Open a new tab with javascript but stay on current tab using javascript
Categories:
Opening New Tabs in JavaScript While Retaining Focus on the Current Page
Learn how to programmatically open new browser tabs using JavaScript without losing focus on the user's current browsing context, enhancing user experience and workflow.
When developing web applications, there are frequent scenarios where you need to open a new browser tab or window programmatically. A common requirement is to do this without shifting the user's focus away from their current task on the original page. This article explores various JavaScript techniques to achieve this, focusing on methods that ensure the new tab opens in the background, preserving the user's workflow.
The window.open() Method for New Tabs
The primary method for opening new browser windows or tabs in JavaScript is window.open(). This function takes several parameters: the URL to load, the window name (or target), and a string of window features. The key to opening a new tab without stealing focus lies in how browsers interpret these parameters, especially the target and the browser's security policies.
window.open('https://www.example.com', '_blank');
Basic usage of window.open() to open a new tab.
By default, when window.open() is called, many browsers will open the new tab and immediately switch focus to it. This can be disruptive. The _blank target is crucial here, as it instructs the browser to open the URL in a new, unnamed window or tab. However, simply using _blank doesn't guarantee background opening across all browsers and user settings.
Ensuring Background Opening with window.open()
To reliably open a new tab in the background, you often need to combine window.open() with a slight delay or by manipulating the focus after the new window is opened. Modern browsers have become more restrictive about automatically opening tabs in the background to prevent malicious pop-ups. The most consistent approach involves opening the tab and then immediately returning focus to the original window.
function openInBackground(url) {
const newWindow = window.open(url, '_blank');
if (newWindow) {
newWindow.blur(); // Attempt to blur the new window
window.focus(); // Return focus to the current window
}
}
// Example usage:
openInBackground('https://www.google.com');
Function to open a new tab in the background and retain focus.
window.open() and focus management can vary significantly due to security policies and user preferences. Some browsers might still bring the new tab to the foreground, especially if it's not triggered by a direct user action (e.g., a click event).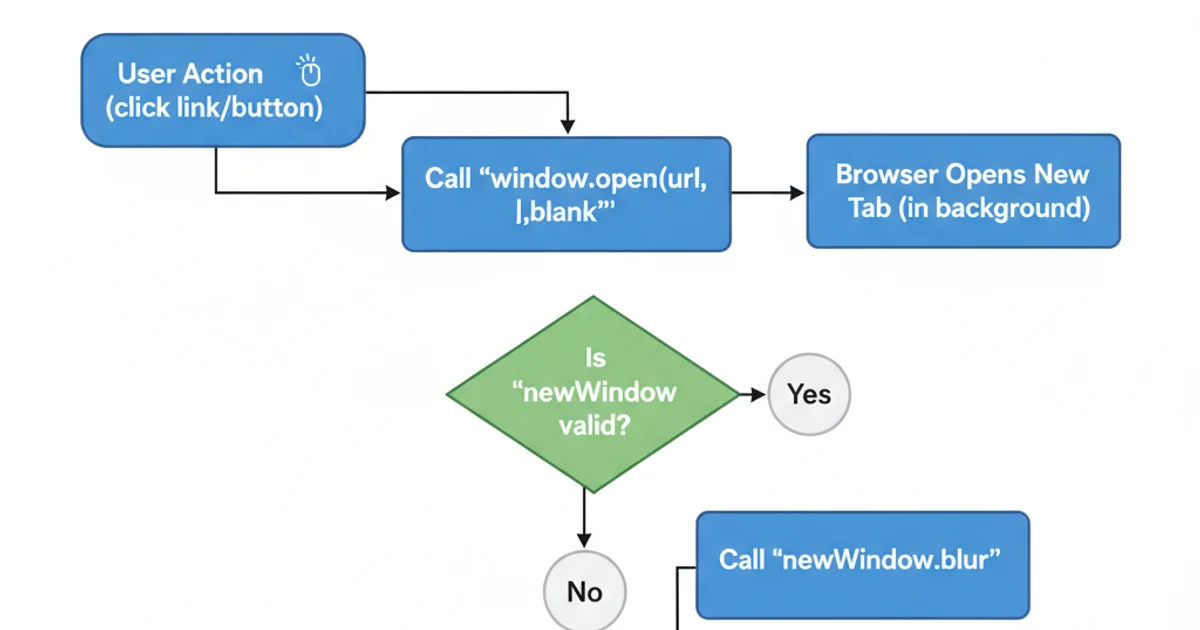
Workflow for opening a new tab while maintaining current tab focus.
Alternative: Using an Anchor Tag with target="_blank"
For scenarios where the new tab is opened as a direct result of a user click, using a standard HTML anchor tag with target="_blank" is often the most reliable and user-friendly method. Browsers are designed to handle these interactions gracefully, typically opening the new tab in the background without stealing focus, especially when the user explicitly clicks a link.
<a href="https://www.example.com" target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer">Open Example in New Tab</a>
HTML anchor tag for opening a new tab.
rel="noopener noreferrer" when using target="_blank" for security reasons. This prevents the newly opened page from having access to the window.opener property of your original page, mitigating potential phishing and performance attacks.Handling Asynchronous Operations and User Gestures
When opening tabs after an asynchronous operation (e.g., an AJAX request completes), it's crucial that the window.open() call is still considered a direct result of a user gesture. If window.open() is called too long after the initial user interaction, browsers might block it as a pop-up or force it into the foreground. The best practice is to initiate the window.open() call immediately on user interaction, even if the URL is a placeholder, and then update the URL later if needed (though this is less common for new tabs).
1. Step 1: Identify User Interaction
Ensure the window.open() call is directly triggered by a user event like a click or form submission.
2. Step 2: Use _blank Target
Pass '_blank' as the second argument to window.open() to instruct the browser to open a new tab.
3. Step 3: Attempt Focus Restoration
Immediately after window.open(), call newWindow.blur() on the returned window object and then window.focus() on the current window to try and restore focus.
4. Step 4: Consider HTML Anchor Tags
For simple link-based navigation, prefer <a target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer"> for better browser compatibility and user experience.