How can I insert a new line in a Linux shell script?
Categories:
Mastering Newlines in Linux Shell Scripts: A Comprehensive Guide
Learn how to effectively insert newlines in your Linux shell scripts using various commands and techniques, enhancing readability and output formatting.
Inserting newlines is a fundamental aspect of formatting output and controlling script flow in Linux shell scripting. Whether you're printing messages, generating reports, or manipulating text files, understanding how to properly introduce line breaks is crucial. This article will guide you through the most common and effective methods for adding newlines in Bash and other shells, ensuring your scripts are both functional and user-friendly.
The Basics: echo and printf
The echo and printf commands are your primary tools for outputting text to the terminal, and both offer distinct ways to handle newlines. While echo often adds a newline by default, printf provides more granular control, especially when dealing with formatted output.
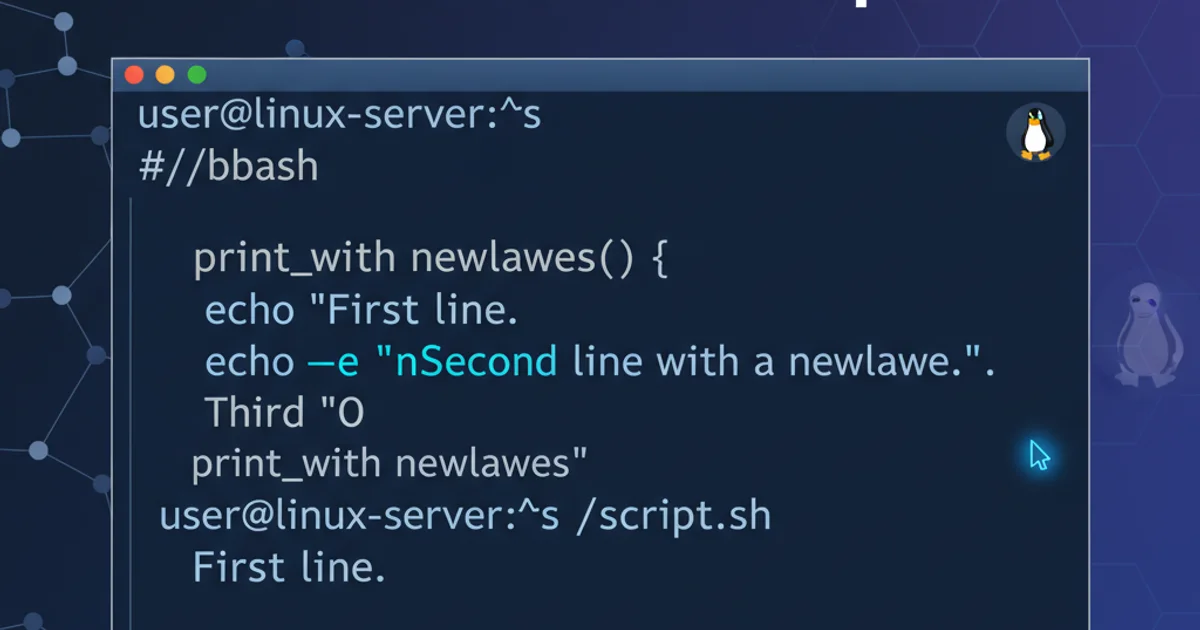
# Using echo with default newline
echo "Hello, World!"
echo "This is on a new line."
# Suppressing newline with -n
echo -n "This will be on the same line as the next output. "
echo "Continuing here."
# Explicit newline with \n (requires -e for interpretation)
echo -e "Line 1\nLine 2\nLine 3"
# Using printf for explicit newlines
printf "First line.\nSecond line.\n"
printf "Name: %s\nAge: %d\n" "Alice" 30
Examples of using echo and printf for newline control.
printf over echo for complex formatting or when dealing with variables that might contain backslash escapes, as printf's behavior is more consistent across different shell environments.Newlines in Variables and String Manipulation
Newlines aren't just for direct output; they can also be embedded within shell variables or introduced during string manipulation. This is particularly useful when constructing multi-line messages or file content dynamically.
# Embedding newline directly in a variable
MESSAGE="This is the first line.\nThis is the second line."
echo -e "$MESSAGE"
# Using ANSI C quoting (Bash specific)
MULTILINE_VAR=$'Line A\nLine B\nLine C'
echo "$MULTILINE_VAR"
# Appending newlines during string concatenation
FILE_CONTENT="Header line"
FILE_CONTENT+=$'\nData line 1'
FILE_CONTENT+=$'\nData line 2'
echo "$FILE_CONTENT" > output.txt
cat output.txt
Embedding newlines in shell variables and strings.
