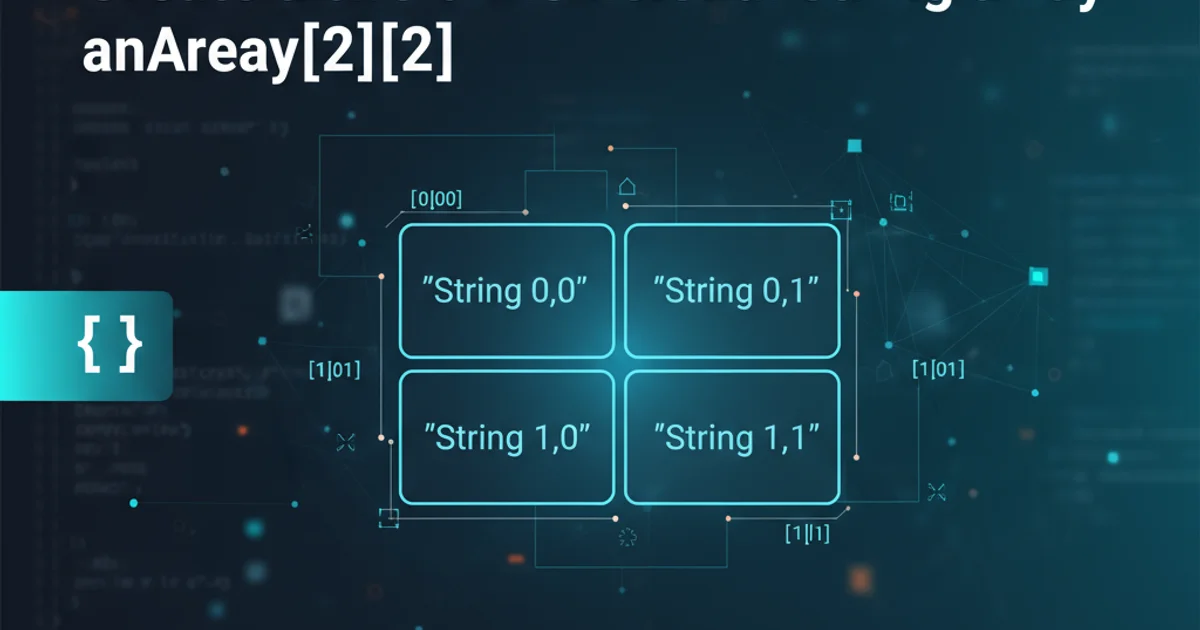
A two-dimensional array in Java is essentially an array of arrays. Each element of the main array is itself another array. When you declare anArray[2][2], you're creating an array that can hold 2 rows, and each of those rows can hold 2 columns. For a string array, each cell anArray[row][column] will store a String value. This structure is incredibly useful for representing tabular data, game boards, or any data that naturally fits a grid.
graph TD
A[2D String Array]
A --> B[Row 0]
A --> C[Row 1]
B --> B0[Column 0]
B --> B1[Column 1]
C --> C0[Column 0]
C --> C1[Column 1]
B0["anArray[0][0]"]
B1["anArray[0][1]"]
C0["anArray[1][0]"]
C1["anArray[1][1]"]Conceptual structure of a 2x2 two-dimensional array
Declaring and Initializing a 2D String Array
Declaring a two-dimensional array involves specifying the data type (in this case, String), followed by two sets of square brackets [][], and then the array name. Initialization can be done in several ways: directly at declaration, or by first declaring and then allocating memory and assigning values.
// Method 1: Declare, allocate, and assign values separately
String[][] anArray = new String[2][2];
anArray[0][0] = "Hello";
anArray[0][1] = "World";
anArray[1][0] = "Java";
anArray[1][1] = "Arrays";
// Method 2: Declare and initialize directly
String[][] anotherArray = {
{"Alpha", "Beta"},
{"Gamma", "Delta"}
};
Different ways to declare and initialize a 2D string array.
anArray[2][2], you're creating an array with 2 rows and 2 columns, totaling 4 elements.Accessing and Iterating Through Elements
To access an element in a two-dimensional array, you use its row and column indices, like anArray[rowIndex][columnIndex]. Remember that array indices in Java are zero-based, meaning the first row is at index 0 and the first column is at index 0. Iterating through a 2D array typically involves nested loops: an outer loop for rows and an inner loop for columns.
String[][] anArray = {
{"Hello", "World"},
{"Java", "Arrays"}
};
// Accessing a specific element
System.out.println("Element at [0][1]: " + anArray[0][1]); // Output: World
// Iterating using nested for loops
System.out.println("\nIterating with traditional for loops:");
for (int i = 0; i < anArray.length; i++) { // Loop through rows
for (int j = 0; j < anArray[i].length; j++) { // Loop through columns of current row
System.out.print(anArray[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println(); // New line after each row
}
// Iterating using enhanced for loops (for-each)
System.out.println("\nIterating with enhanced for loops:");
for (String[] row : anArray) { // For each row array
for (String element : row) { // For each string element in the row
System.out.print(element + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
Accessing and iterating through a 2D string array.
anArray.length property gives you the number of rows. anArray[i].length gives you the number of columns in the i-th row. This is important because Java allows for 'jagged' arrays where rows can have different numbers of columns, though for anArray[2][2], all rows will have the same length.