Efficient System.arraycopy on multidimensional arrays
Categories:
Efficient System.arraycopy on Multidimensional Arrays in Java

Explore the nuances of using System.arraycopy for efficient data manipulation in Java, specifically focusing on its application and limitations with multidimensional arrays.
In Java, System.arraycopy is a native method renowned for its performance in copying contiguous blocks of data within arrays. It's often significantly faster than manual loop-based copying, especially for large arrays, because it leverages low-level memory operations. However, its direct application to multidimensional arrays requires a deeper understanding of how these arrays are structured in Java.
Understanding Multidimensional Arrays in Java
Before diving into System.arraycopy, it's crucial to remember that Java does not truly have 'multidimensional arrays' in the C/C++ sense. Instead, a multidimensional array in Java is an 'array of arrays.' For example, a int[][] is an array where each element is a reference to another int[] array. This distinction is fundamental to understanding how System.arraycopy interacts with them.
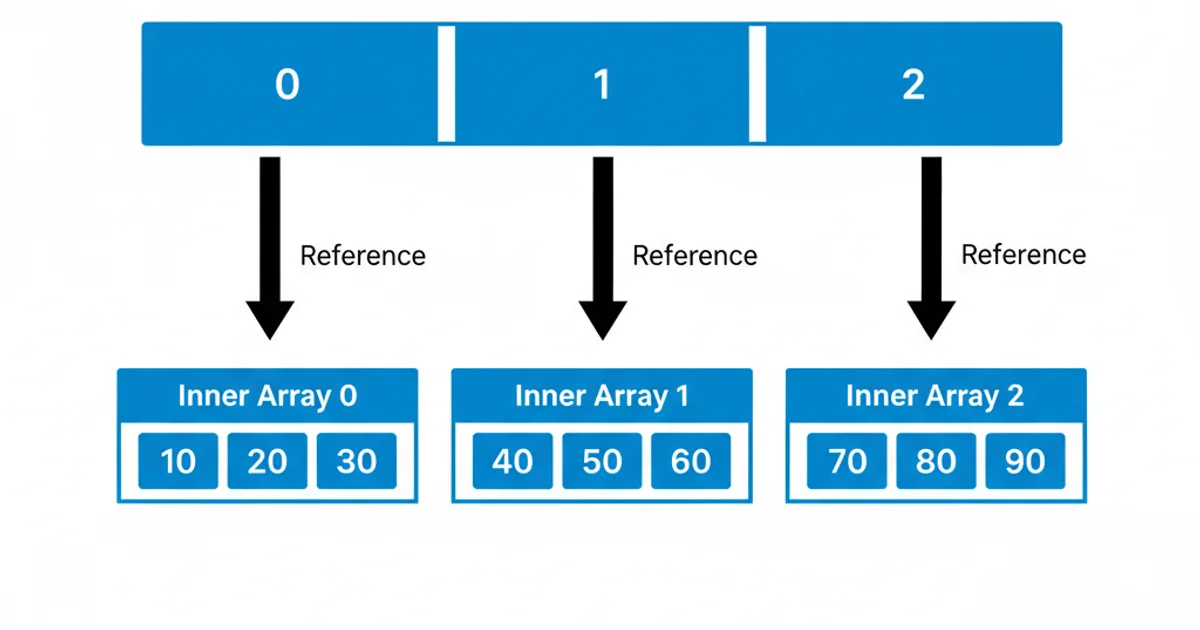
Java's 'Array of Arrays' structure for a 2D array.
Direct System.arraycopy on the Outer Array
When you apply System.arraycopy to a multidimensional array, you are copying references, not the actual nested arrays themselves. If you copy the outer array, you are copying the references to the inner arrays. This results in a 'shallow copy' of the multidimensional array.
public class ShallowCopyExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] original = {{1, 2}, {3, 4}, {5, 6}};
int[][] shallowCopy = new int[original.length][];
// Copying references to inner arrays
System.arraycopy(original, 0, shallowCopy, 0, original.length);
// Modifying an element in the original array's inner array
original[0][0] = 99;
System.out.println("Original[0][0]: " + original[0][0]); // Output: 99
System.out.println("ShallowCopy[0][0]: " + shallowCopy[0][0]); // Output: 99 (reflects change)
}
}
Shallow copy of a 2D array using System.arraycopy.
Performing a Deep Copy of Multidimensional Arrays
To achieve a 'deep copy' – where all nested arrays are also independently copied – you cannot rely solely on a single System.arraycopy call. You must iterate through the outer array and perform a System.arraycopy on each inner array individually. This ensures that each element (which is itself an array) is duplicated, creating entirely new, independent nested arrays.
public class DeepCopyExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] original = {{1, 2}, {3, 4}, {5, 6}};
int[][] deepCopy = new int[original.length][];
for (int i = 0; i < original.length; i++) {
deepCopy[i] = new int[original[i].length]; // Initialize inner array
System.arraycopy(original[i], 0, deepCopy[i], 0, original[i].length);
}
// Modifying an element in the original array's inner array
original[0][0] = 99;
System.out.println("Original[0][0]: " + original[0][0]); // Output: 99
System.out.println("DeepCopy[0][0]: " + deepCopy[0][0]); // Output: 1 (does NOT reflect change)
}
}
Deep copy of a 2D array using System.arraycopy within a loop.
Cloneable interface or using a copy constructor.Performance Considerations
While System.arraycopy is highly optimized, the overhead of looping for a deep copy of a multidimensional array can still be significant for very large datasets. However, it will almost always outperform manual element-by-element copying within a nested loop structure. For extremely performance-critical applications with very large multidimensional arrays, consider alternative data structures or specialized libraries that might offer more optimized deep copying mechanisms, though for most use cases, the loop with System.arraycopy is the standard and efficient approach.