How to get infinite scroll to work?
Categories:
Mastering Infinite Scroll: A Comprehensive Guide

Learn how to implement infinite scrolling efficiently using JavaScript and jQuery to enhance user experience on dynamic web pages.
Infinite scroll, also known as endless scroll, is a web design technique that loads content continuously as the user scrolls down the page, eliminating the need for pagination. This approach is widely adopted by social media platforms and news sites to keep users engaged and provide a seamless browsing experience. This article will guide you through the core concepts and practical implementation of infinite scroll using JavaScript and jQuery.
Understanding the Core Mechanism
The fundamental idea behind infinite scroll is to detect when the user has scrolled near the bottom of the page and then trigger an AJAX request to fetch more content. Once the new content is received, it's appended to the existing content on the page. This process repeats as the user continues to scroll, creating the illusion of an endlessly loading page.
flowchart TD
A[User Scrolls Down] --> B{Is User Near Bottom?}
B -->|No| A
B -->|Yes| C[Trigger AJAX Request]
C --> D[Fetch More Content]
D --> E[Append Content to Page]
E --> F[Update Scroll Position/State]
F --> AFlowchart illustrating the infinite scroll mechanism.
Implementing Infinite Scroll with jQuery
jQuery simplifies DOM manipulation and AJAX requests, making it a popular choice for implementing infinite scroll. The key steps involve listening for the scroll event on the window object, calculating the user's scroll position relative to the document height, and then making an AJAX call if the threshold is met. It's crucial to manage a 'loading' state to prevent multiple simultaneous AJAX requests.
$(window).scroll(function() {
if ($(window).scrollTop() + $(window).height() >= $(document).height() - 100 && !isLoading) {
isLoading = true;
$('#loading-indicator').show();
$.ajax({
url: 'load_more.php',
type: 'GET',
data: { page: currentPage },
success: function(response) {
if (response) {
$('#content-container').append(response);
currentPage++;
} else {
// No more content to load
$(window).off('scroll'); // Disable further scrolling
}
},
complete: function() {
isLoading = false;
$('#loading-indicator').hide();
}
});
}
});
let currentPage = 1;
let isLoading = false;
Best Practices and Considerations
While infinite scroll can be highly effective, it's important to implement it thoughtfully. Consider the following best practices:
- Performance: Optimize your AJAX requests and server-side content generation to ensure quick load times. Large DOM trees can impact performance.
- SEO: Ensure that search engines can still crawl all your content. Server-side rendering or providing a fallback pagination option can help.
- User Experience: Provide a clear 'back to top' button for long pages. Also, consider if infinite scroll is appropriate for all types of content; sometimes traditional pagination is better for discoverability or specific item access.
- State Management: If a user navigates away and then returns, they should ideally return to their previous scroll position. This requires storing and restoring the scroll state, often using browser history APIs or local storage.
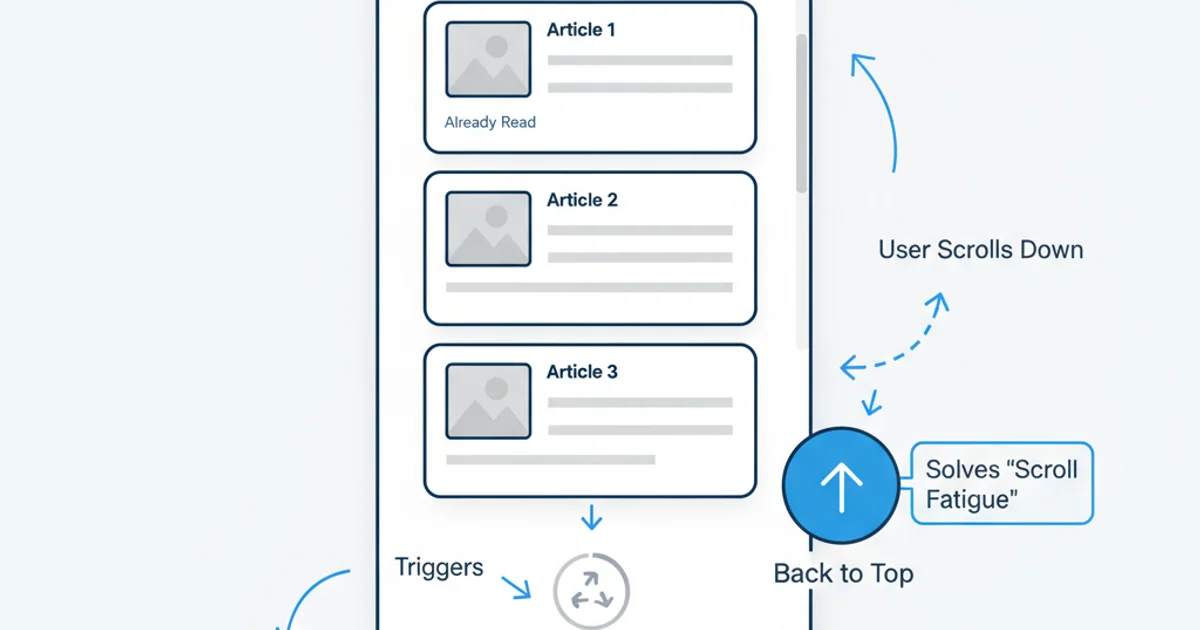
Key UX elements for an effective infinite scroll implementation.