When to use JavaScript template engines?
Categories:
When to Use JavaScript Template Engines: A Comprehensive Guide

Explore the benefits, use cases, and considerations for integrating JavaScript template engines into your web development workflow, focusing on separation of concerns and performance.
JavaScript template engines are powerful tools that allow developers to generate dynamic HTML content on the client-side or server-side. They separate presentation logic from application logic, making code more maintainable, readable, and reusable. While modern frameworks often include their own templating solutions, understanding standalone template engines is crucial for projects with specific needs, legacy systems, or when building lightweight applications without a full-fledged framework.
The Core Purpose of Template Engines: Separation of Concerns
At its heart, a template engine addresses the 'separation of concerns' principle. This means keeping your HTML structure (presentation) distinct from your JavaScript data manipulation (logic). Without a template engine, you might find yourself concatenating strings of HTML within your JavaScript code, leading to unreadable, error-prone, and difficult-to-maintain applications. Template engines provide a syntax, often resembling HTML with special directives, to embed data placeholders and control structures (like loops and conditionals) directly into your markup.
flowchart TD
A[Data Source (e.g., API)] --> B{JavaScript Logic}
B --> C[Data Object]
C --> D[Template Engine]
D --> E[HTML Template]
E --> F[Rendered HTML]
F --> G[Browser Display]Workflow of a JavaScript Template Engine
function renderUserList(users) {
let html = '<ul>';
for (const user of users) {
html += '<li>' + user.name + ' (Age: ' + user.age + ')</li>';
}
html += '</ul>';
return html;
}
// With a hypothetical template engine (e.g., Handlebars-like syntax)
// Template: `<ul>{{#each users}}<li>{{this.name}} (Age: {{this.age}})</li>{{/each}}</ul>`
// Engine.render(template, { users: users });
Comparing manual HTML string concatenation vs. a template engine's approach
Key Scenarios for Using Template Engines
While modern JavaScript frameworks like React, Vue, and Angular come with their own component-based rendering mechanisms that often abstract away traditional templating, there are still several compelling reasons and scenarios where standalone template engines shine:
1. Server-Side Rendering (SSR) for SEO and Performance
When building applications that require strong SEO or faster initial page loads, template engines can render the initial HTML on the server. This sends fully formed HTML to the browser, which search engines can easily crawl and users can see immediately, improving perceived performance.
2. Legacy Application Modernization
For older applications that rely heavily on server-side languages for HTML generation, introducing a client-side template engine can be a gradual step towards modernization without a full rewrite. It allows for dynamic updates to parts of the page without full reloads.
3. Lightweight Client-Side Applications
For smaller, less complex applications or widgets where the overhead of a full-fledged framework is unnecessary, a lightweight template engine can provide efficient dynamic content generation without the added bundle size and complexity.
4. Email Templating and Static Site Generation
Beyond web applications, template engines are excellent for generating dynamic email content, reports, or even static websites from data sources, ensuring consistency and reducing manual effort.
5. Micro-frontends and Component Libraries
In a micro-frontend architecture, different teams might use different technologies. A common template engine can serve as a shared rendering layer for certain components or sections, promoting consistency across disparate tech stacks.
Potential Pitfalls: Memory Leaks and Performance
While beneficial, template engines are not without their considerations. Improper use, especially in client-side rendering, can lead to performance issues or memory leaks. Repeatedly rendering large templates or failing to properly clean up DOM elements can consume excessive memory. It's crucial to optimize data binding, use efficient rendering techniques, and understand the lifecycle of your rendered content.
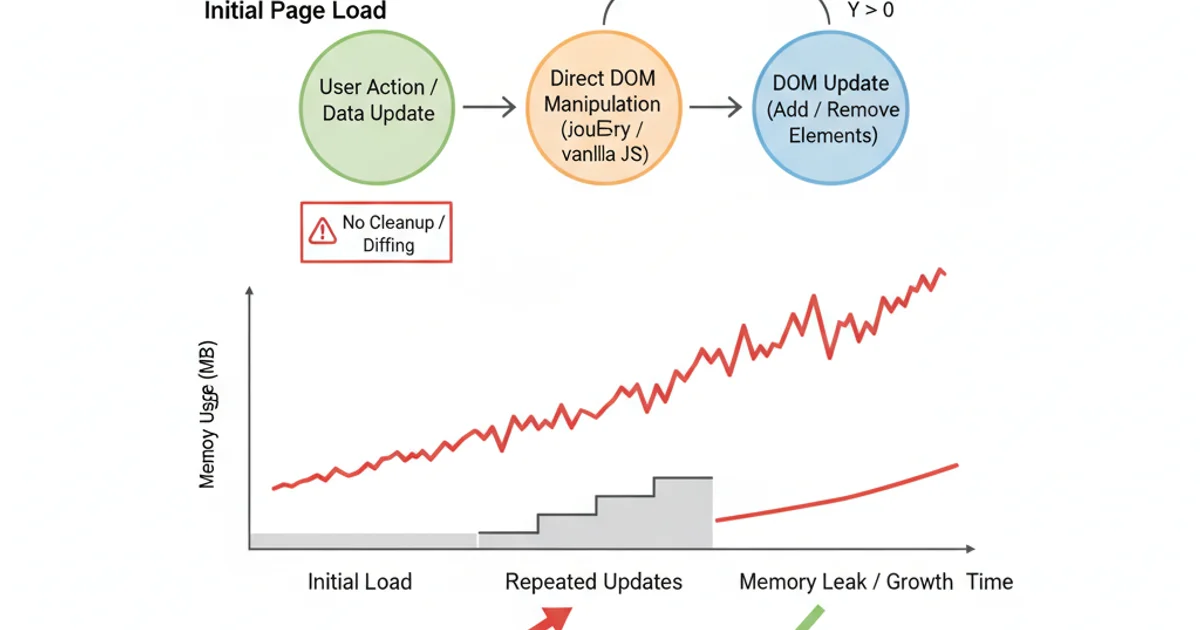
Unoptimized DOM manipulation can lead to memory leaks.
// Example of potential memory leak if not managed carefully
const container = document.getElementById('app');
function renderLoop() {
// Imagine a template engine rendering a complex list here
// If old elements are not removed or replaced efficiently,
// and event listeners are not detached, memory can accumulate.
container.innerHTML = someTemplateEngine.render(template, data);
// If event listeners were attached to previous elements, they might still be in memory
// even if the elements are no longer in the DOM.
}
// To mitigate, ensure proper cleanup or use frameworks that handle this automatically.
// e.g., container.innerHTML = ''; before new content, or using a virtual DOM approach.
Illustrating a scenario where memory leaks can occur with improper DOM updates.