What should I put in header comments at the top of source files?
Categories:
Crafting Effective Header Comments for Source Files

Explore best practices for writing header comments in source code, ensuring clarity, maintainability, and collaboration across all programming languages.
Header comments, often found at the very top of a source file, serve as a crucial first point of contact for anyone reading your code. They provide essential metadata and high-level context, making it easier to understand a file's purpose, origin, and how to use it. While specific content can vary by project, language, and team standards, a well-crafted header comment significantly improves code maintainability, collaboration, and long-term understanding.
Why Header Comments Matter
Beyond mere documentation, header comments act as a quick reference guide. They help new team members onboard faster, remind seasoned developers of a file's intricacies, and assist automated tools in generating documentation or enforcing licensing. Neglecting them can lead to confusion, duplicated effort, and a higher barrier to entry for contributors.
flowchart TD
A[New Developer Views File] --> B{Header Comment Present?}
B -->|Yes| C[Quickly Understands Purpose & Context]
C --> D[Faster Onboarding & Contribution]
B -->|No| E[Struggles to Understand File]
E --> F[Wasted Time & Potential Errors]
D --> G[Improved Codebase Health]
F --> H[Decreased Codebase Health]Impact of Header Comments on Developer Understanding
Essential Elements of a Header Comment
While the exact format can be flexible, certain pieces of information are almost universally beneficial to include. These elements provide a comprehensive overview without delving into implementation details, which are better suited for inline comments or dedicated documentation.
Here's a breakdown of common and recommended elements:
1. File Name
Clearly state the name of the file. This might seem redundant, but it's useful when viewing printed code or code snippets out of context.
2. Brief Description
A one-to-two sentence summary of the file's primary purpose. What does this file do? What problem does it solve? (e.g., "Manages user authentication logic," "Defines the API routes for product management.")
3. Author(s)
The name(s) of the primary author(s) or the team responsible for the file. This helps with attribution and knowing whom to contact for questions.
4. Creation Date
The date the file was initially created. Useful for historical context.
5. Last Modified Date
The date of the most recent significant modification. This can be automatically updated by version control systems or manually maintained.
6. Copyright/License Information
Crucial for open-source projects or proprietary code. Include the copyright holder and the applicable license (e.g., MIT, Apache 2.0, proprietary license statement). This often includes a link to the full license text.
7. Version (Optional)
If the file or project has a specific versioning scheme, including the relevant version number can be helpful.
8. Dependencies (Optional)
For smaller files or modules, listing key external dependencies (libraries, other modules) can provide quick context.
Example Header Comment Structures
The structure and syntax of header comments will vary based on the programming language. However, the underlying principles remain consistent. Here are examples for common languages.
Python
#!/usr/bin/env python3
-- coding: utf-8 --
""" File: user_service.py Description: This module handles all user-related business logic, including creation, retrieval, and updates. Author: Jane Doe jane.doe@example.com Created: 2023-10-26 Last Modified: 2024-03-15 Copyright (c) 2024 ExampleCorp. All rights reserved. License: MIT License (see LICENSE file for details) """
JavaScript
/**
- @file userController.js
- @description Express controller for managing user authentication and profile operations.
- @author John Smith john.smith@example.com
- @date 2023-11-01
- @lastModified 2024-03-20
- @copyright 2024 ExampleApp. All rights reserved.
- @license Apache-2.0 (https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0) */
Java
/**
- File: UserService.java
- Description: Provides core business logic for user management within the application.
- Author: Alice Johnson alice.johnson@example.com
- Created: 2023-09-15
- Last Modified: 2024-02-28
- Copyright (c) 2024 MyCompany. All rights reserved.
- License: Proprietary */ package com.mycompany.service;
C++
/**
- @file data_processor.h
- @brief Defines the interface for a generic data processing utility.
- @author Bob Williams bob.williams@example.com
- @date 2023-12-05
- @lastModified 2024-01-10
- @copyright 2024 MyProject. All rights reserved.
- @license GPLv3 (see COPYING for details) */
#ifndef DATA_PROCESSOR_H #define DATA_PROCESSOR_H
Maintaining Header Comments
Header comments are not static; they should evolve with the file. While version control systems track changes, manually updating the 'Last Modified' date or adding a brief note about significant changes can be beneficial. However, avoid turning the header into a full change log; that's what Git history is for.
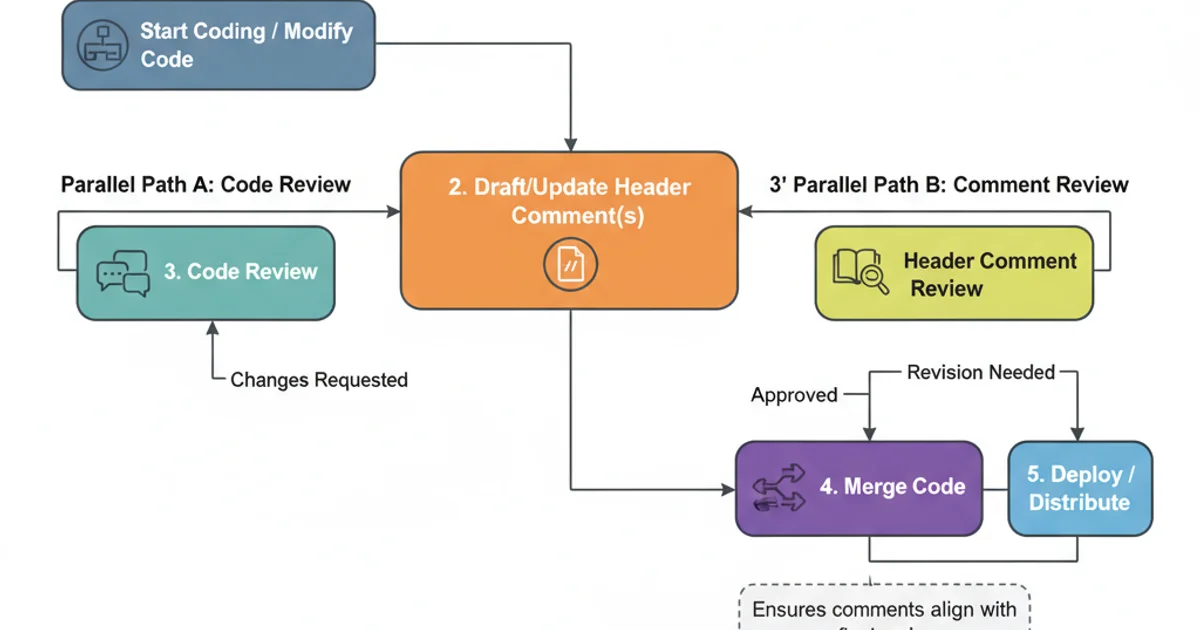
Integrating Header Comment Maintenance into the Development Workflow
Establishing a clear standard for header comments within your team or project is key. Document these standards in your project's CONTRIBUTING.md or developer guidelines. Tools like linters can also be configured to check for the presence and basic format of header comments, ensuring adherence to your defined conventions.