Using a backslash (%5c) in a REST WCF URL
Categories:
Handling Backslashes in WCF REST URLs: A Practical Guide
Discover how to correctly configure WCF REST services to accept and process URLs containing backslashes, a common challenge due to URI parsing rules.
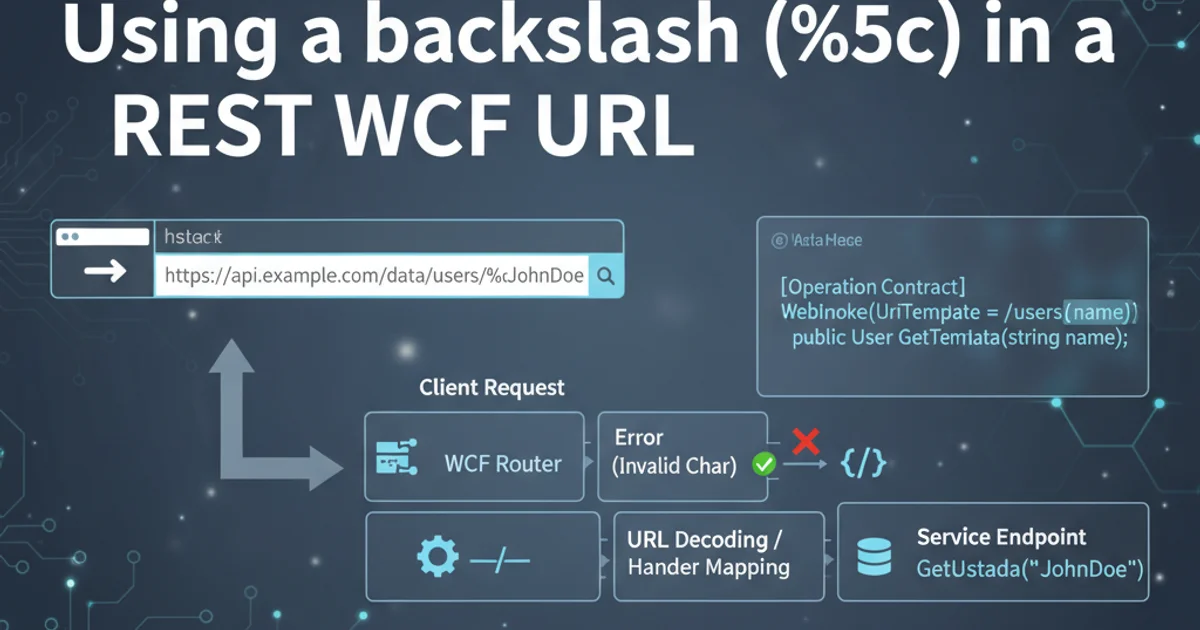
When developing WCF REST services, you might encounter scenarios where your URL paths need to include special characters, such as the backslash (\). While the backslash is a reserved character in URIs (often used as a path segment separator in Windows file paths), it's not directly supported in standard URI paths. This article will guide you through the necessary configurations and considerations to successfully use backslashes (encoded as %5c) within your WCF REST service URLs.
Understanding URI Encoding and WCF Defaults
URIs (Uniform Resource Identifiers) have strict rules for character sets. The backslash character (\) is not a valid character in the path segment of a URI according to RFC 3986. Browsers and HTTP clients typically encode it as %5c. However, WCF's default URI parsing mechanism is often configured to reject such encoded characters for security and compliance reasons, leading to 400 Bad Request errors or unexpected routing issues.
sequenceDiagram
participant Client
participant WCFService
Client->>WCFService: GET /api/resource/path%5cwith%5cbackslash
WCFService-->>Client: HTTP 400 Bad Request (Default behavior)
Note right of WCFService: WCF rejects encoded backslash by default
Client->>WCFService: GET /api/resource/path%5cwith%5cbackslash (After config change)
WCFService-->>Client: HTTP 200 OK (Configured behavior)
Note right of WCFService: WCF accepts encoded backslash after configurationSequence diagram illustrating WCF's default and configured behavior with encoded backslashes.
Configuring WCF to Accept Encoded Backslashes
To allow WCF to correctly parse URLs containing encoded backslashes, you need to modify the httpRuntime section in your web.config file. Specifically, you must set relaxedUrlToFileSystemMapping to true and requestPathInvalidCharacters to remove the backslash character. Additionally, for .NET 4.0 and above, you might need to configure uri settings to allow unescaped backslashes.
<configuration>
<system.web>
<httpRuntime relaxedUrlToFileSystemMapping="true" requestPathInvalidCharacters="<,>,*,%,&,\" />
</system.web>
<system.uri>
<schemeSettings>
<add name="http" genericUriParserOptions="DontUnescapePathDotsAndSlashes" />
<add name="https" genericUriParserOptions="DontUnescapePathDotsAndSlashes" />
</schemeSettings>
</system.uri>
<system.serviceModel>
<serviceHostingEnvironment multipleSiteBindingsEnabled="true" />
<standardEndpoints>
<webHttpEndpoint>
<standardEndpoint name="webHttp" helpEnabled="true" automaticFormatSelectionEnabled="true" />
</webHttpEndpoint>
</standardEndpoints>
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>
Web.config configuration to allow encoded backslashes in WCF REST URLs.
relaxedUrlToFileSystemMapping="true" and modifying requestPathInvalidCharacters can potentially expose your application to security vulnerabilities if not handled carefully. Ensure that your application logic properly validates and sanitizes all input from the URL to prevent path traversal or other attacks.Implementing the WCF Service Contract
Once the configuration is in place, your WCF service contract needs to define the URI template to match the expected path. You can use a wildcard (*) to capture the remaining path segments, which will include the encoded backslashes. WCF will then pass the full, unescaped path to your service method.
using System.ServiceModel;
using System.ServiceModel.Web;
[ServiceContract]
public interface IMyService
{
[OperationContract]
[WebGet(UriTemplate = "resource/{*path}")]
string GetDataWithPath(string path);
}
public class MyService : IMyService
{
public string GetDataWithPath(string path)
{
// 'path' will contain the unescaped backslashes (e.g., "folder\subfolder\file.txt")
return $"Received path: {path}";
}
}
WCF Service Contract and implementation to handle paths with backslashes.
{*path} in your UriTemplate, the path parameter in your service method will receive the entire remaining part of the URL, including any backslashes, already unescaped. You do not need to manually decode %5c.1. Step 1: Modify web.config
Add or update the <httpRuntime> and <system.uri> sections in your web.config file as shown in the example above to relax URL parsing rules and allow encoded backslashes.
2. Step 2: Define Service Contract
Create your WCF service interface ([ServiceContract]) and define an operation ([OperationContract]) with WebGet or WebInvoke and a UriTemplate that uses a wildcard ({*path}) to capture the dynamic path segment.
3. Step 3: Implement Service Logic
Implement the service method, which will receive the full path string. Remember to implement robust validation and sanitization for the received path to mitigate security risks.
4. Step 4: Test Your Service
Deploy your WCF service and test it using a client that sends requests with encoded backslashes (e.g., /api/resource/folder%5csubfolder/file.txt). Verify that the service correctly processes the request and returns the expected response.