What are DDL and DML?
Understanding DDL and DML in SQL: The Language of Databases

Explore the fundamental differences and uses of Data Definition Language (DDL) and Data Manipulation Language (DML) in SQL, crucial for managing database structures and data.
SQL (Structured Query Language) is the standard language for managing and manipulating relational databases. Within SQL, operations are broadly categorized into several sub-languages, with Data Definition Language (DDL) and Data Manipulation Language (DML) being the most fundamental. Understanding the distinction between DDL and DML is crucial for anyone working with databases, as it clarifies how you interact with both the structure (schema) and the content (data) of your database.
What is Data Definition Language (DDL)?
Data Definition Language (DDL) commands are used to define, modify, and delete database objects like tables, indexes, views, sequences, and stored procedures. These commands deal with the database schema rather than the data itself. DDL operations are typically auto-committed, meaning changes are permanently saved to the database immediately after execution and cannot be rolled back.
flowchart TD
A[DDL Commands] --> B{Database Schema Management}
B --> C[CREATE: Define new objects]
B --> D[ALTER: Modify existing objects]
B --> E[DROP: Delete objects]
B --> F[TRUNCATE: Remove all records from a table]
B --> G[RENAME: Change object names]
C --> H[CREATE TABLE, INDEX, VIEW]
D --> I[ALTER TABLE ADD COLUMN]
E --> J[DROP TABLE, INDEX]
F --> K[TRUNCATE TABLE]
G --> L[RENAME TABLE]Flowchart illustrating common DDL commands and their functions.
Key DDL commands include:
CREATE TABLE Employees (
EmployeeID INT PRIMARY KEY,
FirstName VARCHAR(50),
LastName VARCHAR(50),
DepartmentID INT
);
ALTER TABLE Employees
ADD Email VARCHAR(100);
DROP TABLE Employees;
TRUNCATE TABLE AuditLogs;
Examples of DDL commands: CREATE, ALTER, DROP, and TRUNCATE.
ROLLBACK statement. Always exercise caution when performing DDL operations, especially in production environments.What is Data Manipulation Language (DML)?
Data Manipulation Language (DML) commands are used for managing data within schema objects. These commands allow you to retrieve, insert, update, and delete records in a database. Unlike DDL, DML operations are not auto-committed and can be rolled back if necessary, providing a safety net for data changes.
flowchart TD
A[DML Commands] --> B{Data Management within Objects}
B --> C[SELECT: Retrieve data]
B --> D[INSERT: Add new data]
B --> E[UPDATE: Modify existing data]
B --> F[DELETE: Remove data]
C --> G[SELECT * FROM Users]
D --> H[INSERT INTO Products VALUES (...)]
E --> I[UPDATE Orders SET Status = 'Shipped']
F --> J[DELETE FROM Customers WHERE ID = 101]Flowchart illustrating common DML commands and their functions.
Key DML commands include:
INSERT INTO Employees (EmployeeID, FirstName, LastName, DepartmentID)
VALUES (1, 'John', 'Doe', 101);
SELECT FirstName, LastName FROM Employees WHERE DepartmentID = 101;
UPDATE Employees
SET Email = 'john.doe@example.com'
WHERE EmployeeID = 1;
DELETE FROM Employees
WHERE EmployeeID = 1;
Examples of DML commands: INSERT, SELECT, UPDATE, and DELETE.
DDL vs. DML: A Quick Comparison
The primary distinction lies in their scope: DDL affects the database structure, while DML affects the data stored within that structure. Think of DDL as building or modifying the house (the database schema), and DML as furnishing, arranging, or removing items within that house (the data).
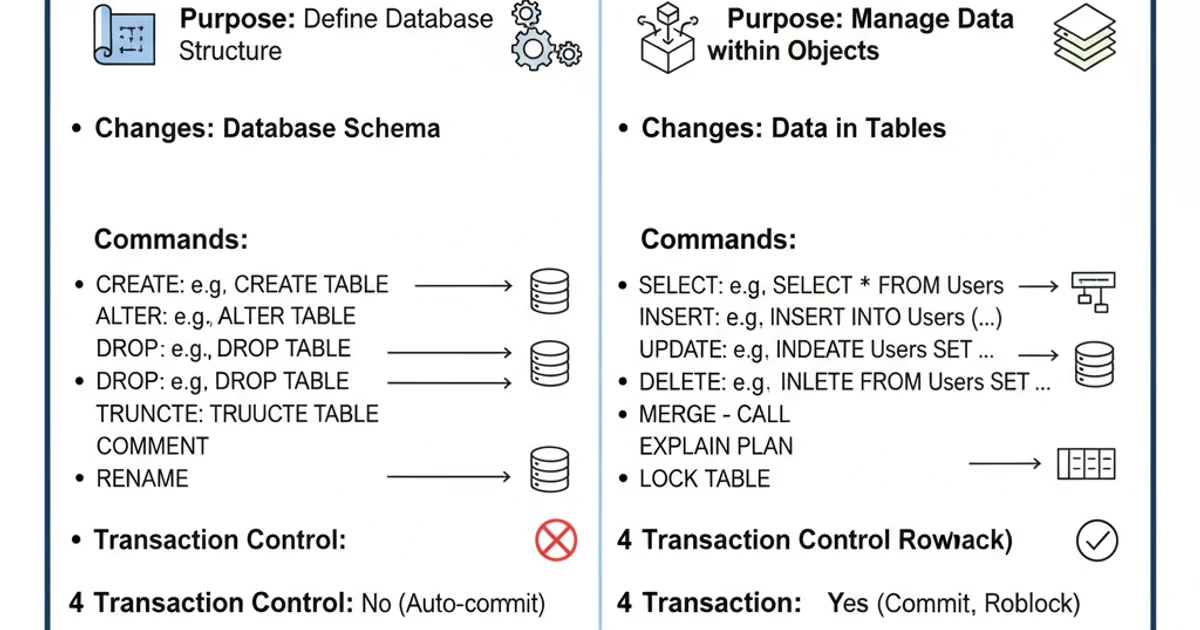
Key differences between DDL and DML.
Understanding these two categories is fundamental for effective database management and development. DDL provides the framework, and DML populates and interacts with the data within that framework.