Windows-1252 to UTF-8 encoding
Categories:
Mastering Character Encoding: Converting Windows-1252 to UTF-8

Understand the critical differences between Windows-1252 and UTF-8, and learn practical methods to convert your data reliably, preventing common encoding errors.
Character encoding is a fundamental concept in computing, dictating how text is represented and stored. While modern systems predominantly use UTF-8, legacy data often originates from older encodings like Windows-1252. Misinterpreting these encodings leads to 'mojibake' – unreadable characters that can corrupt data, break applications, and frustrate users. This article will guide you through the intricacies of Windows-1252 and UTF-8, explain why conversion is necessary, and provide robust methods for achieving accurate data transformation.
Understanding Windows-1252 and UTF-8
Before diving into conversion, it's crucial to grasp the nature of these two encodings. Windows-1252, also known as CP-1252, is a single-byte character encoding primarily used by Microsoft Windows for Western European languages. It's an extension of ISO-8859-1, adding several printable characters in the 0x80-0x9F range that were undefined in ISO-8859-1, such as the euro sign (€), smart quotes (‘ ’ “ ”), and the trademark symbol (™).
UTF-8 (Unicode Transformation Format - 8-bit) is a variable-width character encoding that can represent every character in the Unicode character set. It is the dominant encoding for the web and modern software due to its ability to handle virtually all written languages. UTF-8 is backward compatible with ASCII, meaning ASCII characters (0-127) are represented by a single byte, identical to their ASCII values. Characters outside this range are represented by sequences of 2 to 4 bytes.
flowchart TD
A[Input Data] --> B{Is Encoding Declared?}
B -- No --> C[Assume Windows-1252]
B -- Yes --> D[Use Declared Encoding]
C --> E[Decode to Unicode (Internal Representation)]
D --> E
E --> F[Encode to UTF-8]
F --> G[Output Data (UTF-8)]General process for character encoding conversion
Why Conversion is Essential
The primary reason for converting Windows-1252 to UTF-8 is interoperability and data integrity. Modern applications, databases, and web services almost universally expect and operate with UTF-8. When Windows-1252 encoded data is treated as UTF-8 without proper conversion, characters specific to Windows-1252 (especially those in the 0x80-0x9F range) will be misinterpreted. For example, a euro sign (€, 0x80 in Windows-1252) might appear as a black diamond with a question mark () or a sequence of other seemingly random characters when read as UTF-8.
This can lead to:
- Data Corruption: Storing incorrectly interpreted characters in a UTF-8 database.
- Display Issues: 'Mojibake' appearing in user interfaces or web pages.
- Search Failures: Inability to find text containing special characters.
- Security Vulnerabilities: In rare cases, encoding issues can be exploited.
Converting ensures that your data is correctly interpreted across different platforms and applications, preserving its meaning and integrity.
Practical Conversion Methods
Converting from Windows-1252 to UTF-8 typically involves two steps: decoding the source data using its original encoding (Windows-1252) into an internal Unicode representation, and then encoding that Unicode representation into the target encoding (UTF-8). Most programming languages and tools provide robust functions for this.
Python
Python example for string conversion
windows_1252_bytes = b'This is a test with € and “quotes”.'
Decode from Windows-1252 to a Unicode string
unicode_string = windows_1252_bytes.decode('windows-1252') print(f"Decoded Unicode: {unicode_string}")
Encode the Unicode string to UTF-8 bytes
utf8_bytes = unicode_string.encode('utf-8') print(f"Encoded UTF-8 bytes: {utf8_bytes}")
To convert a file:
with open('input.txt', 'r', encoding='windows-1252') as infile:
content = infile.read()
with open('output.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as outfile:
outfile.write(content)
Java
// Java example for string conversion import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class EncodingConverter { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String windows1252String = new String(new byte[]{ 'T', 'h', 'i', 's', ' ', 'i', 's', ' ', 'a', ' ', 't', 'e', 's', 't', ' ', 'w', 'i', 't', 'h', ' ', (byte) 0x80, // Euro sign ' ', 'a', 'n', 'd', ' ', (byte) 0x93, // Left double quote 'q', 'u', 'o', 't', 'e', 's', (byte) 0x94, // Right double quote '.'}, "Windows-1252");
System.out.println("Windows-1252 String: " + windows1252String);
// Convert to UTF-8 bytes
byte[] utf8Bytes = windows1252String.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
String utf8String = new String(utf8Bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("UTF-8 String: " + utf8String);
}
}
PHP
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
Encoding issues can be notoriously difficult to debug. Here are some best practices to minimize problems:
- Explicitly Declare Encoding: Always specify the encoding when reading from or writing to files, databases, or network streams. Never rely on default system encodings.
