how to read a fasta file in python?
Categories:
Mastering FASTA File Parsing in Python
Learn various techniques to efficiently read and parse FASTA files in Python, from basic line-by-line processing to using specialized bioinformatics libraries.
FASTA is a text-based format for representing nucleotide or peptide sequences, in which nucleotides or amino acids are represented using single-letter codes. It's a fundamental format in bioinformatics, and being able to read and parse these files efficiently in Python is a crucial skill. This article will guide you through different methods, from manual parsing to leveraging powerful libraries, ensuring you can handle FASTA data effectively.
Understanding the FASTA Format
Before diving into parsing, it's essential to understand the structure of a FASTA file. Each sequence in a FASTA file begins with a single-line description, or header, starting with a '>' (greater-than) symbol. This header can contain information like the sequence identifier, name, and other relevant details. Subsequent lines contain the actual sequence data. The sequence can be broken into multiple lines, and there are no fixed line lengths, though 60-80 characters per line is common.
flowchart TD
A[Start] --> B{Read Line}
B --'>' Symbol--> C[Header Line]
C --> D{Store Header}
B --'No >' Symbol--> E[Sequence Line]
E --> F{Append to Current Sequence}
F --> B
D --> B
B --'End of File'--> G[End]Basic FASTA file parsing logic
Method 1: Manual Parsing with Basic Python
For smaller FASTA files or when you want full control, manual parsing using Python's built-in file I/O is a straightforward approach. This involves iterating through the file line by line, identifying header lines, and accumulating sequence data until the next header or the end of the file is reached.
def parse_fasta_manual(filepath):
sequences = {}
current_sequence_id = None
current_sequence_data = []
with open(filepath, 'r') as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
if not line: # Skip empty lines
continue
if line.startswith('>'):
if current_sequence_id and current_sequence_data:
sequences[current_sequence_id] = ''.join(current_sequence_data)
current_sequence_id = line[1:].split(' ')[0] # Get ID, ignore description
current_sequence_data = []
else:
current_sequence_data.append(line)
# Add the last sequence after the loop finishes
if current_sequence_id and current_sequence_data:
sequences[current_sequence_id] = ''.join(current_sequence_data)
return sequences
# Example usage:
# with open('example.fasta', 'w') as f:
# f.write('>seq1 description one\nATGCATGC\nGCATGCAT\n>seq2 description two\nCGTACGTA\nGTACGTAG\n')
#
# fasta_data = parse_fasta_manual('example.fasta')
# print(fasta_data)
# # Expected output: {'seq1': 'ATGCATGCGCATGCAT', 'seq2': 'CGTACGTAGTACGTAG'}
Python function for manual FASTA file parsing.
line.strip()) to avoid issues with leading/trailing spaces or newline characters. Also, handle the last sequence in the file, as it won't be added until the loop finishes.Method 2: Using Biopython's SeqIO Module
For robust and efficient handling of biological sequences, the Biopython library is the de facto standard in Python. Its SeqIO module provides a powerful and convenient way to parse various sequence file formats, including FASTA. It handles many edge cases and provides SeqRecord objects, which encapsulate sequence data along with metadata.
from Bio import SeqIO
def parse_fasta_biopython(filepath):
sequences = {}
for record in SeqIO.parse(filepath, "fasta"):
sequences[record.id] = str(record.seq)
return sequences
# Example usage:
# # Assuming 'example.fasta' exists with content from previous example
# fasta_data_biopython = parse_fasta_biopython('example.fasta')
# print(fasta_data_biopython)
# # Expected output: {'seq1': 'ATGCATGCGCATGCAT', 'seq2': 'CGTACGTAGTACGTAG'}
Parsing FASTA files using Biopython's SeqIO module.
pip install biopython. The SeqIO.parse() function is a generator, which is memory-efficient for large files as it yields one record at a time.Choosing the Right Method
The best method depends on your specific needs:
- Manual Parsing: Ideal for small, simple FASTA files, learning purposes, or when you need highly customized parsing logic without external dependencies.
- Biopython's SeqIO: Recommended for most bioinformatics tasks. It's robust, well-tested, handles various edge cases (like wrapped sequences, different header formats), and provides rich
SeqRecordobjects for further analysis. It's also highly efficient for large files due to its generator-based approach.
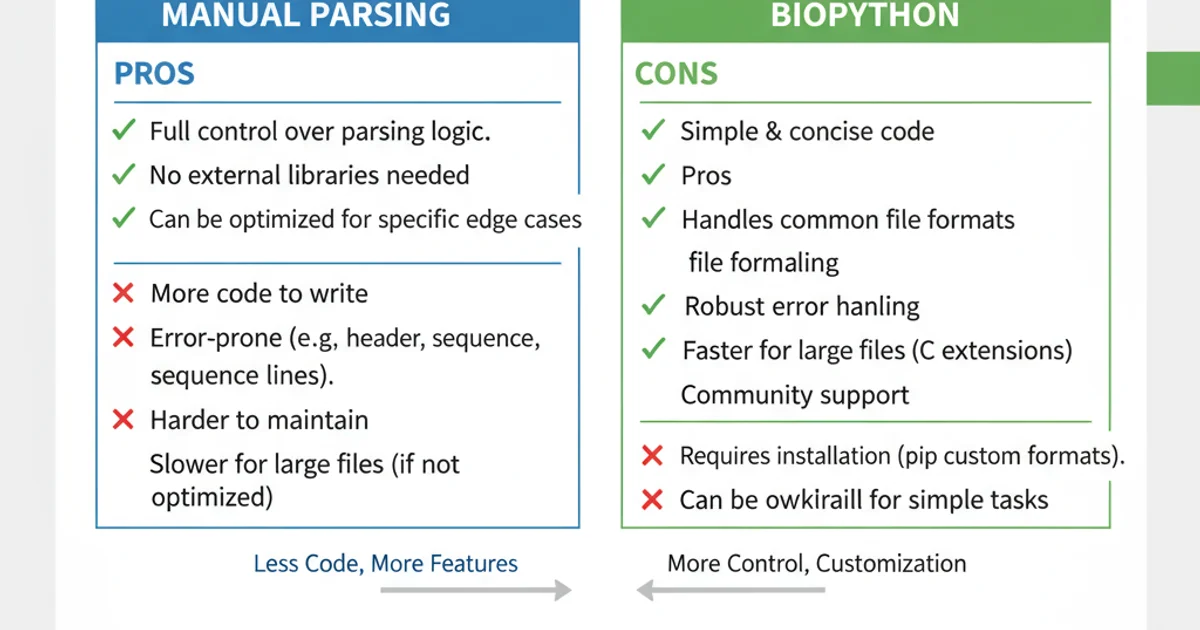
Comparison of manual parsing vs. Biopython for FASTA files.
Both methods provide effective ways to read FASTA files in Python. For general bioinformatics work, Biopython is the preferred tool due to its comprehensive features and reliability. However, understanding manual parsing provides valuable insight into file formats and basic programming concepts.