Convert string "Jun 1 2005 1:33PM" into datetime
Categories:
Converting String to Datetime in Python: A Comprehensive Guide

Learn how to parse date and time strings into Python datetime objects using the datetime module, handling various formats and potential errors.
Working with dates and times is a fundamental aspect of many programming tasks. In Python, the datetime module provides powerful tools for handling date and time objects. A common requirement is to convert a date and time represented as a string into a datetime object, allowing for calculations, formatting, and comparisons. This article will guide you through the process, focusing on the strptime() method, and demonstrate how to handle a specific format like "Jun 1 2005 1:33PM".
Understanding datetime.strptime()
The datetime.strptime() method (string parse time) is your primary tool for converting strings to datetime objects. It takes two main arguments: the date/time string you want to parse, and a format code string that tells Python how to interpret the input string. The format codes are crucial for successful parsing, as they define the exact structure of your date and time components.
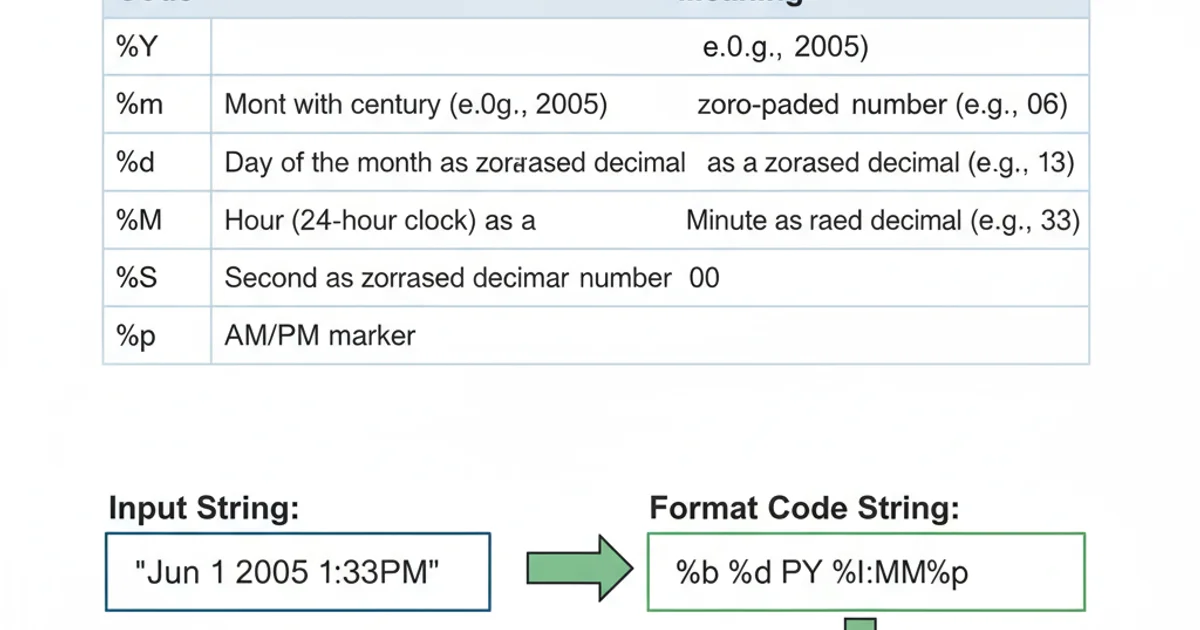
Parsing the String "Jun 1 2005 1:33PM"
Let's break down the specific string "Jun 1 2005 1:33PM" and identify the corresponding format codes needed for strptime().
flowchart TD
A["Input String: 'Jun 1 2005 1:33PM'"] --> B{"Identify Components"}
B --> C["Month Abbreviation: 'Jun' -> %b"]
B --> D["Day of Month: '1' -> %d"]
B --> E["Year: '2005' -> %Y"]
B --> F["Hour (12-hour): '1' -> %I"]
B --> G["Minute: '33' -> %M"]
B --> H["AM/PM Indicator: 'PM' -> %p"]
C & D & E & F & G & H --> I["Construct Format String: '%b %d %Y %I:%M%p'"]
I --> J["Call `datetime.strptime(input_string, format_string)`"]
J --> K["Output: datetime object"]
K --> L["Example: datetime(2005, 6, 1, 13, 33)"]Process for converting a specific date string to a datetime object.
Based on the breakdown, the format string will be "%b %d %Y %I:%M%p". Let's see this in action with a Python code example.
from datetime import datetime
date_string = "Jun 1 2005 1:33PM"
format_string = "%b %d %Y %I:%M%p"
try:
datetime_object = datetime.strptime(date_string, format_string)
print(f"Original string: {date_string}")
print(f"Converted datetime object: {datetime_object}")
print(f"Type of object: {type(datetime_object)}")
except ValueError as e:
print(f"Error converting string to datetime: {e}")
# Example of accessing components
print(f"Year: {datetime_object.year}")
print(f"Month: {datetime_object.month}")
print(f"Day: {datetime_object.day}")
print(f"Hour: {datetime_object.hour}") # Note: %I converts to 24-hour format internally
print(f"Minute: {datetime_object.minute}")
Python code to convert the string "Jun 1 2005 1:33PM" to a datetime object.
The output demonstrates that the string is successfully parsed into a datetime object. Notice how 1:33PM is correctly converted to 13:33 in the 24-hour format within the datetime object.
Common Format Codes
Here's a quick reference for some of the most commonly used format codes:
Essential strptime() Format Codes
%b for month abbreviation) can be locale-dependent. If your application needs to handle dates from various locales, consider using locale.setlocale() or more robust parsing libraries.Handling Errors and Variations
It's good practice to wrap your strptime() calls in a try-except block to gracefully handle ValueError exceptions that occur if the string does not match the specified format. If you encounter multiple possible date formats, you might need to try parsing with several format strings sequentially.
from datetime import datetime
def parse_date_string(date_str):
formats = [
"%b %d %Y %I:%M%p", # e.g., Jun 1 2005 1:33PM
"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", # e.g., 2023-10-27 14:30:00
"%m/%d/%Y %H:%M", # e.g., 10/27/2023 14:30
]
for fmt in formats:
try:
return datetime.strptime(date_str, fmt)
except ValueError:
continue
raise ValueError(f"Unable to parse date string '{date_str}' with any known format.")
# Test cases
print(parse_date_string("Jun 1 2005 1:33PM"))
print(parse_date_string("2023-10-27 14:30:00"))
print(parse_date_string("10/27/2023 14:30"))
try:
parse_date_string("Invalid Date String")
except ValueError as e:
print(e)
Handling multiple date formats with a fallback mechanism.