- Standardize on UTF-8: For all new projects and data, use UTF-8 as the default and preferred encoding. This simplifies interoperability.
- Validate Input: If you're receiving data from external sources, try to validate its encoding. Some libraries can detect common encodings or flag invalid byte sequences.
- Test Edge Cases: Pay special attention to characters in the 0x80-0x9F range for Windows-1252, as these are the most common source of 'mojibake'. Test with various special characters, accented letters, and symbols.
- Use Robust Libraries: Leverage built-in functions or well-tested libraries in your programming language for encoding conversions. Avoid manual byte manipulation unless absolutely necessary and you fully understand the implications.
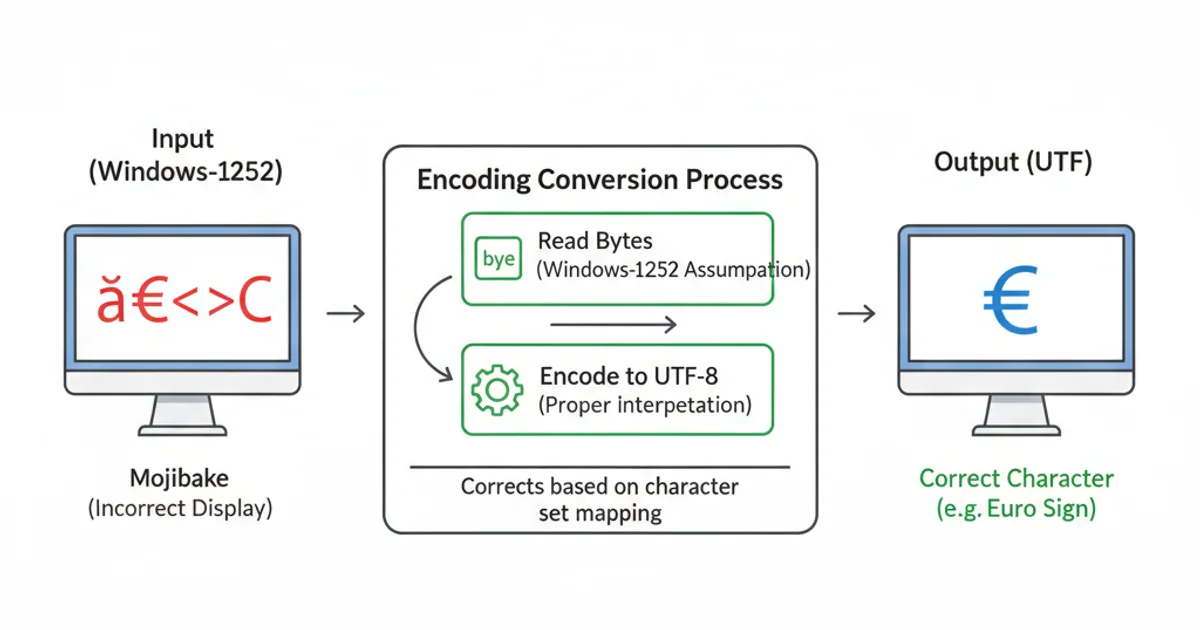
The transformation of 'mojibake' into correctly displayed characters through proper encoding.
By understanding the nuances of Windows-1252 and UTF-8 and applying these conversion techniques and best practices, you can effectively manage character encoding, ensuring your data remains accurate and accessible across diverse computing environments.