Can I see SSL Certificate from browser developer tools
Categories:
How to View SSL Certificates in Your Browser's Developer Tools
Learn how to inspect SSL/TLS certificates directly from your web browser, understand their key details, and verify website security.
When you visit a website over HTTPS, your browser establishes a secure connection using an SSL/TLS certificate. This certificate verifies the identity of the website and encrypts the communication between your browser and the server. As a developer, security professional, or even a curious user, you might often need to inspect these certificates to check their validity, issuer, expiration date, or other critical details. Fortunately, all modern web browsers provide built-in developer tools that make this process straightforward.
Why Inspect SSL Certificates?
Inspecting an SSL certificate can be crucial for several reasons:
- Verify Authenticity: Ensure you are connecting to the legitimate website and not a phishing site.
- Check Expiration: Certificates expire, and an expired certificate can lead to security warnings and service interruptions.
- Understand Trust Chain: See the Certificate Authority (CA) that issued the certificate and the entire chain of trust.
- Debug Issues: Identify problems with certificate installation, misconfigurations, or mixed content warnings.
- Security Audits: For developers and security professionals, examining certificate details is a routine part of security audits and vulnerability assessments.
flowchart TD
A[User Navigates to HTTPS Site] --> B{Browser Initiates TLS Handshake}
B --> C[Server Sends SSL Certificate]
C --> D{Browser Validates Certificate?}
D -- Yes --> E[Secure Connection Established]
D -- No --> F[Security Warning Displayed]
E --> G[User Inspects Certificate via DevTools]Simplified flow of SSL certificate validation and inspection.
Accessing Certificate Details in Popular Browsers
While the exact steps might vary slightly between browsers, the general principle remains the same: look for the padlock icon in the address bar.
1. Google Chrome
- Click the Padlock Icon: In the address bar, click the padlock icon to the left of the URL.
- Select 'Connection is secure': A small pop-up will appear. Click on 'Connection is secure'.
- View Certificate: Click on 'Certificate is valid' (or 'Certificate is invalid' if there's an issue). This will open the certificate viewer, showing details like issuer, validity period, and subject.
2. Mozilla Firefox
- Click the Padlock Icon: Similar to Chrome, click the padlock icon in the address bar.
- Select 'Connection secure': A panel will drop down. Click on 'Connection secure'.
- More Information: Click 'More information...' at the bottom of the panel.
- View Certificate: In the new 'Page Info' window, go to the 'Security' tab and click 'View Certificate'.
3. Microsoft Edge
- Click the Padlock Icon: Click the padlock icon in the address bar.
- Select 'Connection is secure': A small pop-up will appear. Click on 'Connection is secure'.
- View Certificate: Click on 'Show certificate'. This will display the certificate details.
4. Apple Safari
- Enable Developer Menu: If not already enabled, go to Safari > Preferences > Advanced and check 'Show Develop menu in menu bar'.
- Open Web Inspector: Go to Develop > Show Web Inspector (or press Option + Command + I).
- Navigate to Security Tab: In the Web Inspector, select the 'Security' tab.
- View Certificate: You will see details about the certificate, including the issuer and validity. Click 'View Certificate' for more comprehensive information.
Understanding Certificate Details
Once you open the certificate viewer, you'll typically see several tabs or sections:
- General/Summary: Provides a high-level overview, including the certificate's purpose, validity period (from/to dates), and the subject (the website it's issued for).
- Details: This is the most comprehensive section, listing all the fields within the certificate. Key fields include:
- Subject: The domain name(s) the certificate is issued for (e.g.,
Common Name,Subject Alternative Names). - Issuer: The Certificate Authority (CA) that issued the certificate.
- Serial Number: A unique identifier for the certificate.
- Public Key: Information about the cryptographic key used.
- Signature Algorithm: The algorithm used to sign the certificate.
- Thumbprint/Fingerprint: A hash of the certificate, often used for quick identification.
- Subject: The domain name(s) the certificate is issued for (e.g.,
- Certification Path/Trust Chain: Shows the hierarchy of certificates, from the website's certificate up to the root CA certificate. This chain establishes trust.
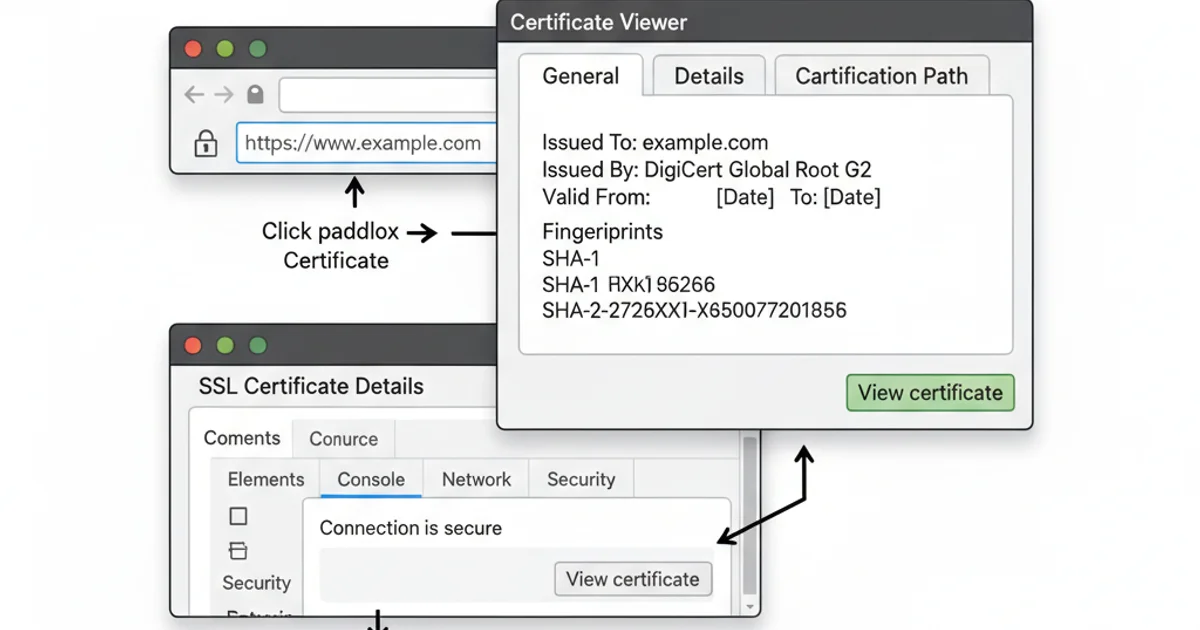
Example of a certificate viewer showing detailed information.
Inspecting SSL certificates is a fundamental skill for anyone interacting with the web, providing transparency and control over your online security. By understanding how to access and interpret these details, you can make informed decisions about the trustworthiness of the websites you visit.