How many bytes is a gigabyte (GB)?
Categories:
Understanding a Gigabyte: How Many Bytes Are There?
Explore the precise definition of a gigabyte (GB), differentiate between binary and decimal interpretations, and understand its practical implications in computing and storage.
In the world of computing and digital storage, terms like 'megabyte,' 'gigabyte,' and 'terabyte' are thrown around constantly. While most people have a general idea that a gigabyte (GB) is a large unit of data, the exact number of bytes it represents can be a source of confusion. This article will clarify the precise definition of a gigabyte, explain the different interpretations, and illustrate why this distinction matters.
The Decimal vs. Binary Dilemma
The core of the confusion surrounding data unit sizes stems from two different systems of measurement: the decimal (base-10) system and the binary (base-2) system. Historically, computer scientists and engineers, working with binary systems, often used metric prefixes (kilo, mega, giga) to refer to powers of two that were close to the corresponding powers of ten. This led to an ambiguity that persists today.
flowchart TD
A[Data Unit Prefixes] --> B{Decimal (SI) vs. Binary (IEC)}
B --> C["Decimal (SI): Base 10"]
B --> D["Binary (IEC): Base 2"]
C --> C1["Kilobyte (KB) = 1,000 bytes"]
C --> C2["Megabyte (MB) = 1,000,000 bytes"]
C --> C3["Gigabyte (GB) = 1,000,000,000 bytes"]
D --> D1["Kibibyte (KiB) = 1,024 bytes"]
D --> D2["Mebibyte (MiB) = 1,024^2 bytes"]
D --> D3["Gibibyte (GiB) = 1,024^3 bytes"]
C3 --> E["Commonly used by storage manufacturers"]
D3 --> F["Commonly used by operating systems & software"]
E & F --> G[Discrepancy in reported storage sizes]Comparison of Decimal (SI) and Binary (IEC) Data Unit Prefixes
The Standard (Decimal) Definition
According to the International System of Units (SI), which is the modern form of the metric system, prefixes like kilo, mega, and giga represent powers of 10. This is the definition typically used by hard drive manufacturers and telecommunications companies.
1 Kilobyte (KB) = 10^3 bytes = 1,000 bytes
1 Megabyte (MB) = 10^6 bytes = 1,000,000 bytes
1 Gigabyte (GB) = 10^9 bytes = 1,000,000,000 bytes
1 Terabyte (TB) = 10^12 bytes = 1,000,000,000,000 bytes
Decimal (SI) definitions of data units
The Binary (IEC) Definition
Computers, at their fundamental level, operate using binary (base-2) numbers. Therefore, it's often more natural for software and operating systems to measure memory and storage in powers of two. To address the ambiguity, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) introduced new prefixes in 1998 for binary multiples: kibi (Ki), mebi (Mi), gibi (Gi), etc.
1 Kibibyte (KiB) = 2^10 bytes = 1,024 bytes
1 Mebibyte (MiB) = 2^20 bytes = 1,024 * 1,024 bytes = 1,048,576 bytes
1 Gibibyte (GiB) = 2^30 bytes = 1,024 * 1,024 * 1,024 bytes = 1,073,741,824 bytes
1 Tebibyte (TiB) = 2^40 bytes = 1,024^4 bytes = 1,099,511,627,776 bytes
Binary (IEC) definitions of data units
So, How Many Bytes is a Gigabyte?
The answer depends on the context:
- In the decimal (SI) system (used by manufacturers): A gigabyte (GB) is exactly 1,000,000,000 bytes.
- In the binary (IEC) system (used by operating systems, though often mislabeled): A gibibyte (GiB) is exactly 1,073,741,824 bytes. When your operating system reports 'GB', it's usually referring to gibibytes, not true gigabytes.
Therefore, a 1TB hard drive (1,000,000,000,000 bytes) will be reported by an operating system as approximately 0.909 TiB, or roughly 931 GiB (often displayed as 931 GB).
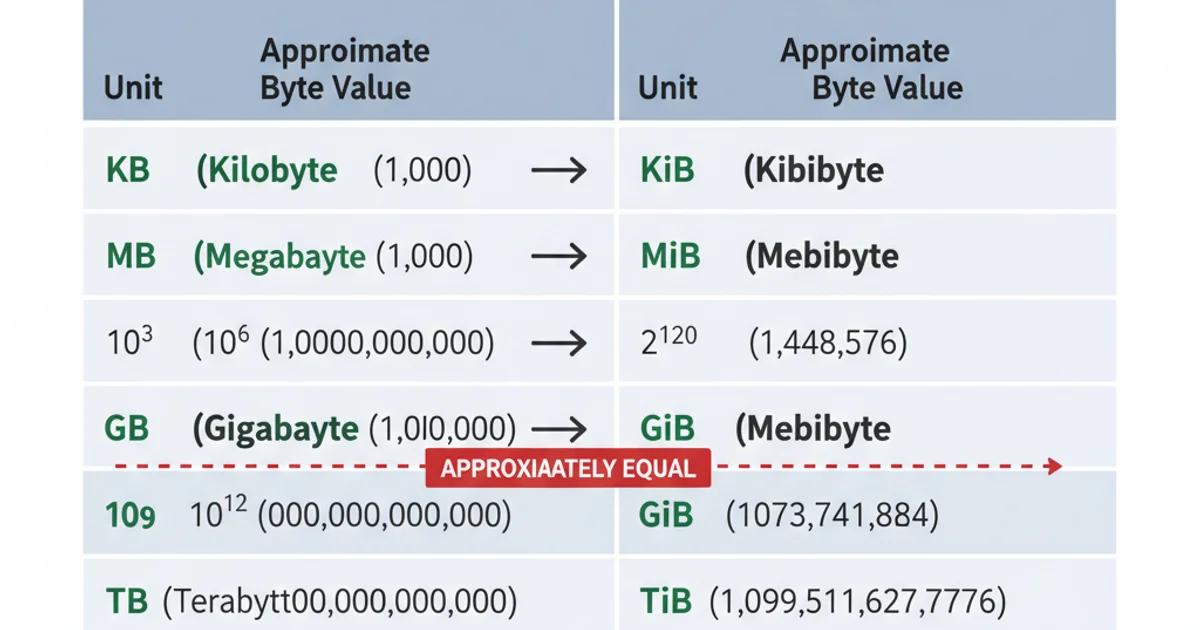
Decimal vs. Binary Data Unit Comparison