What is the difference between JDK and JRE?
Categories:
Understanding JDK vs. JRE: The Core of Java Development

Explore the fundamental differences between the Java Development Kit (JDK) and the Java Runtime Environment (JRE), and learn when to use each for your Java projects.
Java is one of the most popular programming languages in the world, powering everything from enterprise applications to mobile devices. If you're working with Java, you'll frequently encounter the terms JDK and JRE. While often used interchangeably by beginners, they serve distinct purposes in the Java ecosystem. Understanding their differences is crucial for setting up your development environment correctly and deploying Java applications efficiently.
What is JRE (Java Runtime Environment)?
The Java Runtime Environment (JRE) is a software package that provides the minimum requirements for executing a Java application. If you only want to run Java programs and not develop them, the JRE is all you need. It includes the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), core classes, and supporting files. Think of it as the 'player' for Java applications.
flowchart TD
A[Java Application] --> B[JRE]
B --> C[JVM]
B --> D[Java Class Libraries]
C --> E[Operating System]
D --> EComponents of the Java Runtime Environment (JRE)
Key components of the JRE include:
- Java Virtual Machine (JVM): This is the heart of the Java platform. It's an abstract machine that provides a runtime environment in which Java bytecode can be executed. The JVM is responsible for interpreting the bytecode and translating it into machine-specific instructions.
- Java Class Libraries: These are a set of standard classes that Java applications can use. They provide fundamental functionalities like I/O operations, networking, data structures, and more.
- Supporting Files: These include property files, resource files, and other JAR files required by the class libraries.
What is JDK (Java Development Kit)?
The Java Development Kit (JDK) is a superset of the JRE. It contains everything in the JRE, plus development tools like the compiler (javac), debugger (jdb), archiver (jar), and documentation generator (javadoc). The JDK is essential for Java developers who need to write, compile, and debug Java applications. It's the 'toolbox' for creating Java software.
flowchart TD
A[JDK] --> B[JRE]
A --> C[Development Tools]
B --> D[JVM]
B --> E[Java Class Libraries]
C --> F[Compiler (javac)]
C --> G[Debugger (jdb)]
C --> H[Archiver (jar)]
C --> I[Documentation Tool (javadoc)]Components of the Java Development Kit (JDK)
Key components unique to the JDK include:
- Compiler (
javac): Translates Java source code (.javafiles) into Java bytecode (.classfiles). - Debugger (
jdb): Helps developers find and fix errors in their Java programs. - Archiver (
jar): Packages related class files and associated metadata into a single JAR (Java Archive) file. - Documentation Generator (
javadoc): Generates API documentation in HTML format from source code comments. - Other Utilities: Includes tools for monitoring, profiling, and managing Java applications.
Key Differences and Use Cases
The primary distinction between JDK and JRE lies in their purpose. The JDK is for developing Java applications, while the JRE is for running them. This fundamental difference dictates when and where each should be used.
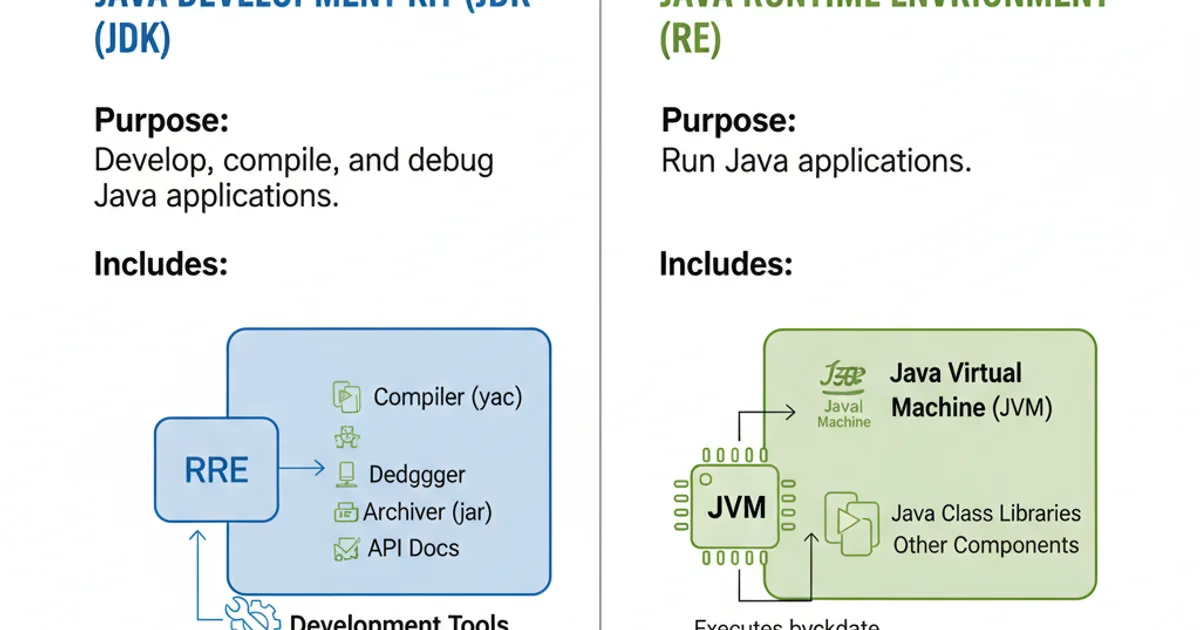
Comparison of JDK and JRE
Here's a summary of their differences:
| Feature | JDK (Java Development Kit) | JRE (Java Runtime Environment) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Develop, compile, debug, and run Java applications | Run Java applications only |
| Includes | JRE + Development Tools (compiler, debugger, etc.) | JVM + Java Class Libraries + Supporting Files |
| Target User | Java Developers | End-users who need to run Java applications |
| Size | Larger (contains JRE and development tools) | Smaller (contains only runtime components) |
| Example | Writing a new Java program, building a web application | Running a Java-based game, using a Java desktop app |
Choosing the Right One
The choice between JDK and JRE is straightforward:
- Choose JDK if you are a Java developer, or if you plan to write, compile, or debug Java code. This is the standard choice for anyone actively involved in Java programming.
- Choose JRE if you are an end-user who only needs to execute Java applications and has no intention of developing them. Installing only the JRE saves disk space and reduces potential security attack surfaces by not including unnecessary development tools.
jlink) to minimize the footprint and improve security.