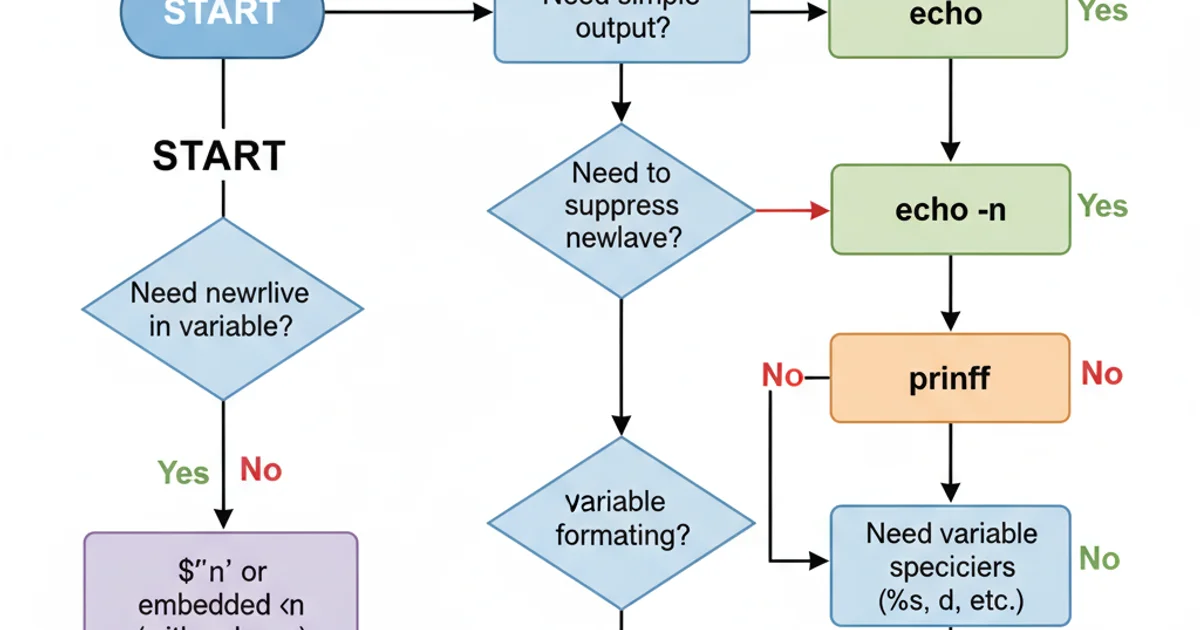
Decision flow for selecting the appropriate newline method.
Advanced Techniques: sed, awk, and Here Documents
For more complex text processing or when generating multi-line blocks of text, commands like sed and awk, along with 'here documents', offer powerful capabilities for inserting and manipulating newlines.
# Using sed to insert a newline after a pattern
echo "Hello World" | sed 's/World/World\nNew Line After/'
# Using awk to print each word on a new line
echo "One Two Three" | awk '{for(i=1;i<=NF;i++) print $i}'
# Using a here document to create a multi-line string or file content
read -r -d '' MULTILINE_TEXT << EOF
This is the first line of a here document.
It preserves all newlines and formatting.
This is very useful for configuration files or long messages.
EOF
echo "$MULTILINE_TEXT"
# Another example of here document for a file
cat << EOL > my_report.txt
Report Title
------------
Date: $(date +%Y-%m-%d)
Summary of findings:
- Item 1
- Item 2
EOL
cat my_report.txt
Advanced newline techniques with sed, awk, and here documents.
sed or awk for newline manipulation, be mindful of the specific syntax for your version, as some subtle differences can exist between GNU and BSD utilities. Always test your commands.1. Choose your command
Decide whether echo, printf, or a text processing tool like sed or awk is most appropriate for your task.
2. Insert the newline character
Use \n with printf or echo -e. For variables, use $'\n' for Bash-specific ANSI C quoting.
3. Test your script
Always run your script or command with sample data to ensure newlines are inserted as expected and output formatting is correct.
4. Review for readability
Ensure that the added newlines enhance the readability of your script's output, making it easier for users to understand.