HTTP redirect: 301 (permanent) vs. 302 (temporary)
Categories:
HTTP Redirects: 301 (Permanent) vs. 302 (Temporary)

Understand the critical differences between HTTP 301 and 302 redirects, their impact on SEO, caching, and user experience, and when to use each for optimal web performance.
HTTP redirects are fundamental mechanisms for guiding users and search engines from one URL to another. While they serve the same basic purpose – moving traffic – the choice between a 301 (Moved Permanently) and a 302 (Found / Moved Temporarily) redirect carries significant implications for search engine optimization (SEO), caching, and overall website management. Understanding these differences is crucial for maintaining a healthy and performant web presence.
HTTP 301: Moved Permanently
A 301 redirect signals to browsers and search engines that a resource has been permanently moved to a new location. This is the most common type of redirect for SEO purposes because it passes almost all of the original page's link equity (PageRank) to the new URL. When a search engine encounters a 301, it updates its index to reflect the new URL, effectively transferring the old page's authority to the new one. Browsers will also cache this redirect, meaning subsequent requests to the old URL will automatically go to the new one without needing to hit the original server first.
sequenceDiagram
participant User
participant Browser
participant OldServer
participant NewServer
User->>Browser: Requests old_url.com/page
Browser->>OldServer: GET old_url.com/page
OldServer-->>Browser: HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently\nLocation: new_url.com/new-page
Browser->>Browser: Caches 301 redirect
Browser->>NewServer: GET new_url.com/new-page
NewServer-->>Browser: HTTP/1.1 200 OK\nContent: New Page Content
Browser->>User: Displays New Page ContentSequence diagram illustrating a 301 Permanent Redirect flow.
HTTP 302: Found / Moved Temporarily
In contrast, a 302 redirect (originally 'Moved Temporarily', now more commonly 'Found' in HTTP/1.1 and later) indicates that the resource is temporarily located at a different URI. This means that search engines should not update their index with the new URL and should continue to associate the original URL with the resource. Link equity is generally not passed with a 302 redirect, as it implies the move is not permanent. Browsers typically do not cache 302 redirects as aggressively as 301s, meaning they will re-request the original URL more often to check for changes. This makes 302s suitable for short-term changes where the original URL is expected to return to service.
sequenceDiagram
participant User
participant Browser
participant OldServer
participant NewServer
User->>Browser: Requests old_url.com/page
Browser->>OldServer: GET old_url.com/page
OldServer-->>Browser: HTTP/1.1 302 Found\nLocation: temp_url.com/page
Browser->>NewServer: GET temp_url.com/page
NewServer-->>Browser: HTTP/1.1 200 OK\nContent: Temporary Page Content
Browser->>User: Displays Temporary Page Content
Note over Browser,OldServer: Browser typically does not cache 302 permanentlySequence diagram illustrating a 302 Temporary Redirect flow.
Key Differences and Use Cases
The choice between 301 and 302 boils down to the permanence of the URL change and its impact on SEO and caching. Here's a summary of their core distinctions and appropriate use cases:
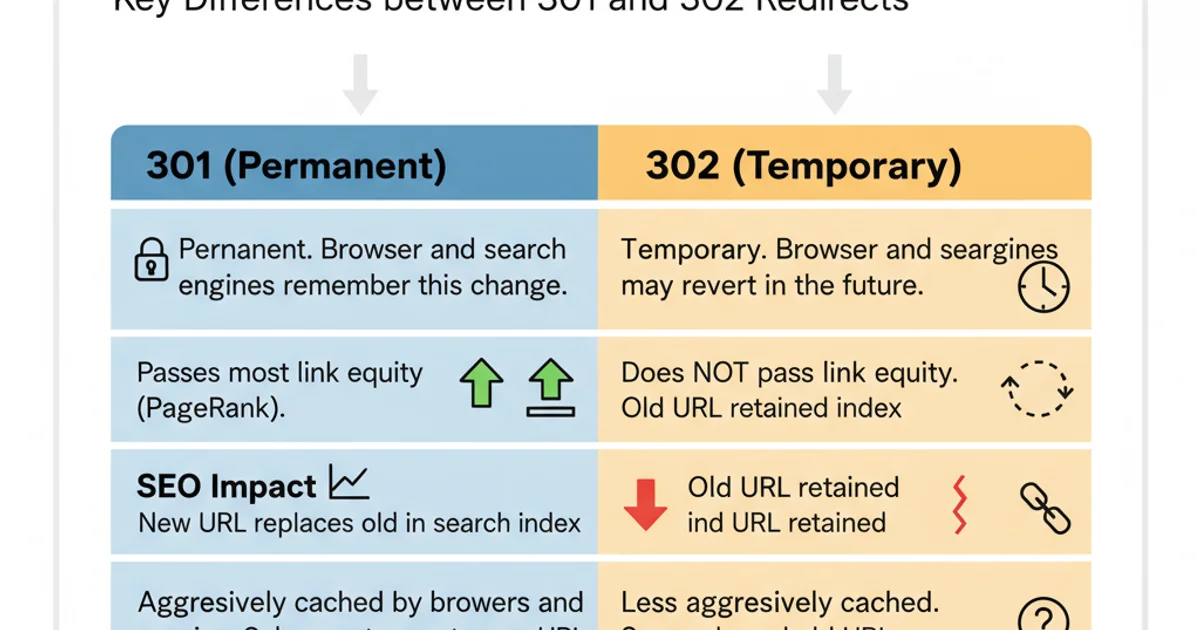
Key Differences between 301 and 302 Redirects
Implementing Redirects
Redirects can be implemented at various levels, from server configuration files to application-level code. Here are common examples for different environments:
.htaccess (Apache)
301 Permanent Redirect
Redirect 301 /old-page.html /new-page.html
302 Temporary Redirect
Redirect 302 /temporary-old-page.html /temporary-new-page.html
Nginx
301 Permanent Redirect
location /old-page { return 301 /new-page; }
302 Temporary Redirect
location /temporary-old-page { return 302 /temporary-new-page; }
PHP
Node.js (Express)
const express = require('express'); const app = express();
// 301 Permanent Redirect app.get('/old-page', (req, res) => { res.redirect(301, '/new-page'); });
// 302 Temporary Redirect app.get('/temporary-old-page', (req, res) => { res.redirect(302, '/temporary-new-page'); });
app.listen(3000, () => console.log('Server running on port 3000'));